(Press-News.org) The public doesn't need to know how Artificial Intelligence works to trust it. They just need to know that someone with the necessary skillset is examining AI and has the authority to mete out sanctions if it causes or is likely to cause harm.
Dr Bran Knowles, a senior lecturer in data science at Lancaster University, says: "I'm certain that the public are incapable of determining the trustworthiness of individual AIs... but we don't need them to do this. It's not their responsibility to keep AI honest."
Dr Knowles presents (March 8) a research paper 'The Sanction of Authority: Promoting Public Trust in AI' at the ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency (ACM FAccT).
The paper is co-authored by John T. Richards, of IBM's T.J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, New York.
The general public are, the paper notes, often distrustful of AI, which stems both from the way AI has been portrayed over the years and from a growing awareness that there is little meaningful oversight of it.
The authors argue that greater transparency and more accessible explanations of how AI systems work, perceived to be a means of increasing trust, do not address the public's concerns.
A 'regulatory ecosystem', they say, is the only way that AI will be meaningfully accountable to the public, earning their trust.
"The public do not routinely concern themselves with the trustworthiness of food, aviation, and pharmaceuticals because they trust there is a system which regulates these things and punishes any breach of safety protocols," says Dr Richards.
And, adds Dr Knowles: "Rather than asking that the public gain skills to make informed decisions about which AIs are worthy of their trust, the public needs the same guarantees that any AI they might encounter is not going to cause them harm."
She stresses the critical role of AI documentation in enabling this trustworthy regulatory ecosystem. As an example, the paper discusses work by IBM on AI Factsheets, documentation designed to capture key facts regarding an AI's development and testing.
But, while such documentation can provide information needed by internal auditors and external regulators to assess compliance with emerging frameworks for trustworthy AI, Dr Knowles cautions against relying on it to directly foster public trust.
"If we fail to recognise that the burden to oversee trustworthiness of AI must lie with highly skilled regulators, then there's a good chance that the future of AI documentation is yet another terms and conditions-style consent mechanism - something no one really reads or understands," she says.
The paper calls for AI documentation to be properly understood as a means to empower specialists to assess trustworthiness.
"AI has material consequences in our world which affect real people; and we need genuine accountability to ensure that the AI that pervades our world is helping to make that world better," says Dr Knowles.
ACM FAccT is a computer science conference that brings together researchers and practitioners interested in fairness, accountability, and transparency in socio-technical systems.
INFORMATION:
Lowering the operating temperature of solar panels by just a few degrees can dramatically increase the electricity they generate over their lifetime, KAUST researchers have shown. The hotter a panel gets, the lower its solar power conversion efficiency (PCE) and the faster it will degrade and fail. Finding ways to keep solar panels cool could significantly improve the return on investment of solar-power systems.
The long-standing focus of photovoltaics (PV) research has been to improve solar modules' PCE and make solar power more cost-competitive than nonrenewable power ...
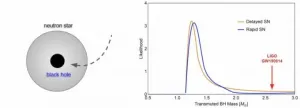
What is the origin of black holes and how is that question connected with another mystery, the nature of dark matter? Dark matter comprises the majority of matter in the Universe, but its nature remains unknown.
Multiple gravitational wave detections of merging black holes have been identified within the last few years by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), commemorated with the 2017 physics Nobel Prize to Kip Thorne, Barry Barish, and Rainer Weiss. A definitive confirmation of the existence of black holes was celebrated with the 2020 physics Nobel Prize awarded to Andrea Ghez, Reinhard Genzel and ...
To effectively fight off SARS-CoV-2, the immune system depends on both antibodies and T cells, a type of white blood cell, which work together to eradicate the virus. However, little was known about virus-specific T cells in asymptomatic patients.
"We now know that many people are getting infected with SARS-CoV-2 without realising it, as they stay healthy and don't develop any symptoms. These asymptomatic infections may provide the key to understanding how the immune system can control the virus without triggering pathological processes," explained Dr Nina Le Bert, Senior Research Fellow ...
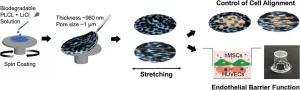
A Korean research group has developed a technology that allows for the differentiation of stem cells into desired cell types, such as vascular mural cells or osteoblasts, without special pretreatment. This technology is expected to facilitate the production of artificial organs for preclinical studies or artificial tissues for transplants such as artificial skin and cardiac patches.
The Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) announced that the research group led by Dr. Youngmee Jung of the Center for Biomaterials has developed a new cell co-culture platform ...
In recent years there has been an increased focus on the circular economy and a heightened demand for products made of recyclable materials, however many materials can only be recycled so many times before they begin to wear out.
This is the case with carbon fibre reinforced polymer (CFRP) composites, non-biodegradable materials which, until now, have lacked a viable recycling method.
CRFP composites are present in products such as wind turbines, aeroplane parts, vehicles such as cars and ships, and everyday technology such as laptops and mobile ...
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
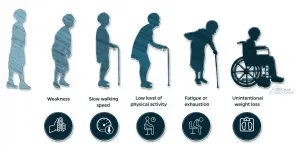
Physicians understand frailty as a dysregulation among multiple systems in the body that make it less resilient and unable to recover completely when faced with a physical challenge such as injury or illness. "Defining frailty on a scientific level, however, has been a challenging task," explains END ...
SPOKANE, Wash. - New clues as to why night shift workers are at increased risk of developing certain types of cancer are presented in a new study conducted at Washington State University Health Sciences Spokane. ...
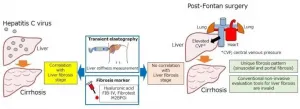
It is well-known that patients who undergo Fontan surgery slowly develop liver fibrosis for years post-operatively. In the past decade, these incidences have been steadily increasing and this is due partly to the need for an accurate diagnostic method. A research group led by Dr. Daisuke Tokuhara, Associate Professor of Pediatrics, Osaka City University Graduate School of Medicine and Dr. Yuki Cho have found that the conventional methods of ultrasound elastography and biomarkers via blood tests do not show the actual status of postoperative liver ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- In a study conducted shortly before COVID-19 vaccines became available in the U.S., more than two-thirds of nursing home and assisted living staff in Indiana indicated willingness to receive a vaccine immediately or in the future. The study was led by researchers from Regenstrief Institute, Indiana University and the State of Indiana. Vaccine uptake by front-line staff is important because it will help protect against serious illness and death for the high-risk people who receive care in these facilities.
"The vaccines offer the opportunity to return to a more normal life within the nursing ...
Native to the southeastern United States, a weedy grass has spread northward to Canada and also made its way to Australia and Japan. Andropogon virginicus grows densely packed and up to seven feet tall, disrupting growth patterns of other plants and competing for resources. When burned, it grows back stronger. There is no way to effectively remove the weed once it has invaded. But there might be a way to use it to human advantage.
An international team of researchers has found that A. virginicus extracts appear to be effective against several human diseases, including diabetes and cancer. The results were published on Dec. 31, 2020, in a special issue of Plants, titled ...