Chip simplifies COVID-19 testing, delivers results on a phone
Programmed magnetic nanobeads enable diagnostic device designed at Rice University
2021-02-25
(Press-News.org) HOUSTON - (Feb. 25, 2021) - COVID-19 can be diagnosed in 55 minutes or less with the help of programmed magnetic nanobeads and a diagnostic tool that plugs into an off-the-shelf cell phone, according to Rice University engineers.
The Rice lab of mechanical engineer Peter Lillehoj has developed a stamp-sized microfluidic chip that measures the concentration of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein in blood serum from a standard finger prick. The nanobeads bind to SARS-CoV-2 N protein, a biomarker for COVID-19, in the chip and transport it to an electrochemical sensor that detects minute amounts of the biomarker.
The researchers argued their process simplifies sample handling compared to swab-based PCR tests that are widely used to diagnose COVID-19 and need to be analyzed in a laboratory.
"What's great about this device is that doesn't require a laboratory," Lillehoj said. "You can perform the entire test and generate the results at the collection site, health clinic or even a pharmacy. The entire system is easily transportable and easy to use."
The research appears in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Sensors.
Lillehoj and Rice graduate student and lead author Jiran Li took advantage of existing biosensing tools and combined them with their own experience in developing simple diagnostics, like a microneedle patch introduced last year to diagnose malaria.
The new tool relies on a slightly more complex detection scheme but delivers accurate, quantitative results in a short amount of time. To test the device, the lab relied on donated serum samples from people who were healthy and others who were COVID-19-positive.
Lillehoj said a longer incubation yields more accurate results when using whole serum. The lab found that 55 minutes was an optimum amount of time for the microchip to sense SARS-CoV-2 N protein at concentrations as low as 50 picograms (billionths of a gram) per milliliter in whole serum. The microchip could detect N protein in even lower concentrations, at 10 picograms per milliliter, in only 25 minutes by diluting the serum fivefold.
Paired with a Google Pixel 2 phone and a plug-in potentiostat, it was able to deliver a positive diagnosis with a concentration as low as 230 picograms for whole serum.
"There are standard procedures to modify the beads with an antibody that targets a particular biomarker," Lillehoj said. "When you combine them with a sample containing the biomarker, in this case SARS-CoV-2 N protein, they bond together."
A capillary tube is used to deliver the sample to the chip, which is then placed on a magnet that pulls the beads toward an electrochemical sensor coated with capture antibodies. The beads bind to the capture antibodies and generate a current proportional to the concentration of biomarker in the sample.
The potentiostat reads that current and sends a signal to its phone app. If there are no COVID-19 biomarkers, the beads do not bind to the sensor and get washed away inside the chip.
Lillehoj said it would not be difficult for industry to manufacture the microfluidic chips or to adapt them to new COVID-19 strains if and when that becomes necessary.
INFORMATION:
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation and the Rice University COVID-19 Research Fund supported the research.
Read the abstract at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acssensors.0c02561.
This news release can be found online at https://news.rice.edu/2021/02/25/chip-simplifies-covid-19-testing-delivers-results-on-a-phone/
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
Related materials:
Lillehoj Research Group: http://lillehoj.rice.edu
Department of Mechanical Engineering: https://mech.rice.edu
George R. Brown School of Engineering: https://engineering.rice.edu
Images for download:
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/02/0215_PHONE-1-WEB.jpg
A system developed by Rice University engineers employs a stamp-sized microfluidic chip that measures the concentration of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in blood serum to diagnose COVID-19 in less than an hour. The system uses an off-the-shelf cellphone and potentiostat to deliver the results. (Credit: Lillehoj Research Group/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/02/0215_PHONE-2-WEB.jpg
Programmed magnetic nanobeads paired with an off-the-shelf cellphone and plug-in diagnostic tool can diagnose COVID-19 in 55 minutes or less, according to Rice University engineers. (Credit: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/02/0215_PHONE-3-WEB.jpg
Rice University mechanical engineer Peter Lillehoj, left, and graduate student Jiran Li developed a system that uses programmable magnetic nanobeads, an off-the-shelf cellphone and a plug-in diagnostic tool to diagnose COVID-19 in 55 minutes or less. (Credit: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University)
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,978 undergraduates and 3,192 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Jeff Falk
713-348-6775
jfalk@rice.edu
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
mikewilliams@rice.edu
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-25
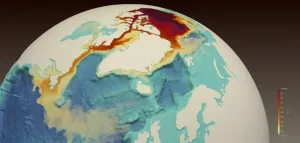
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., February 24, 2021--The Beaufort Sea, the Arctic Ocean's largest freshwater reservoir, has increased its freshwater content by 40 percent over the last two decades, putting global climate patterns at risk. A rapid release of this freshwater into the Atlantic Ocean could wreak havoc on the delicate climate balance that dictates global climate.
"A freshwater release of this size into the subpolar North Atlantic could impact a critical circulation pattern, called the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, which has a significant influence on northern-hemisphere climate," ...
2021-02-25
After traveling several billion miles toward the Sun, a wayward young comet-like object orbiting among the giant planets has found a temporary parking place along the way. The object has settled near a family of captured ancient asteroids, called Trojans, that are orbiting the Sun alongside Jupiter. This is the first time a comet-like object has been spotted near the Trojan population.
The unexpected visitor belongs to a class of icy bodies found in space between Jupiter and Neptune. Called "Centaurs," they become active for the first time when heated as they approach the Sun, and dynamically transition into becoming more comet-like.
Visible-light snapshots by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reveal that the vagabond object shows signs of comet activity, such as a tail, ...
2021-02-25
Researchers have discovered that there may be a new pathway in the brain that provides pain relief and reduces cravings for opioids.
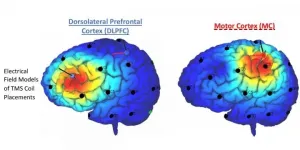
Over a third of the U.S. population suffers from chronic pain, with little to no reported relief from medication. Transcranial magnetic brain stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation that may offer a new treatment option for these underserved members of our community.
In a recent paper in Drug and Alcohol Dependence, researchers at the Medical University of South Carolina evaluated two different strategies for relieving pain with TMS: applying TMS to the motor cortex and the ...
2021-02-25
When birds see a predator in their midst, one defensive strategy is to call out loudly, attracting other birds of the same or different species to do the same. Sometimes individuals within this "mobbing flock" will fly over or at the predator or attack it directly. Now, researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on February 25 have found that male superb lyrebirds do something rather unexpected: they imitate a mobbing flock in courtship and even in the act of mating with a female.
"Our paper shows that male superb lyrebirds regularly create a remarkable acoustic illusion of a flock of mobbing birds ...
2021-02-25
Researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research have discovered a new type of bone cell that may reveal new therapeutic approaches for osteoporosis and other skeletal diseases.
The new cells, which the researchers term 'osteomorphs', are found in the blood and bone marrow, and fuse together to form osteoclasts, specialised cells that break down bone tissue. They have a unique genomic profile that reveals promising and as yet unexplored targets for therapy.
"This discovery is a game-changer, which not only helps us understand bone biology but presents significant new in-roads for osteoporosis therapy," says co-senior ...
2021-02-25
A 20% shift in beverage sales from small to medium-sized plastic bottles could reduce the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) waste in the USA by over 9,000 tonnes annually, a study in Scientific Reports suggests.
PET is the dominant material used in plastic bottles containing non-alcoholic beverages. Rafael Becerril-Arreola and Randolph Bucklin weighed 187 differently sized PET bottles sold by the best-selling beverage brands in Minnesota, USA, to identify which bottles sizes were the most efficient at delivering the highest volume of beverage for the lowest packaging weight. To validate their findings, the researchers combined data on sales of different sized PET bottles ...
2021-02-25
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have found a new way to harness properties of light waves that can radically increase the amount of data they carry. They demonstrated the emission of discrete twisting laser beams from antennas made up of concentric rings roughly equal to the diameter of a human hair, small enough to be placed on computer chips.
The new work, reported in a paper published Thursday, Feb. 25, in the journal Nature Physics, throws wide open the amount of information that can be multiplexed, or simultaneously transmitted, by a coherent light source. A common example of multiplexing is the transmission of multiple telephone calls ...
2021-02-25
Never before in over 1000 years the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), also known as Gulf Stream System, has been as weak as in the last decades. This is the result of a new study by scientists from Ireland, Britain and Germany. The researchers compiled so-called proxy data, taken mainly from natural archives like ocean sediments or ice cores, reaching back many hundreds of years to reconstruct the flow history of the AMOC. They found consistent evidence that its slowdown in the 20th century is unprecedented in the past millennium; it is likely linked to human-caused climate change. The giant ocean circulation is relevant for weather patterns ...
2021-02-25
More intense and frequent fires are reducing the size of tree communities in many regions of the world.
Slower-growing tree species are better at surviving fires, but these may capture less atmospheric carbon and reduce nutrient availability in the soil.
Not all regions are suitable for planting trees to tackle climate change; schemes must consider local wildfire frequency, vegetation cover and climate, and how these might change over time.
Researchers have analysed decades' worth of data on the impact of repeated fires on ecosystems across the world. Their results, published today in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution, show that repeated fires are driving long-term changes to tree communities and reducing their population ...
2021-02-25
Until recently, scientists believed that the primary cilium - an antenna-like structure found on the surface of most human cells - was largely vestigial and had little bearing on the day-to-day lives of human beings. But more recently, a relatively small number of people have been found to have rare genetic disorders affecting the cilium, characterized by a number of health problems, including common conditions like diabetes, kidney failure, and liver fibrosis. Now, an analysis of genes involved in the function of the cilium found that the same genes causing its rare diseases might ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Chip simplifies COVID-19 testing, delivers results on a phone
Programmed magnetic nanobeads enable diagnostic device designed at Rice University