(Press-News.org) Paleo-ecologists from The University of New Mexico and at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln have demonstrated that the offspring of enormous carnivorous dinosaurs, such as Tyrannosaurus rex may have fundamentally re-shaped their communities by out-competing smaller rival species.
The study, released this week in the journal Science, is the first to examine community-scale dinosaur diversity while treating juveniles as their own ecological entity.
"Dinosaur communities were like shopping malls on a Saturday afternoon ? jam-packed with teenagers" explained Kat Schroeder, a graduate student in the UNM Department of Biology who led the study. "They made up a significant portion of the individuals in a species and would have had a very real impact on the resources available in communities."
Because they were born from eggs, dinosaurs like T. rex necessarily were born small ? about the size of a house cat. This meant as they grew to the size of a city bus, these "megatheropods," weighing between one and eight tons, would have changed their hunting patterns and prey items. It's long been suspected by paleontologists that giant carnivorous dinosaurs would change behavior as they grew. But how that might have affected the world around them remained largely unknown.
"We wanted to test the idea that dinosaurs might be taking on the role of multiple species as they grew, limiting the number of actual species that could co-exist in a community," said Schroeder.
The number of different types of dinosaurs known from around the globe is low, particularly among small species.
"Dinosaurs had surprisingly low diversity. Even accounting for fossilization biases, there just really weren't that many dinosaur species," said Felisa Smith, professor of Biology at UNM and Schroeder's graduate advisor.
To approach the question of decreased dinosaur diversity, Schroeder and her coauthors collected data from well-known fossil localities from around the globe, including over 550 dinosaur species. Organizing dinosaurs by mass and diet, they examined the number of small, medium and large dinosaurs in each community.
They found a strikingly clear pattern:
"There is a gap - very few carnivorous dinosaurs between 100-1000kg [200 pounds to one ton] exist in communities that have megatheropods," Schroeder said. "And the juveniles of those megatheropods fit right into that space."
Schroeder also notes that looking at dinosaur diversity through time was key. Jurassic communities (200-145 million years ago) had smaller gaps and Cretaceous communities (145-65 million years ago) had large ones.
"Jurassic megatheropods don't change as much ? the teenagers are more like the adults, which leaves more room in the community for multiple families of megatheropods as well as some smaller carnivores," Schroeder explained. "The Cretaceous, on the other hand, is completely dominated by Tyrannosaurs and Abelisaurs, which change a lot as they grow."
To tell whether the gap was really caused by juvenile megatheropods, Schroeder and her colleagues rebuilt communities with the teens taken into account. By combining growth rates from lines found in cross-sections of bones, and the number of infant dinosaurs surviving each year based on fossil mass-death assemblages, the team calculated what proportion of a megatheropod species would have been juveniles.
Schroeder explained that this research is important because it (at least partially) elucidates why dinosaur diversity was lower than expected based on other fossil groups. It also explains why there are many more very large species of dinosaurs than small, which is the opposite of what would be expected. But most importantly, she added, it demonstrates the results of growth from very small infants to very large adults on an ecosystem.
"Dinosaurs have been a life-long passion. I was, and still very much am a 'dinosaur kid.' My interest in dinosaur diversity came about when I realized that no one was really looking at dinosaurs the way we look at modern mammals and birds," Schroeder said. "There's a ton to be gained from applying the methods of modern and paleo-ecology to dinosaurs. Fortunately, we're now in an age of dinosaur research where a lot of information is available digitally, so the big data-intensive questions of ecology are now becoming more plausible for dinosaur paleontology."
INFORMATION:
An international team of scientists has developed a system that can generate random numbers over a hundred times faster than current technologies, paving the way towards faster, cheaper, and more secure data encryption in today's digitally connected world.
The random generator system was jointly developed by researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), Yale University, and Trinity College Dublin, and made in NTU.
Random numbers are used for a variety of purposes, such as generating data encryption keys and one-time ...
As Covid-19 impacts lives around the world- a new skeleton study is reconstructing ancient pandemics to assess human's evolutionary ability to fight off leprosy, tuberculosis and treponematoses with help from declining rates of transmission when the germs became widespread.
The researchers state the germs mutated to infect ancient humans so they could replicate- hopping across to as many new hosts as possible- but the severity of the diseases reduced as a result.
The analysis by Adjunct Professor in Archaeology Maciej Henneberg and Dr Teghan Lucas at Flinders ...
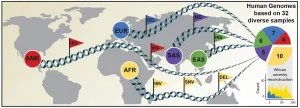
In 2001, the International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium announced the first draft of the human genome reference sequence. The Human Genome Project, as it was called, had taken more than eleven years of work and involved more than 1000 scientists from 40 countries. This reference, however, did not represent a single individual but instead is a composite of humans that could not accurately capture the complexity of human genetic variation.
Building on this, scientists have carried out many sequencing projects over the last 20 years to identify and catalog genetic differences between an individual and the reference genome. Those differences usually ...
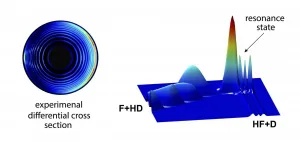
A chemical reaction can be understood in detail at the quantum state-resolved level, through a combined study of molecular crossed beam experiments and theoretical quantum molecular reaction dynamics simulations.
At a single collision condition, the molecular crossed beam apparatus is able to detect the scattering angle-resolved product with rotational state-resolution. Whereas, with accurate global potential energy surface, quantum reactive scattering theory is able to predict the corresponding reactive scattering information.
In previous studies, the chemical reaction dynamics was revealed only with the product rotational state-resolution. And the investigation of a reaction ...
Although the value of vaccines for COVID-19 may seem obvious, government action and investment in vaccines have not been commensurate with the enormous scale of benefits they offer, argue Juan Camilo Castillo and colleagues in this Policy Forum. Since even one extra month of exposure to COVID-19 kills hundreds of thousands, reduces global gross domestic product (GDP) by hundreds of billions of dollars, and generates large losses to human capital by harming education and health, expanding vaccine capacity even further would generate substantial global benefits. Castillo et al. report results of two related exercises: estimating the global benefits from vaccine capacity already in place, and estimating the benefits ...
The pandemic has made clear the threat that some viruses pose to people. But viruses can also infect life-sustaining bacteria and a Johns Hopkins University-led team has developed a test to determine if bacteria are sick, similar to the one used to test humans for COVID-19.
"If there was a COVID-like pandemic occurring in important bacterial populations it would be difficult to tell, because before this study, we lacked the affordable and accurate tools necessary to study viral infections in uncultured bacterial populations," said study corresponding author Sarah ...
Bladder cancer is more aggressive and more advanced in South Texas residents than in many parts of the country, a study by the Mays Cancer Center, home to UT Health San Antonio MD Anderson, indicates.
The disease is also deadlier in Latinos and women, regardless of where they live nationwide, according to the research.
The team from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio), which includes the Mays Cancer Center, compared bladder cancer cases in the Texas Cancer Registry with cases in the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program. SEER, which collects data on cancer cases from various locations and sources across the U.S., does not include Texas statistics.
Cases covered the years ...
A Skoltech researcher has developed a theoretical model of wave formation in straits and channels that accounts for nonlinear effects in the presence of a coastline. This research can improve wave prediction, making maritime travel safer and protecting coastline infrastructure. The paper was published in the journal Ocean Dynamics.
Predicting surface weather at sea has always been a challenging task with very high stakes; for instance, over 4,000 people died due to rough seas during Operation Overlord at Normandy in June 1944, an allied incursion where poor forecasting altered the course of the operation quite significantly. Current wave forecasting models used, for example, by NOAA in the US, are imperfect, but they have many tunable parameters to ensure a reasonably good prediction.
However, ...
Low blood levels of immune cells called lymphocytes, in combination with higher levels of inflammation on PET/CT scans, are indicators of active sarcoidosis -- an inflammatory disease that attacks multiple organs, particularly the lungs and lymph nodes -- which disproportionately affects African Americans. The discovery by researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago could help guide disease treatment. Their findings are published in the journal Frontiers in Medicine.
The researchers were looking for biomarkers -- both in the blood and in PET/CT scan findings -- ...
Large carnivores are generally sensitive to ecosystem changes because their specialized diet and position at the top of the trophic pyramid is associated with small population sizes. This in turn leads to lower genetic diversity in top predators compared to animals lower down the food chain. Genetic diversity is very important for a species' ability to survive and adapt to future changes.
Extraordinary genetic diversity in an extraordinary cat
In this study, the researchers sequenced the complete genome of 53 African leopards and compared them to the Amur leopards and other big cat species. To their surprise, the researchers found that the genetic diversity of African leopards is extremely high: Almost four times ...