(Press-News.org) Black men and women, as well as adolescent boys and girls, may react differently to perceived racial discrimination, with Black women and girls engaging in more exercise and better eating habits than Black men and boys when faced with discrimination, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
"In this study, Black women and girls didn't just survive in the face of racism, they actually responded in a positive manner, in terms of their health behavior," said lead researcher Frederick Gibbons, PhD, with the University of Connecticut. "This gives us some hope that despite the spike in racism across the country, some people are finding healthy ways to cope."
For a paper published in the journal Health Psychology, researchers evaluated data collected over 14 years from an ongoing study on the impacts of racism on the physical and mental well-being of Black people. The analysis looked at 889 families living in Iowa and Georgia who have been participants in the Family and Community Health Study. The families consisted of an adolescent, the adolescent's primary caregiver and in 289 cases, an older sibling. The first analysis examined the correlation between perceived racial discrimination and participants' body mass index. Researchers then looked at how participants responded to survey questions on optimism and on eating and exercise habits.
The relationship between perceived racial discrimination and healthy habits in Black males was insignificant, the study found. Black women and adolescent girls, on the other hand, showed improvements in healthy eating and exercise as their perceptions of racism increased. And there was an even more significant increase in healthy behaviors for Black women who indicated they had an optimistic view of their lives and the future, according to the researchers. There was no correlation between racial discrimination and BMI in either Black males or Black females.
"The findings were surprising and suggest that adaptive coping strategies may lead to resiliency," Gibbons said. "This contrasts with the avoidant coping strategies that we might see out of someone who is less optimistic."
The findings should be placed in the context of the larger body of research on this issue, which has shown a correlation between perceived racial discrimination and unhealthy behaviors, including those leading to higher BMI, according to Gibbons.
"The question is why are these results different from the ones we've found in previous studies?" he said. "There are several possible explanations, including the fact that participants in previous studies may have conflated weight-based discrimination with perceived racial discrimination. It could also be that studies not finding a connection between perceived racial discrimination and poor health outcomes are less likely to be published."
If the findings are confirmed in subsequent research, they could be used in resiliency programs targeting people of color and underserved populations, according to the researchers.
"There are programs already in place that work to instill a sense of resiliency and optimism in disenfranchised youth," Gibbons said. "The findings from this study would suggest that these programs are on the right track, and that perhaps we should be developing more programs that focus on these types of coping skills."
INFORMATION:
Article: "Perceived Racial Discrimination and Healthy Behavior Among African Americans," by Frederick X. Gibbons, PhD, Meg Gerrard, PhD, and Mary E. Fleischli, PhD, University of Connecticut; Ronald L. Simons, PhD, University of Georgia; and John H. Kingsbury, PhD, Minnesota Department of Health. Health Psychology, published online Feb. 25, 2021.
Contact: Frederick Gibbons, PhD, can be reached at rick.gibbons@uconn.edu.
Full text of the article is available online at https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/releases/hea-hea0001056.pdf.
The American Psychological Association, in Washington, D.C., is the largest scientific and professional organization representing psychology in the United States. APA's membership includes nearly 122,000 researchers, educators, clinicians, consultants and students. Through its divisions in 54 subfields of psychology and affiliations with 60 state, territorial and Canadian provincial associations, APA works to advance the creation, communication and application of psychological knowledge to benefit society and improve people's lives.
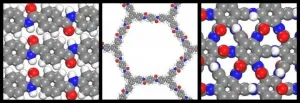
ADELPHI, Md. -- Army researchers reached a breakthrough in the nascent science of two-dimensional polymers thanks to a collaborative program that enlists the help of lead scientists and engineers across academia known as joint faculty appointments.
Researchers from the U.S. Army Combat Capabilities Development Command, now known as DEVCOM, Army Research Laboratory partnered with Prof. Steve Lustig, a joint faculty appointment at Northeastern University, to accelerate the development of 2D polymers for military applications.
The collaboration with ARL Northeast led to a groundbreaking study published in the peer-reviewed scientific journal Macromolecules. Editors featured the research in a cover article.
"2D polymers have been studied very seriously from a synthetic ...
Researchers have developed a tool to identify security and privacy risks associated with Covid-19 contact tracing apps.
COVIDGuardian, the first automated security and privacy assessment tool, tests contact tracing apps for potential threats such as malware, embedded trackers and private information leakage.
Using the COVIDGuardian tool, cybersecurity experts assessed 40 Covid-19 contact tracing apps that have been employed worldwide for potential privacy and security threats. Their findings include that:
72.5 per cent of the apps use at least one insecure cryptographic ...
Medical researchers have long understood that a pregnant mother's diet has a profound impact on her developing fetus's immune system and that babies -- especially those born prematurely -- who are fed breast milk have a more robust ability to fight disease, suggesting that even after childbirth, a mother's diet matters. However, the biological mechanisms underlying these connections have remained unclear.
Now, in a study published Feb. 15, 2021, in the journal Nature Communications, a Johns Hopkins Medicine research team reports that pregnant mice fed a diet rich in a molecule found abundantly in cruciferous vegetables -- such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts and cauliflower -- gave birth to pups with stronger protection against necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). ...
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as various forms of senile dementia or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), have one thing in common: large amounts of certain RNA-protein complexes (snRNPs) are produced and deposited in the nerve cells of those affected - and this hinders the function of the cells. The overproduction is possibly caused by a malfunction in the assembly of the protein complexes.
How the production of these protein complexes is regulated was unknown until now. Researchers from Martinsried and Würzburg in Bavaria, Germany, have solved the puzzle and now report on it in the open access journal Nature Communications. They describe in detail a signaling pathway that prevents the overproduction of snRNPs when they are not needed. The results should ...
A diet rich in human food may be wreaking havoc on the health of urban coyotes, according to a new study by University of Alberta biologists.
The research team from the Faculty of Science examined the stomach contents, gut microbiome and overall health of nearly 100 coyotes in Edmonton's capital region. Their results also show coyotes that consume more human food have more human-like gut bacteria--with potential impact on their nutrition, immune function and, based on similar findings in dogs, even behaviour.
"If eating human food disturbs the 'natural' coyote gut bacteria, it is possible that eating human food has the potential to affect all ...
The answer to the age-old mystery of the evolutionary origins of vertebrate eyes may lie in hagfish, according to a new study by biologists at the University of Alberta.
"Hagfish eyes can help us understand the origins of human vision by expanding our understanding of the early steps in vertebrate eye evolution," explained lead author Emily Dong, who conducted the research during her graduate studies with Ted Allison, a professor in the Faculty of Science and member of the U of A's Neuroscience and Mental Health Institute. "Our findings solidify the hagfish's place among vertebrates and open the door to further research to uncover the finer details ...
Blocking seizures after a head injury could slow or prevent the onset of dementia, according to new research by University of Alberta biologists.
"Traumatic brain injury is a major risk factor for dementia, but the reason this is the case has remained mysterious," said Ted Allison, co-author and professor in the Department of Biological Sciences in the Faculty of Science. "Through this research, we have discovered one important way they are linked--namely, post-injury seizures."
"There is currently no treatment for the long-term effects of traumatic brain injury, which includes developing dementia," added lead author Hadeel Alyenbaawi, who recently completed her PhD dissertation on this topic in the Department of Medical Genetics in the Faculty ...
INFORMS Journal Management Science Study Key Takeaways:
Changing an employee's hours during their shift, typically by having them stay longer, hurts restaurant revenue.
Checks for parties handled by servers who'd been asked to stay longer during their shift dropped by 4.4%, on average.
Servers asked to stay longer reduced the effort spent on upselling and cross-selling additional menu items.
CATONSVILLE, MD, February 25, 2021 - Short notice versus no advance notice makes a huge difference when it comes to employee scheduling in the restaurant industry. New research in the INFORMS journal Management Science finds checks for parties handled by servers who were asked (with ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - In many cases, unions in Europe have helped nonunionized workers whose jobs are precarious, according to new Cornell University research.
In "Dualism or Solidarity? Conditions for Union Success in Regulating Precarious Work," published in December in the European Journal of Industrial Relations, the researchers surveyed academic articles to see how often they would find evidence of unions helping nonunionized workers or helping only their own members, and which conditions were associated with each outcome.
The paper was co-authored by Laura Carver, M.S. 20, and Virginia Doellgast, associate ...
On a low-lying island in the Caribbean, the future of the critically endangered Bahama Oriole just got a shade brighter. A new study led by researchers at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County (UMBC) estimates the population of these striking black and yellow birds at somewhere between 1300 and 2800 individuals in the region they surveyed, suggesting the overall population is likely several thousand. Older studies estimated the entire population at fewer than 300, so the new results indicate there are at least 10 times as many Bahama Orioles as previously understood. The research ...