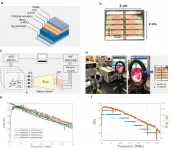
Scientists at the USC Wrigley Institute for Environmental Studies on Santa Catalina Island, working with private industry, report that a new aquaculture technique on the California coast dramatically increases kelp growth, yielding four times more biomass than natural processes. The technique employs a contraption called the "kelp elevator" that optimizes growth for the bronze-colored floating algae by raising and lowering it to different depths.
The team's newly published findings suggest it may be possible to use the open ocean to grow kelp crops for low-carbon biofuel similar to how land is used to harvest fuel feedstocks such as corn and sugarcane -- and with potentially fewer adverse environmental impacts.
The National Research Council has indicated that generating biofuels from feedstocks like corn and soybeans can increase water pollution. Farmers use pesticides and fertilizers on the crops that can end up polluting streams, rivers and lakes. Despite those well-evidenced drawbacks, 7% of the nation's transportation fuel still comes from major food crops. And nearly all of it is corn-based ethanol.
"Forging new pathways to make biofuel requires proving that new methods and feedstocks work. This experiment on the Southern California coast is an important step because it demonstrates kelp can be managed to maximize growth," said Diane Young Kim, corresponding author of the study, associate director of special projects at the USC Wrigley Institute and a professor of environmental studies at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.
The study was published on Feb. 19 in the journal Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. The authors include researchers from USC Dornsife, which is home to the Wrigley Institute, and the La Cañada, California-based company Marine BioEnergy, Inc., which designed and built the experimental system for the study and is currently designing the technology for open-ocean kelp farms.
Though not without obstacles, kelp shows serious promise as biofuel crop
Government and industry see promise in a new generation of climate-friendly biofuels to reduce net carbon dioxide emissions and dependence on foreign oil. New biofuels could either supplement or replace gasoline, diesel, jet fuel and natural gas.
If it lives up to its potential, kelp is a more attractive option than the usual biofuel crops -- corn, canola, soybeans and switchgrass -- for two very important reasons. For one, ocean crops do not compete for fresh water, agricultural land or artificial fertilizers. And secondly, ocean farming does not threaten important habitats when marginal land is brought into cultivation.
The scientists focused on giant kelp, Macrocystis pyrifera, the seaweed that forms majestic underwater forests along the California coast and elsewhere and washes onto beaches in dense mats. Kelp is one of nature's fastest-growing plants and its life cycle is well understood, making it amenable to cultivation.
But farming kelp requires overcoming a few obstacles. To thrive, kelp has to be anchored to a substrate and only grows in sun-soaked waters to about 60 feet deep. But in open oceans, the sunlit surface layer lacks nutrients available in deeper water.
To maximize growth in this ecosystem, the scientists had to figure out how to give kelp a foothold to hang onto, lots of sunlight and access to abundant nutrients. And they had to see if kelp could survive deeper below the surface. So, Marine BioEnergy invented the concept of depth-cycling the kelp, and USC Wrigley scientists conducted the biological and oceanographic trial.
The kelp elevator consists of fiberglass tubes and stainless-steel cables that support the kelp in the open ocean. Juvenile kelp is affixed to a horizontal beam, and the entire structure is raised and lowered in the water column using an automated winch.
Beginning in 2019, research divers collected kelp from the wild, affixed it to the kelp elevator and then deployed it off the northwest shore of Catalina Island, near Wrigley's marine field station. Every day for about 100 days, the elevator would raise the kelp to near the surface during the day so it could soak up sunlight, then lower it to about 260 feet at night so it could absorb nitrate and phosphate in the deeper water. Meantime, the researchers continually checked water conditions and temperature while comparing their kelp to control groups raised in natural conditions.
"We found that depth-cycled kelp grew much faster than the control group of kelp, producing four times the biomass production," Kim said.
The push to develop a new generation of biofuels
Prior to the experiment, it was unclear whether kelp could effectively absorb the nutrients in the deep, cold and dark environment. Nitrate is a big limiting factor for plants and algae, but the study suggests that the kelp found all it needed to thrive when lowered into deep water at night. Equally important, the kelp was able to withstand the greater underwater pressure.
Brian Wilcox, co-founder and chief engineer of Marine BioEnergy, said: "The good news is the farm system can be assembled from off-the-shelf products without new technology. Once implemented, depth-cycling farms could lead to a new way to produce affordable, carbon-neutral fuel year-round."
Cindy Wilcox, co-founder and president of Marine BioEnergy, estimates that it would take a Utah-sized patch of ocean to make enough kelp biofuel to replace 10% of the liquid petroleum consumed annually in the United States. One Utah would take up only 0.13% of the total Pacific Ocean.
Developing a new generation of biofuels has been a priority for California and the federal government. The U.S. Department of Energy's Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy invested $22 million in efforts to increase marine feedstocks for biofuel production, including $2 million to conduct the kelp elevator study. The Department of Energy has a study to locate a billion tons of feedstock per year for biofuels; Cindy Wilcox of Marine BioEnergy said the ocean between California, Hawaii and Alaska could contribute to that goal, helping make the U.S. a leader in this new energy technology.
INFORMATION:
The study authors include Ignacio A. Navarrete, Diane Kim, David W. Ginsburg, Jessica M. Dutton, John Heidelberg and Yubin Raut of the USC Wrigley Institute; Cindy Wilcox and Brian Howard Wilcox of Marine BioEnergy; and Daniel C. Reed at the Marine Science Institute at UC Santa Barbara.
The research was supported by ARPA-E, U.S. Department of Energy Award Number DE-AR0000689 and by Marine BioEnergy, Inc., which has a commercial interest in the research and contributed part of its $2.6 million federal grant to cover the cost of the USC Wrigley Institute study.
You Tube video of diver inspecting open-ocean kelp (via Marine BioEnergy co.): https://www.youtube.com/watch?time_continue=1&v=idHh7P9D2ws&feature=emb_logo