Scientists uncover new details of SARS-CoV-2 interactions with human cells
In order to infect cells, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, needs to insert itself into the membrane of human cells; new molecular models show what parts of SARS-CoV-2 are critical for that interaction, revealing new potential drug targets
2021-02-25
(Press-News.org) ROCKVILLE, MD - If the coronavirus were a cargo ship, it would need to deliver its contents to a dock in order to infect the host island. The first step of infection would be anchoring by the dock, and step two would be tethering to the dock to bring the ship close enough that it could set up a gangplank and unload. Most treatments and vaccines have focused on blocking the ability of the ship to anchor, but the next step is another potential target. New research by Defne Gorgun, a graduate student, and colleagues in the lab of Emad Tajkhorshid at the University of Illinois addresses the molecular details of this second step, which could inform the design of drugs that block it. Gorgun will present her research on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society to be held virtually.
In order to infect our cells, the virus that causes COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, first attaches a molecule on our cell surface, but then it has to fuse with human cells. Before the pandemic, Gorgun was studying the interactions of molecules that stick to and insert into cell membranes, and when COVID-19 began to spread, Gorgun quickly pivoted her studies to understand how SARS-CoV-2 fused with cells.
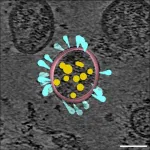
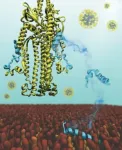
A small region of the SARS-CoV-2 outer spike protein called the "fusion peptide," inserts itself into the human cell membrane to begin the fusion process. Scientists knew the location and approximate shape of the fusion peptide; however, they did not know exactly how it interacted with and penetrated into the human cell membrane and whether there would be changes in its shape when it stuck to the membrane. Without knowing the three-dimensional interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 fusion peptide and the cell membrane, it is not possible to design drugs that specifically disrupt that interaction.
Using computer simulations, the team merged what is known about the SARS-CoV-2 fusion peptide with the established three-dimensional structures and behaviors of other coronavirus fusion peptides and simulated its interaction with a model human cell membrane. Their simulations reveal how the SARS-CoV-2 fusion peptide interacts with, and penetrates, the cell membrane. "Our study shows which parts of the fusion peptide are important and how it sticks to and sits in the membrane," Gorgun says.
Because their model is theoretical, the next step is to repeat their computer experiments in the lab with pieces of SARS-CoV-2 and cell membranes. But having already revealed parts of the fusion peptide that are likely to be critical to its function, those experiments will likely be completed faster and more efficiently. After that, Gorgun says, it will be possible to start testing drugs that disrupt the interaction and could help block SARS-CoV-2 from docking at our cells.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-25
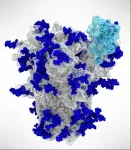
ROCKVILLE, MD - The virus that causes COVID-19 belongs to the family of coronaviruses, "corona" referring to the spikes on the viral surface. These spikes are not static--to infect cells, they change shapes. Maolin Lu, an associate research scientist at Yale University, directly visualized the changing shapes of those spike proteins and monitored how the shapes change when COVID-19 patient antibodies attach. Her work, which was published in Cell Host & Microbe in December 2020 and will be presented on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society informs the development of ...
2021-02-25
ROCKVILLE, MD - One thing that makes SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, elusive to the immune system is that it is covered in sugars called glycans. Once SARS-CoV-2 infects someone's body, it becomes covered in that person's unique glycans, making it difficult for the immune system to recognize the virus as something it needs to fight. Those glycans also play an important role in activating the virus. Terra Sztain-Pedone, a graduate student, and colleagues in the labs of Rommie Amaro at the University of California, San Diego and Lillian Chong at the University of Pittsburgh, studied exactly how the glycans activate SARS-CoV-2. Sztain-Pedone will present the research on Thursday, February 25 at the 65th Annual Meeting ...
2021-02-25
(Thursday, Feb. 25, 2021, Toronto)--Results of a world-first Canadian pilot study on patients treated with gene therapy for Fabry disease show that the treatment is working and safe.
The Canadian research team was the first to use gene therapy in 2017 to treat patients with Fabry disease, a rare, chronic illness that can damage major organs and shorten lives. They report their findings today in the journal Nature Communications.
"Being one of the first people in the world to receive this treatment, and seeing how much better I felt afterward, it definitely gives me hope that this can help many other Fabry patients and potentially those with other single gene mutation disorders," says Ryan Deveau, one of the ...
2021-02-25
Chimpanzees and humans "overlap" in their use of forests and even villages, new research shows.
Scientists used camera traps to track the movements of western chimpanzees - a critically endangered species - in Guinea-Bissau.
Chimpanzees used areas away from villages and agriculture more intensively, but entered land used by humans to get fruit - especially when wild fruits were scarce.
Researchers from the University of Exeter and Oxford Brookes University say the approach used in this study could help to inform a "coexistence strategy" for chimpanzees ...
2021-02-25
Allergy sufferers are no strangers to problems with pollen. But now - due to climate change - the pollen season is lasting longer and starting earlier than ever before, meaning more days of itchy eyes and runny noses. Warmer temperatures cause flowers to bloom earlier, while higher CO2 levels cause more pollen to be produced.
The effects of climate change on the pollen season have been studied at-length, and END ...
2021-02-25
Although guidelines do not recommend use of opioids to manage pain for individuals with knee osteoarthritis, a recent study published early online in END ...
2021-02-25
Liquid structures - liquid droplets that maintain a specific shape - are useful for a variety of applications, from food processing to cosmetics, medicine, and even petroleum extraction, but researchers have yet to tap into these exciting new materials' full potential because not much is known about how they form.
Now, a research team led by Berkeley Lab has captured real-time high-resolution videos of liquid structures taking shape as nanoparticle surfactants (NPSs) - soap-like particles just billionths of a meter in size - jam tightly together, ...
2021-02-25
Pheasants fall into two groups in terms of how they find their way around - and the different types prefer slightly different habitats, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists tested whether individual pheasants used landmarks (allocentric) or their own position (egocentric) to learn the way through a maze.
The captive-bred pheasants were later released into the wild, and their choice of habitat was observed.
All pheasants favoured woodland, but allocentric navigators spent more time out in the open, where their landmark-based style is more useful.
"Humans tend to use both of these navigational tactics and quite frequently combine them, ...
2021-02-25
In a major advance in the treatment of multiple myeloma, a CAR T-cell therapy has generated deep, sustained remissions in patients who had relapsed from several previous therapies, an international clinical trial has found.
In a study posted online today by the New England Journal of Medicine, trial leaders report that almost 75% of the participants responded to the therapy, known as idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel), and one-third of them had a complete response, or disappearance of all signs of their cancer. These rates, and the duration of the responses, are significantly ...
2021-02-25
The genetic tool CRISPR has been likened to molecular scissors for its ability to snip out and replace genetic code within DNA.
But CRISPR has a capability that could make it useful beyond genetic repairs. "CRISPR can precisely locate specific genes," says Lacramioara Bintu, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Stanford. "What we did was attach CRISPR to nanobodies to help it perform specific actions when it reached the right spot on DNA."
Her lab recently used this combo technique to transform CRISPR from a gene-editing scissors into a nanoscale control agent that can toggle specific genes on and off, like a light switch, to start or stop the flow of some health-related protein inside a cell.
"There are a lot of things you can't fix ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists uncover new details of SARS-CoV-2 interactions with human cells
In order to infect cells, SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, needs to insert itself into the membrane of human cells; new molecular models show what parts of SARS-CoV-2 are critical for that interaction, revealing new potential drug targets