Study shows opioid use among US patients with knee osteoarthritis costs 14 billion dollars in societal costs
2021-02-25
(Press-News.org) Although guidelines do not recommend use of opioids to manage pain for individuals with knee osteoarthritis, a recent study published early online in END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
On the line: Watching nanoparticles get in shape
2021-02-25
Liquid structures - liquid droplets that maintain a specific shape - are useful for a variety of applications, from food processing to cosmetics, medicine, and even petroleum extraction, but researchers have yet to tap into these exciting new materials' full potential because not much is known about how they form.
Now, a research team led by Berkeley Lab has captured real-time high-resolution videos of liquid structures taking shape as nanoparticle surfactants (NPSs) - soap-like particles just billionths of a meter in size - jam tightly together, ...
A-maze-ing pheasants have two ways of navigating
2021-02-25
Pheasants fall into two groups in terms of how they find their way around - and the different types prefer slightly different habitats, new research shows.
University of Exeter scientists tested whether individual pheasants used landmarks (allocentric) or their own position (egocentric) to learn the way through a maze.
The captive-bred pheasants were later released into the wild, and their choice of habitat was observed.
All pheasants favoured woodland, but allocentric navigators spent more time out in the open, where their landmark-based style is more useful.
"Humans tend to use both of these navigational tactics and quite frequently combine them, ...
CAR T-cell therapy generates lasting remissions in patients with multiple myeloma
2021-02-25
In a major advance in the treatment of multiple myeloma, a CAR T-cell therapy has generated deep, sustained remissions in patients who had relapsed from several previous therapies, an international clinical trial has found.
In a study posted online today by the New England Journal of Medicine, trial leaders report that almost 75% of the participants responded to the therapy, known as idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel), and one-third of them had a complete response, or disappearance of all signs of their cancer. These rates, and the duration of the responses, are significantly ...
Fantastic voyage: Nanobodies could help CRISPR turn genes on and off
2021-02-25
The genetic tool CRISPR has been likened to molecular scissors for its ability to snip out and replace genetic code within DNA.
But CRISPR has a capability that could make it useful beyond genetic repairs. "CRISPR can precisely locate specific genes," says Lacramioara Bintu, an assistant professor of bioengineering at Stanford. "What we did was attach CRISPR to nanobodies to help it perform specific actions when it reached the right spot on DNA."
Her lab recently used this combo technique to transform CRISPR from a gene-editing scissors into a nanoscale control agent that can toggle specific genes on and off, like a light switch, to start or stop the flow of some health-related protein inside a cell.
"There are a lot of things you can't fix ...
Baby mice have a skill that humans want - and this microchip might help us learn it
2021-02-25
Baby mice might be small, but they're tough, too.
For their first seven days of life, they have the special ability to regenerate damaged heart tissue.
Humans, on the other hand, aren't so lucky: any heart injuries we suffer could lead to permanent damage. But what if we could learn to repair our hearts, just like baby mice?
A team of researchers led by UNSW Sydney have developed a microchip that can help scientists study the regenerative potential of mice heart cells. This microchip - which combines microengineering with biomedicine - could help pave the way for new regenerative heart medicine research.
The study is featured on the cover ...
New discoveries on the containment of COVID-19 finds travel bans are of limited value
2021-02-25
BROOKLYN, New York, Wednesday, February 24, 2021 - Travel bans have been key to efforts by many countries to control the spread of COVID-19. But new research aimed at providing a decision support system to Italian policy makers, recently published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface, suggests that reducing individual activity (i.e., social distancing, closure of non-essential business, etc.) is far superior in controlling the dissemination of Sars-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
The research, which has implications for the United States and other countries, found that limiting personal mobility through travel restrictions and similar tactics is effective only in the first phases of the epidemic, and reduces in proportion to the ...
UM scientists achieve breakthrough in culturing corals and sea anemones cells
2021-02-25
MIAMI--Researchers have perfected the recipe for keeping sea anemone and coral cells alive in a petri dish for up to 12 days. The new study, led by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, has important applications to study everything from evolutionary biology to human health.
Cnidarians are emerging model organisms for cell and molecular biology research. Yet, successfully keeping their cells in a laboratory setting has proved challenging due to contamination from the many microorganisms that live within these marine organisms or because the whole tissue survive in a culture environment.
UM cell ...
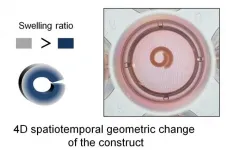
New shape-changing 4D materials hold promise for morphodynamic tissue engineering
2021-02-25
New hydrogel-based materials that can change shape in response to psychological stimuli, such as water, could be the next generation of materials used to bioengineer tissues and organs, according to a team of researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago.
In a new paper published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, the research team -- led by Eben Alsberg, the Richard and Loan Hill Professor of Biomedical Engineering -- that developed the substances show that the unique materials can curl into tubes in response to water, making the materials good candidates for bioengineering blood vessels or other tubular structures.
In nature, embryonic development and tissue healing often involve ...
Apollo rock samples capture key moments in the Moon's early history, study find
2021-02-24
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Volcanic rock samples collected during NASA's Apollo missions bear the isotopic signature of key events in the early evolution of the Moon, a new analysis found. Those events include the formation of the Moon's iron core, as well as the crystallization of the lunar magma ocean -- the sea of molten rock thought to have covered the Moon for around 100 million years after the it formed.
The analysis, published in the journal Science Advances, used a technique called secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) to study volcanic glasses returned ...
COVID-19 isolation linked to increased domestic violence, researchers suggest
2021-02-24
While COVID-19-related lockdowns may have decreased the spread of a deadly virus, they appear to have created an ideal environment for increased domestic violence.c
Data collected in surveys of nearly 400 adults for 10 weeks beginning in April 2020 suggest that more services and communication are needed so that even front-line health and food bank workers, for example -- rather than only social workers, doctors and therapists -- can spot the signs and ask clients questions about potential intimate partner violence. They could then help lead victims to resources, said Clare Cannon, assistant professor of social and environmental justice in the Department of Human Ecology and the lead author of the study.
The paper, "COVID-19, intimate partner violence, and communication ...