(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have found a new way to harness properties of light waves that can radically increase the amount of data they carry. They demonstrated the emission of discrete twisting laser beams from antennas made up of concentric rings roughly equal to the diameter of a human hair, small enough to be placed on computer chips.
The new work, reported in a paper published Thursday, Feb. 25, in the journal Nature Physics, throws wide open the amount of information that can be multiplexed, or simultaneously transmitted, by a coherent light source. A common example of multiplexing is the transmission of multiple telephone calls over a single wire, but there had been fundamental limits to the number of coherent twisted lightwaves that could be directly multiplexed.
"It's the first time that lasers producing twisted light have been directly multiplexed," said study principal investigator Boubacar Kanté, the Chenming Hu Associate Professor at UC Berkeley's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. "We've been experiencing an explosion of data in our world, and the communication channels we have now will soon be insufficient for what we need. The technology we are reporting overcomes current data capacity limits through a characteristic of light called the orbital angular momentum. It is a game-changer with applications in biological imaging, quantum cryptography, high-capacity communications and sensors."
Kanté, who is also a faculty scientist in the Materials Sciences Division at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), has been continuing this work at UC Berkeley after having started the research at UC San Diego. The first author of the study is Babak Bahari, a former Ph.D. student in Kanté's lab.
Kanté said that current methods of transmitting signals through electromagnetic waves are reaching their limit. Frequency, for example, has become saturated, which is why there are only so many stations one can tune into on the radio. Polarization, where lightwaves are separated into two values -- horizontal or vertical -- can double the amount of information transmitted. Filmmakers take advantage of this when creating 3D movies, allowing viewers with specialized glasses to receive two sets of signals -- one for each eye -- to create a stereoscopic effect and the illusion of depth.
Harnessing the potential in a vortex
But beyond frequency and polarization is orbital angular momentum, or OAM, a property of light that has garnered attention from scientists because it offers exponentially greater capacity for data transmission. One way to think about OAM is to compare it to the vortex of a tornado.
"The vortex in light, with its infinite degrees of freedom, can, in principle, support an unbounded quantity of data," said Kanté. "The challenge has been finding a way to reliably produce the infinite number of OAM beams. No one has ever produced OAM beams of such high charges in such a compact device before."
The researchers started with an antenna, one of the most important components in electromagnetism and, they noted, central to ongoing 5G and upcoming 6G technologies. The antennas in this study are topological, which means that their essential properties are retained even when the device is twisted or bent.
Creating rings of light
To make the topological antenna, the researchers used electron-beam lithography to etch a grid pattern onto indium gallium arsenide phosphide, a semiconductor material, and then bonded the structure onto a surface made of yttrium iron garnet. The researchers designed the grid to form quantum wells in a pattern of three concentric circles -- the largest about 50 microns in diameter -- to trap photons. The design created conditions to support a phenomenon known as the photonic quantum Hall effect, which describes the movement of photons when a magnetic field is applied, forcing light to travel in only one direction in the rings.
"People thought the quantum Hall effect with a magnetic field could be used in electronics but not in optics because of the weak magnetism of existing materials at optical frequencies," said Kanté. "We are the first to show that the quantum Hall effect does work for light."
By applying a magnetic field perpendicular to their two-dimensional microstructure, the researchers successfully generated three OAM laser beams traveling in circular orbits above the surface. The study further showed that the laser beams had quantum numbers as large as 276, referring to the number of times light twists around its axis in one wavelength.
"Having a larger quantum number is like having more letters to use in the alphabet," said Kanté. "We're allowing light to expand its vocabulary. In our study, we demonstrated this capability at telecommunication wavelengths, but in principle, it can be adapted to other frequency bands. Even though we created three lasers, multiplying the data rate by three, there is no limit to the possible number of beams and data capacity."
Kanté said the next step in his lab is to make quantum Hall rings that use electricity as power sources.
INFORMATION:
This research was primarily supported by the Office of Naval Research, the National Science Foundation and Berkeley Lab's Laboratory Directed Research and Development Program.
Never before in over 1000 years the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), also known as Gulf Stream System, has been as weak as in the last decades. This is the result of a new study by scientists from Ireland, Britain and Germany. The researchers compiled so-called proxy data, taken mainly from natural archives like ocean sediments or ice cores, reaching back many hundreds of years to reconstruct the flow history of the AMOC. They found consistent evidence that its slowdown in the 20th century is unprecedented in the past millennium; it is likely linked to human-caused climate change. The giant ocean circulation is relevant for weather patterns ...
More intense and frequent fires are reducing the size of tree communities in many regions of the world.
Slower-growing tree species are better at surviving fires, but these may capture less atmospheric carbon and reduce nutrient availability in the soil.
Not all regions are suitable for planting trees to tackle climate change; schemes must consider local wildfire frequency, vegetation cover and climate, and how these might change over time.
Researchers have analysed decades' worth of data on the impact of repeated fires on ecosystems across the world. Their results, published today in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution, show that repeated fires are driving long-term changes to tree communities and reducing their population ...
Until recently, scientists believed that the primary cilium - an antenna-like structure found on the surface of most human cells - was largely vestigial and had little bearing on the day-to-day lives of human beings. But more recently, a relatively small number of people have been found to have rare genetic disorders affecting the cilium, characterized by a number of health problems, including common conditions like diabetes, kidney failure, and liver fibrosis. Now, an analysis of genes involved in the function of the cilium found that the same genes causing its rare diseases might ...
What The Study Did: Researchers in this observational study of more than 10,000 U.S. Air Force basic trainees examined whether symptoms and laboratory results on the first day of COVID-19 diagnosis are associated with development of a case cluster in a congregate setting.
Authors: Joseph E. Marcus, M.D., of the Brooke Army Medical Center at Joint Base San Antonio Fort Sam Houston, Texas, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0202)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
What The Study Did: This research letter describes the various otolaryngologic manifestations in patients 18 years or younger with pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2.
Authors: Ryan C. T. Cheong, B.Sc.(Hons), M.B.B.S., of the Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust in London, United Kingdom, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5698)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
What The Study Did: Data from five studies were pooled to investigate whether cognitive decline among older U.S. adults varied by sex.
Authors: Deborah A. Levine, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0169)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial ...
What The Study Did: Researchers looked at whether state legalization of recreational cannabis was associated with changes in use by women before, during and after pregnancy.
Authors: Kara R. Skelton, Ph.D., of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0138)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
Antarctica's northern George VI Ice Shelf experienced record melting during the 2019-2020 summer season compared to 31 previous summers of dramatically lower melt, a University of Colorado Boulder-led study found. The extreme melt coincided with record-setting stretches when local surface air temperatures were at or above the freezing point.
"During the 2019-2020 austral summer, we observed the most widespread melt and greatest total number of melt days of any season for the northern George VI Ice Shelf," said CIRES Research Scientist Alison Banwell, lead author of the study published in The Cryosphere.
Banwell and her co-authors--scientists at ...
Nanoengineers at the University of California San Diego have discovered new fundamental insights for developing lithium metal batteries that perform well at ultra-low temperatures; mainly, that the weaker the electrolyte holds on to lithium ions, the better. By using such a weakly binding electrolyte, the researchers developed a lithium metal battery that can be repeatedly recharged at temperatures as low as -60 degrees Celsius--a first in the field.
Researchers report their work in a paper published Feb. 25 in Nature Energy.
In tests, the proof-of-concept battery retained 84% and 76% of its capacity over 50 cycles at -40 and -60 degrees Celsius, respectively. Such performance is unprecedented, researchers ...
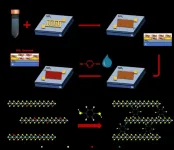
The exfoliation of graphite into graphene layers inspired the investigation of thousands of layered materials: amongst them transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). These semiconductors can be used to make conductive inks to manufacture printed electronic and optoelectronic devices. However, defects in their structure may hinder their performance. Now, Graphene Flagship researchers have overcome these hurdles by introducing 'molecular bridges'- small molecules that interconnect the TMD flakes, thereby boosting the conductivity and overall performance.
The results, published in Nature Nanotechnology, come from a multidisciplinary collaboration between Graphene Flagship partners the University of Strasbourg and CNRS, France, AMBER and Trinity College Dublin, Ireland, ...