(Press-News.org) BUFFALO, N.Y. -- New research from the University at Buffalo suggests that breast cancer patients who drink sugar-sweetened beverages regularly are at increased risk for death from any cause and breast cancer in particular.
Compared to women who never or rarely drank non-diet soda, those who reported drinking non-diet soda five times or more per week had a 62% higher likelihood of dying from any causes, and were 85% more likely to die from breast cancer specifically. The findings were published online ahead of print March 2 in Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
Research on soda and breast cancer is fairly new, says study first author Nadia Koyratty, a PhD candidate in the Department of Epidemiology and Environmental Health in UB's School of Public Health and Health Professions. Because breast cancer is so common, recommendations regarding lifestyle choices to breast cancer survivors are of considerable importance. And, despite the negative health outcomes associated with drinking soda, such as weight gain, Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, many people continue to drink sugar-sweetened sodas.
There have been only a few observational studies examining the association between sugar-sweetened beverages and cancer mortality. "This study is one of the few that looks at the prognosis of women with breast cancer with respect to non-diet soda consumption," Koyratty says.
Researchers assessed the relationship between sugar-sweetened soda and both all-cause and breast cancer mortality among 927 women who had been diagnosed with breast cancer, aged 35 to 79. Participants were enrolled in the Western New York Exposures and Breast Cancer (WEB) Study, and followed for a median of nearly 19 years.
The study used a food frequency questionnaire to assess participants' food and beverage intake in the 12 to 24 months prior to diagnosis of breast cancer. Of the more than 900 women diagnosed with breast cancer, 41% had died by the end of the follow-up period. Among the participants who had died, there was a higher percentage of women who reported high frequency of sugar-sweetened soda consumption compared to the women who were still living.
The associations did not change when researchers included diet soda consumption as a variable.
Why the focus on non-diet soda?
"Non-diet sodas are the highest contributors of sugar and extra calories to the diet, but they do not bring anything else that is nutritionally beneficial," Koyratty explains. "On the other hand, teas, coffees and 100% fruit juices, unless sugars are added, are healthier beverage options because they do add to the nutritive value through antioxidants and vitamins."
Sugar-sweetened sodas contain large quantities of sucrose and fructose, which give them the highest glycemic load compared to other foods or beverages. These higher concentrations of glucose and insulin may lead to conditions that have been associated with higher risk of breast cancer, the researchers note.
"There are more than 3.5 million breast cancer survivors alive in the U.S. today. We need to better understand the factors that affect their health," said study senior author Jo L. Freudenheim, PhD, SUNY Distinguished Professor in the Department of Epidemiology and Environmental Health in UB's School of Public Health and Health Professions.
"While we need more studies to confirm our findings, this study provides evidence that diet may impact longevity of women after breast cancer," Freudenheim added.
INFORMATION:
Study co-authors include Susan McCann, PhD, of Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center; Amy Millen, PhD, associate professor of epidemiology and environmental health at UB; and Maurizio Trevisan, MD, of Vin University.
The research was supported in part by grants from the Army Medical Research and Material Command, National Cancer Institute and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
Contact: David Hill, davidhil@buffalo.edu
University at Buffalo
716-645-4651
Researchers at Uppsala University have developed a digital self-test that trains users to assess news items, images and videos presented on social media. The self-test has also been evaluated in a scientific study, which confirmed the researchers' hypothesis that the tool genuinely improved the students' ability to apply critical thinking to digital sources.
The new tool and the scientific review of it are part of the News Evaluator project to investigate new methods of enhancing young people's capacity for critical awareness of digital sources, a key component of digital literacy.
"As ...
Philadelphia, March 9, 2021--Combining computational mining of big data with experimental testing in the lab, researchers at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have identified RNA editing events that influence gene expression and, in turn, the phenotypic manifestation of that expression. In analyzing so-called A-to-I RNA editing, in which the adenosine of an RNA molecule is chemically modified into an inosine, the researchers describe how a single nucleotide change by RNA editing can have large downstream effects. The findings were published today in Genome Biology.
"Millions of A-to-I RNA editing sites have been identified across the human transcriptome, but the functions of most RNA editing ...
If travel to distant stars within an individual's lifetime is going to be possible, a means of faster-than-light propulsion will have to be found. To date, even recent research about superluminal (faster-than-light) transport based on Einstein's theory of general relativity would require vast amounts of hypothetical particles and states of matter that have "exotic" physical properties such as negative energy density. This type of matter either cannot currently be found or cannot be manufactured in viable quantities. In contrast, new research carried out at the University of Göttingen gets around this problem by constructing a new class of hyper-fast 'solitons' ...
Researchers have demonstrated that a slimy, yet tough, type of biofilm that certain bacteria make for protection and to help them move around can also be used to separate water and oil. The material may be useful for applications such as cleaning contaminated waters.
In the journal Langmuir, North Carolina State University researchers reported the findings of an experiment in which they used a material produced by the bacteria Gluconacetobacter hansenii as a filter to separate water from an oil mixture.
"It's really remarkable to think that these little bugs can make this stuff that is so perfect in many ways," said Lucian Lucia, the study's corresponding author and an associate professor of forest biomaterials and chemistry at NC State.
The biofilm the bacteria make and ...
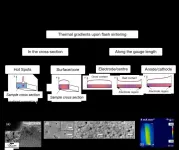
Flash sintering is a ceramic processing technique which uses electric current to intensively heat the ceramic sample internally rather than using only external furnace heating. The process can lower ceramic processing temperatures and durations significantly, enabling ceramics to be co-processed with metals or other materials, and reducing energy use.
However, the process can result in low quality ceramics due to weaknesses caused by inhomogeneities in the microstructure.
The origins of these inhomogeneities caused by thermal gradients in the material during flash sintering have been studied by researchers ...
Deforestation may cause an initial increase in malaria infections across Southeast Asia before leading to later decreases, a study published today in eLife suggests.
The results may help malaria control programs in the region develop better strategies for eliminating malaria infections and educating residents on how to protect themselves from infection.
Mosquitos spread the malaria parasite to humans causing infections that can be severe and sometimes deadly. In the area along the Mekong river in Southeast Asia, many residents hunt or harvest wood in the surrounding forests, which can increase their risk of infection. Yet recent outbreaks of malaria in the region have also been linked to deforestation.
"As countries in the region focus their malaria control ...
As the fight against COVID-19 continues, scientists have turned to an unlikely source for a potentially effective treatment: tiny antibodies naturally generated by llamas.
While the world has welcomed the news of multiple vaccines against COVID-19, the search for effective treatments for those who contract the virus is ongoing. Now scientists are looking to what might seem to be an unlikely source: the South American llama.
Researchers are using the ultrabright X-rays of the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility at DOE's Argonne National Laboratory, to help turn naturally generated llama antibodies into potentially effective therapies against ...
Every 12 minutes, someone in the United States dies of pancreatic cancer, which is often diagnosed late, spreads rapidly and has a five-year survival rate at approximately 10 percent. Treatment may involve radiation, surgery and chemotherapy, though often the cancer becomes resistant to drugs.
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center, in collaboration with Sanford-Burnham-Prebys Medical Discovery Institute and Columbia University, demonstrated that a new tumor-penetrating therapy, tested in animal models, may enhance the effects of chemotherapy, reduce metastasis ...
Computational models of air quality have long been used to shed light on pollution control efforts in the United States and Europe, but the tools have not found widespread adoption in Latin America. New work from North Carolina State University and Universidad de La Salle demonstrates how these models can be adapted to offer practical insights into air quality challenges in the Americas outside the U.S.
Computational air quality models can be used in multiple ways. For example, they can be used to determine which sources are responsible for what fraction of air pollution. They can also help authorities predict how air pollution might change if different pollution control methods are adopted.
"Historically, it's been very challenging to apply these modeling ...
Polymer scientists from the University of Groningen and NHL Stenden University of Applied Sciences, both in the Netherlands, have developed a polymer membrane from biobased malic acid. It is a superamphiphilic vitrimer epoxy resin membrane that can be used to separate water and oil. This membrane is fully recyclable. When the pores are blocked by foulants, it can be depolymerized, cleaned and subsequently pressed into a new membrane. A paper describing the creation of this membrane was published in the journal Advanced Materials on 7 March 2021.
How do you clean up an oil spill in ...