Pressure-regulated excitonic feature enhances photocurrent of all-inorganic 2D perovski
2021-03-03
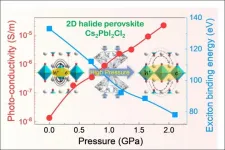
(Press-News.org) HPSTAR scientists Dr. Songhao Guo and Dr. Xujie Lü report three orders of magnitude increase in the photoconductivity of Cs2PbI2Cl2 from its initial value, at the industrially achievable level of 2 GPa, using pressure regulation. Impressively, pressure regulating the 2D perovskite's excitonic features gains it 3D compound characteristics without diminishing its own advantages, making it a more promising material for photovoltaic and photodetector applications. Their study is published as a Cover article in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Two-dimensional (2D) halide perovskites have recently emerged for photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications due to their unique and tunable properties as well as high stability. Despite substantial development progress on developing these materials, how structural regulation affects their excitonic features, which govern their optoelectronic properties, has been unknown until now.
Comprehensive in situ experimental characterization and first-principles calculations reveal that lattice compression effectively regulates the excitonic features of Cs2PbI2Cl2, reducing the exciton binding energy from 133 meV at ambient conditions to 78 meV at 2 GPa. Notably, this reduced exciton binding energy of the 2D perovskite is comparable to typical 3D halide perovskites' values, facilitating the dissociation of photo-excited excitons into free carriers and thus, enhancing the photoconductivity. Further pressurization leads to a layer-sliding-induced phase transition and an anomalous negative-linear compression, which has never been observed in other halide perovskites.
This work reveals the pressure-enhanced photocurrents in 2D halide perovskite for the first time and provides deeper insights into the relationship between their excitonic features and optoelectronic properties, furthering our understanding of their fundamental mechanisms.
INFORMATION:
More information: "Enhanced Photocurrent of All-Inorganic Two-Dimensional Perovskite Cs2PbI2Cl2 via Pressure-Regulated Excitonic Features", Songhao Guo et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c11730 (2021).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-03
New research from The University of Manchester has identified various ways in which UK higher education institutions are beginning to tackle emissions associated with business travel and catering. These are two substantial contributors to emissions in this sector, and difficult to decarbonise. The findings suggest need for further sector-wide efforts to tackle the planet's most pressing issue.
This new study, from The University of Manchester's Tyndall Centre for Climate Change and the Centre for Climate Change and Social Transformations (CAST), analysed publicly available policies of 66 UK universities to identify strategies ...
2021-03-03
Red ginseng, which has long been used as an ingredient in traditional Korean medicine, has recently drawn increased attention as a functional material for its health-promoting effects. The composition and activities of red ginseng vary depending on the processing method, and this has become an active area of research. Recently, a research team in Korea has entered the spotlight as they discovered that red ginseng has inhibitory effects against lung cancer metastasis.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) reported that a joint study conducted by Dr. Jungyeob Ham from the Natural Product Research Center at the KIST Gangneung Institute of Natural Products and Dr. Hyeonseok Ko of Seoul Asan Medical Center revealed that two components of red ginseng, ...
2021-03-03
Researchers from the University of Texas, University of Chicago, University of Notre Dame, and London School of Economics published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines whether entrepreneurs in emerging markets can benefit from marketers' help.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Do Marketers Matter for Entrepreneurs? Evidence from a Field Experiment in Uganda" and is authored by Stephen Anderson, Pradeep Chintagunta, Frank Germann, and Naufel Vilcassim.
Can marketers help improve the world? While this question may seem vast and unknowable, this new study proposes ...
2021-03-03
BINGHAMTON, NY -- Customized diets and lifestyle changes could be key to optimizing mental health, according to new research including faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
"There is increasing evidence that diet plays a major role in improving mental health, but everyone is talking about a healthy diet," said Begdache, an assistant professor of health and wellness studies at Binghamton University and co-author of a new paper in Nutrients.
"We need to consider a spectrum of dietary and lifestyle changes based on different age groups and gender," she said. "There is not one healthy diet that will work for everyone. There is not one fix."
Begdache, who is also a registered dietitian, believes that ...
2021-03-03
Home health visits change to virtual ones during pandemic
'We don't have to rely on mental health professionals'
As perinatal depression soars during pandemic, there's a growing need for treatment
CHICAGO --- Perinatal depression has soared during the pandemic. But many mental health professionals are overwhelmed and can't take on new clients.
Good news comes from a new Northwestern Medicine study finding paraprofessionals generated similar reductions in depressive symptoms as mental health professionals when delivering a group-based cognitive-behavioral therapy intervention.
The study findings are based on ...
2021-03-03
New research has revealed that the diets of early lizards and snakes, which lived alongside dinosaurs around 100 million years ago, were more varied and advanced than previously thought.
The study, led by the University of Bristol and published in Royal Society Open Science, showed lizards, snakes, and mosasaurs in the Cretaceous period already had the full spectrum of diet types, including flesh-eating and plant-based, which they have today.
There are currently some 10,000 species of lizards and snakes, known collectively as squamates. It was originally understood their great diversity was acquired only after the extinction ...
2021-03-03
Patients with type 2 diabetes that were treated with a weekly injection of the breakthrough drug Semaglutide were able to achieve an average weight loss of nearly 10kg, according to a new study published in The Lancet today.
Led by Melanie Davies, Professor of Diabetes Medicine at the University of Leicester and the Co-Director of the Leicester Diabetes Centre, the study showed that two thirds of patients with type 2 diabetes that were treated with weekly injections of a 2.4mg dose of Semaglutide were able to lose at least 5% of their body weight and achieved significant improvement in blood glucose control.
More than a quarter of patients were able to ...
2021-03-03
Pregnant patients in Colorado may be told about parenting and adoption, but not abortion. This is according to a new study led by Kate Coleman-Minahan of the University of Colorado College of Nursing published in the END ...
2021-03-02
Our brains are non-stop consumers. A labyrinth of blood vessels, stacked end-to-end comparable in length to the distance from San Diego to Berkeley, ensures a continuous flow of oxygen and sugar to keep our brains functioning at peak levels.
But how does this intricate system ensure that more active parts of the brain receive enough nourishment versus less demanding areas? That's a century-old problem in neuroscience that scientists at the University of California San Diego have helped answer in a newly published study.
Studying the brains of mice, a team of researchers led by Xiang Ji, David Kleinfeld and their colleagues has deciphered the question of brain energy consumption and blood vessel density through newly developed maps that detail ...
2021-03-02
When you think about your carbon footprint, what comes to mind? Driving and flying, probably. Perhaps home energy consumption or those daily Amazon deliveries. But what about watching Netflix or having Zoom meetings? Ever thought about the carbon footprint of the silicon chips inside your phone, smartwatch or the countless other devices inside your home?
Every aspect of modern computing, from the smallest chip to the largest data center comes with a carbon price tag. For the better part of a century, the tech industry and the field of computation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pressure-regulated excitonic feature enhances photocurrent of all-inorganic 2D perovski