Pressure-regulated excitonic feature enhances photocurrent of all-inorganic 2D perovskite
2021-03-03
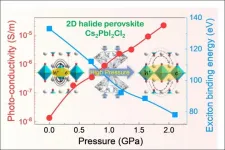
(Press-News.org) HPSTAR scientists Dr. Songhao Guo and Dr. Xujie Lü report three orders of magnitude increase in the photoconductivity of Cs2PbI2Cl2 from its initial value, at the industrially achievable level of 2 GPa, using pressure regulation. Impressively, pressure regulating the 2D perovskite's excitonic features gains it 3D compound characteristics without diminishing its own advantages, making it a more promising material for photovoltaic and photodetector applications. Their study is published as a Cover article in the latest issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Two-dimensional (2D) halide perovskites have recently emerged for photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications due to their unique and tunable properties as well as high stability. Despite substantial development progress on developing these materials, how structural regulation affects their excitonic features, which govern their optoelectronic properties, has been unknown until now.
Comprehensive in situ experimental characterization and first-principles calculations reveal that lattice compression effectively regulates the excitonic features of Cs2PbI2Cl2, reducing the exciton binding energy from 133 meV at ambient conditions to 78 meV at 2 GPa. Notably, this reduced exciton binding energy of the 2D perovskite is comparable to typical 3D halide perovskites' values, facilitating the dissociation of photo-excited excitons into free carriers and thus, enhancing the photoconductivity. Further pressurization leads to a layer-sliding-induced phase transition and an anomalous negative-linear compression, which has never been observed in other halide perovskites.
This work reveals the pressure-enhanced photocurrents in 2D halide perovskite for the first time and provides deeper insights into the relationship between their excitonic features and optoelectronic properties, furthering our understanding of their fundamental mechanisms.
INFORMATION:
More information: "Enhanced Photocurrent of All-Inorganic Two-Dimensional Perovskite Cs2PbI2Cl2 via Pressure-Regulated Excitonic Features", Songhao Guo et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c11730 (2021).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-03
In a report summary released today Thomas McAndrew, a computational scientist and assistant professor at Lehigh University's College of Health includes probabilistic forecasts of the impact of vaccines and variants on the U.S. COVID trajectory over the next few weeks. The goal of the report, says McAndrew, is "to support public health officials, infectious disease modeling groups, and the general public"
Report highlights:
A consensus of 91 forecasters predicts that the B.1.1.7. variant will be found in 42% of all genetic sequences with an S-gene mutation in the first two weeks of March and in 72% in all sequences between ...
2021-03-03
Researchers have captured the first detailed images of newborn babies' lungs as they take their first breaths.
The research, led by the Murdoch Children's Research Institute (MCRI) and published the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, provides a breakthrough in understanding the events around a baby's first breath, why healthy babies cry at birth and provides clues to improving preterm babies' survival chances and long term health outcomes.
About 10 per cent of newborns, and almost all preterm infants, need resuscitation because their lungs do not properly fill with air at birth (a process called lung aeration). Despite ...
2021-03-03
New research from UBC finds that higher life satisfaction is associated with better physical, psychological and behavioural health.
The research, published recently in The Milbank Quarterly, found that higher life satisfaction is linked to 21 positive health and well-being outcomes including:
a 26 per cent reduced risk of mortality
a 46 per cent reduced risk of depression
a 25 per cent reduced risk of physical functioning limitations
a 12 per cent reduced risk of chronic pain
a 14 per cent reduced risk of sleep problem onset
an eight per cent higher likelihood of frequent physical activity
better psychological well-being on ...
2021-03-03
If you've ever swatted a mosquito away from your face, only to have it return again (and again and again), you know that insects can be remarkably acrobatic and resilient in flight. Those traits help them navigate the aerial world, with all of its wind gusts, obstacles, and general uncertainty. Such traits are also hard to build into flying robots, but MIT Assistant Professor Kevin Yufeng Chen has built a system that approaches insects' agility.
Chen, a member of the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and the Research Laboratory of Electronics, has developed insect-sized drones with unprecedented dexterity and resilience. The aerial robots ...
2021-03-03
Green tea supplements modulate facial development of children with Down syndrome
A new study led by Belgian and Spanish researchers published in Scientific Reports adds evidence about the potential benefits of green tea extracts in Down syndrome. The researchers observed that the intake of green tea extracts can reduce facial dysmorphology in children with Down syndrome when taken during the first three years of life. Additional experimental research in mice confirmed the positive effects at low doses. However, they also found that high doses of the extract can disrupt facial and bone development. More research is needed to fully understand the effects of green tea extracts and therefore they should ...
2021-03-03
Imagine a robot.
Perhaps you've just conjured a machine with a rigid, metallic exterior. While robots armored with hard exoskeletons are common, they're not always ideal. Soft-bodied robots, inspired by fish or other squishy creatures, might better adapt to changing environments and work more safely with people.
Roboticists generally have to decide whether to design a hard- or soft-bodied robot for a particular task. But that tradeoff may no longer be necessary.
Working with computer simulations, MIT researchers have developed a concept for a soft-bodied robot that can turn rigid on demand. The approach could enable a new generation of robots that combine the strength and precision of rigid robots with the fluidity and safety of ...
2021-03-03
The models used to produce global climate scenarios may overestimate the energy and emission savings from improved energy efficiency, warns new research led by academics at the University of Sussex Business School and the University of Leeds.
In a review of 33 studies, the researchers find that economy wide rebound effects may erode around half of the energy and emission savings from improved energy efficiency.
These rebound effects result from individuals and businesses responding to the benefits of improved energy efficiency - such as cheaper heating, lighting and travel. These responses improve quality-of-life, raise productivity and boost industrial competitiveness, ...
2021-03-03
Professor Christiani Jeyakumar Henry, Senior Advisor of Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (SIFBI), Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) and his team have developed a Glycaemic Index (GI) glossary of non-Western foods. The research paper (attached PDF) was published in Nutrition & Diabetes on 6 Jan 2021: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-020-00145-w.
Observational studies have shown that the consumption of low glycaemic index (GI) foods is associated with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly less insulin resistance and a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndrome. ...
2021-03-03
Recently, research team led by academician GUO Guangcan from CAS Key Laboratory of Quantum Information of the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of CAS, has made an important progress in quantum information theory. Prof. LI Chuanfeng and Prof. XIANG Guoyong from the team, cooperated with Dr. Strelstov from University of Warsaw, investigated the imaginary part of quantum theory as a resource, and several important results have been obtained. Relevant results are now jointly published as Editors' Suggestion in Physical Review Letters and Physical Review A.
Complex number is a mathematical ...
2021-03-03
It is millions of trillions of times brighter than the sunlight and a whopping 1,000 trillionth of a second, appropriately called the instantaneous light. It is the X-ray Free Electron Laser (XFEL) light that opens a new scientific paradigm. Combining it with AI, an international research team has succeeded in filming and restoring the 3D structure of nanoparticles that share structural similarities with viruses. With the fear of a new pandemic growing around the world due to COVID-19, this discovery is attracting the attention among academic circles for imaging the structure of the virus with both high accuracy and speed.
An international team of researchers from POSTECH, National University of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pressure-regulated excitonic feature enhances photocurrent of all-inorganic 2D perovskite