Graphene nanoparticles and their influence on neurons
New research shows that the nanomaterial acts on the excitatory synapses, interfering with the development of anxiety related behaviours in vertebrates
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) Effective, specific, with a reversible and non-harmful action: the identikit of the perfect biomaterial seems to correspond to graphene flakes, the subject of a new study carried out by SISSA - International School for Advanced Studies of Trieste, Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2) of Barcelona and the National Graphene Institute of the University of Manchester, in the framework of the European Graphene Flagship project. This nanomaterial has demonstrated the ability to interact with the functions of the nervous system in vertebrates in a very specific manner, interrupting the building up of a pathological process that leads to anxiety related behaviour.
"We previously showed that when graphene flakes are delivered to neurons they interfere spontaneously with excitatory synapses by transiently preventing glutamate release from presynaptic terminals" says Laura Ballerini of SISSA, the leader of the team that carried out the research study 'Graphene oxide prevents lateral amygdala dysfunctional synaptic plasticity and reverts long lasting anxiety behavior in rats', recently published in Biomaterials, co-authored by Audrey Franceschi Biagioni, Giada Cellot, Elisa Pati, Neus Lozano, Belén Ballesteros, Raffaele Casani, Norberto Cysne Coimbra, Kostas Kostarelos.
"We investigated whether such a reduction in synaptic activity was sufficient to modify related behaviours, in particular the pathological ones that develop due to a transient and localised hyper-function of excitatory synapses". This approach would fortify the strategy of selective and transient targeting of synapses to prevent the development of brain pathologies by using the so-called precise medicine treatments.
To test this hypothesis, the team focused on post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and carried out the experiments in two phases, in vivo and in vitro.
"We analysed defensive behaviours caused in rats by the presence of a predator, using the exposure to cat odour, to induce an aversive memory" explains Audrey Franceschi Biagioni of SISSA, the first author of the study. "If exposed to the predator odour, the rat has a defensive response, holing up, and this experience is so well-imprinted in the memory, that when the animal is placed in the same context even six days later, the animal remembers the odour of the predator and acts the same protective behaviour. This is a well-known and consolidated model, that we used to reproduce a stress behaviour. Exposure to the predator can modify neuronal connections - a phenomenon that is technically known as plasticity - and increases synaptic activity in a specific area of the amygdala that therefore represented the target of our study to test the effects of the nanomaterial".
Laura Ballerini adds: "We hypothesised that graphene flakes that we showed to temporarily inhibit excitatory synapses (without causing inflammation, damage to neurons or other side effects) could be injected in the lateral amygdala when the plasticity associated with memory was consolidated. If the nanomaterial was efficient in blocking excitatory synapses, it should inhibit plasticity and decrease the anxiety related response. And this is what happened: the animals that were administered with graphene flakes, after six days, "forgot" the anxiety related responses, rescuing their behaviour".
The second part of the research was performed in vitro. "In vivo we could observe only behavioural changes and could not evaluate the impact of the graphene flakes on synapses," explains Giada Cellot, researcher at SISSA and first author of the study together with Audrey Franceschi Biagioni. "In vitro experiments allowed to work on a simplified model, to get insight about the mechanisms through which the graphene flakes can interact with neurons. We used neuronal cultures obtained from the amygdala, the region of the brain where the stress response occurs, and we observed that the effects of nanomaterials were specific for the excitatory synapses and a short exposure to graphene flakes could prevent the pathological plasticity of the synapses".
Thanks to these findings, graphene flakes have shown their potential as nanotools (biomedical tools composed of nanomaterials) that could act in a specific and reversible way on synaptic activity to interrupt a pathological process and therefore they might be used also to transport drugs or for other applications in the field of precision medicine.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-10
Healthcare personnel who were infected with COVID-19 had stronger risk factors outside the workplace than in their hospital or healthcare setting. That is the finding of a new study published today in JAMA Network Open conducted by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers, colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and three other universities.
The study examined survey data from nearly 25,000 healthcare providers in Baltimore, Atlanta, and Chicago including at University of Maryland Medical System (UMMS) hospitals. They found that having a known exposure to someone who tested positive for COVID-19 in the community was the strongest risk factor for testing ...
2021-03-10
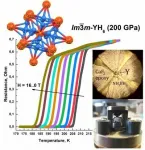
An international team led by Artem R. Oganov, a Professor at Skoltech and MISIS, and Dr. Ivan Troyan from the Institute of Crystallography of RAS performed theoretical and experimental research on a new high-temperature superconductor, yttrium hydride (YH6). Their findings were published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Yttrium hydrides rank among the three highest-temperature superconductors known to date. The leader among the three is a material with an unknown S-C-H composition and superconductivity at 288 K, which is followed by lanthanum hydride, LaH10, superconducting at temperatures up to 259 K), and, finally, yttrium hydrides, YH6 and YH9, with maximum superconductivity temperatures of 224 K and 243 K, respectively. The superconductivity of YH6 ...
2021-03-10
Boston - A new study shows that providing a non-acute care space after hospital discharge for patients with COVID-19 who are experiencing homelessness helped reduce hospitalizations and keep inpatient beds available for those requiring acute care. Published in JAMA Network Open and led by researchers at Boston Medical Center's (BMC) Grayken Center for Addiction, the study demonstrates the importance of developing innovative approaches to tackle issues facing people experiencing homelessness, including their inability to isolate, in order to mitigate additional ...
2021-03-10
Associations between strong predictors of suicidal behaviors over the life course, such as adverse childhood events (ACEs), remain understudied among youth of color. Although not previously considered high risk, suicide attempts among Black youth increased 73% between 1991 and 2017.
Published in the Children and Youth Services Review, University of Minnesota researchers pulled data from the 2016 Minnesota Student Survey (MSS) to examine associations between ACEs, school connectedness and suicide ideation and attempts among Somali, Latino, Hmong and Non-Hispanic ...
2021-03-10
Research published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry shows that the presence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in bald eagle populations is slowly declining. Bald eagles are apex predators that nest and, more importantly, feed along water bodies, making them excellent bioindicators of environmental contaminants that bioaccumulate up the aquatic food web. The findings are both good news for eagles and instructive for regulators tasked with managing surface water quality by setting protective levels for wildlife, as well as fish consumption advisories for humans.
Lead author Bill Route from the National ...
2021-03-10
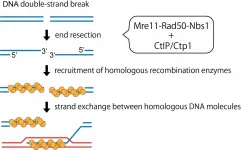
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have uncovered mechanisms underlying the activation of the MRN complex-- the cell's DNA scissors. Using purified yeast proteins, they demonstrated that phosphorylation of Ctp1, a homolog of a tumor-suppressor protein, plays a key role in activating MRN complex's DNA clipping activity. Intriguingly, a short segment of yeast Ctp1 or its human counterpart could stimulate endonuclease activity of their respective MRN complexes, suggesting its conserved function across species.
DNA functions as a roadmap that guides the identity and functions of cells. A glitch in the DNA ...
2021-03-10
BINGHAMTON, NY -- Star employees often get most of the credit when things go right, but also shoulder most of the blame when things go wrong, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The study explored the potential risks and rewards of collaborating with stars - individuals who have a reputation for exhibiting exceptional performance - and how individual performance factors into how much credit and blame is shared with collaborators.
"Stars are human, and they fail from time to time. We wanted to shift the focus away from stars, and find out what happens to the people who collaborate ...
2021-03-10
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Geoscientists at Sandia National Laboratories used 3D-printed rocks and an advanced, large-scale computer model of past earthquakes to understand and prevent earthquakes triggered by energy exploration.
Injecting water underground after unconventional oil and gas extraction, commonly known as fracking, geothermal energy stimulation and carbon dioxide sequestration all can trigger earthquakes. Of course, energy companies do their due diligence to check for faults -- breaks in the earth's upper crust that are prone to earthquakes -- but sometimes ...
2021-03-10
Eye contact is a key to establishing a connection, and teachers use it often to encourage participation. But can a robot do this too? Can it draw a response simply by making "eye" contact, even with people who are less inclined to speak up. A recent study suggests that it can.
Researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology published results of experiments in which robots led a Swedish word game with individuals whose proficiency in the Nordic language was varied. They found that by redirecting its gaze to less proficient players, a robot can elicit involvement from even the most reluctant participants.
Researchers Sarah Gillet and Ronald Cumbal say the results offer evidence that robots could play a productive role in educational settings.
Calling on someone by name isn't ...
2021-03-10
The protein α-synuclein is one of the most abundant proteins in the human brain. It is often referred to as the "Parkinson protein", as deposition of this protein in brain cells is a hallmark of Parkinson's disease. Despite the high interest of biomedical research in the protein, many questions concerning the function and physiology of α-synuclein in living cells still remain to be answered. For example, it was previously unclear whether and to what extent the protein binds to and interacts with internal cell components such as membranes. As such processes could play a role in the development of the disease, the team led by Konstanz-based physical chemist Professor Malte Drescher used the further development of an established measurement method called ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Graphene nanoparticles and their influence on neurons
New research shows that the nanomaterial acts on the excitatory synapses, interfering with the development of anxiety related behaviours in vertebrates