Scientists develop new magnetic nanomaterial for ?ounterfeit money prevention
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) An international research team led by NUST MISIS has developed a new iron-cobalt-nickel nanocomposite with tunable magnetic properties. The nanocomposite could be used to protect money and securities from counterfeiting. The study was published in Nanomaterials.
Presently, research on magnetic nanomaterials with controlled magnetic characteristics is one of the most promising fields. Due to their small size, as well as their excellent magnetic and electric properties these materials have a broad range of potential applications from mobile devices to space technologies.
The new iron-cobalt-nickel nanocomposite was obtained by chemical precipitation, followed by a reduction process.
"This method is simple and, most importantly, it allows the properties of the product to be controlled at each stage of its production, and chemically pure nanopowders to be produced with a given composition, shape, and dispersion", noted Yuri Konyukhov, Deputy Head of the Department of Functional Nanosystems and High-Temperature Materials at NUST MISIS.
Konyukhov also stressed that the new composite was observed to possess high value of coercivity, which makes the technology applicable e.g. to magnetic rubbers and different magnetically coupled devices. Another potential application is protecting money and securities from counterfeiting.
"The efforts of the scientific community have been recently focused on protecting humans and electronic devices from electromagnetic radiation. The development of thin, flexible and relatively transparent metal-polymer composites for EMI shielding is a promising research direction. The use of the new nanocomposite with controlled magnetic properties as the magnetic filler could lead to a breakthrough in EMI protection", added Yuri Konyukhov.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-10
Researchers hope to use an agricultural pest's genetic code against it to prevent billions of dollars in annual losses in the United States.
Stable flies, or Stomoxys calcitrans, are spotted, tan-colored flies found around the world. They are easily mistaken for the common housefly but for one notable distinction: They bite.
"If you get one in your house and it bites you, it's a stable fly," said Joshua Benoit, an assistant professor of biology at the University of Cincinnati.
Stable flies don't bite so much as chomp. They are the scourge of beachgoers in Florida and recreational boaters in upstate New York. According to Thomas Jefferson, they tormented signatories ...
2021-03-10
DALLAS - March 10, 2021 - UT Southwestern scientists have identified key genes involved in brain waves that are pivotal for encoding memories. The END ...
2021-03-10
Bacteria employ many different strategies to regulate gene expression in response to fluctuating, often stressful, conditions in their environments. One type of regulation involves non-coding RNA molecules called small RNAs (sRNAs), which are found in all domains of life. A new study led by researchers at the University of Illinois describes, for the first time, the impacts of sRNA interactions in individual bacterial cells. Their findings are reported in the journal Nature Communications, with the paper selected as an Editors' highlight article.
Bacterial sRNAs are often involved in regulating stress responses using mechanisms that involve base-pairing ...
2021-03-10
While neurological complications of COVID-19 in children are rare, in contrast to adults, an international expert review of positive neuroimaging findings in children with acute and post-infectious COVID-19 found that the most common abnormalities resembled immune-mediated patterns of disease involving the brain, spine, and nerves. Strokes, which are more commonly reported in adults with COVID-19, were much less frequently encountered in children. The study of 38 children, published in the journal Lancet, was the largest to date of central nervous system imaging manifestations of COVID-19 in children.
"Thanks to a major international collaboration, we found that neuroimaging manifestations ...
2021-03-10
When we recall a memory, we retrieve specific details about it: where, when, with whom. But we often also experience a vivid feeling of remembering the event, sometimes almost reliving it. Memory researchers call these processes objective and subjective memory, respectively. A new study from the Center for Mind and Brain at the University of California, Davis, shows that objective and subjective memory can function independently, involve different parts of the brain, and that people base their decisions on subjective memory -- how they feel about a memory -- more than on its accuracy.
"The study distinguishes between ...
2021-03-10
Aspirin is an established, safe, and low-cost medication in long-standing common use in prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, and in the past a pain relief and fever reducing medication. The use of aspirin was very popular during the 1918 Spanish Influenza pandemic, several decades before in-vitro confirmation of its activity against RNA viruses. Studies showed that aspirin, in addition to its well-known anti-inflammatory effects, could modulate the innate and adaptive immune responses helping the human immune system battle some viral infections.
With this information ...
2021-03-10
Computer engineers at the world's largest companies and universities are using machines to scan through tomes of written material. The goal? Teach these machines the gift of language. Do that, some even claim, and computers will be able to mimic the human brain.
But this impressive compute capability comes with real costs, including perpetuating racism and causing significant environmental damage, according to a new paper, "On the Dangers of Stochastic Parrots: Can Language Models Be Too Big? ?" The paper is being presented Wednesday, March 10 at the ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency (ACM FAccT).
This is the first exhaustive review of the literature surrounding the risks that come with rapid growth of language-learning technologies, said ...
2021-03-10
Effective, specific, with a reversible and non-harmful action: the identikit of the perfect biomaterial seems to correspond to graphene flakes, the subject of a new study carried out by SISSA - International School for Advanced Studies of Trieste, Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2) of Barcelona and the National Graphene Institute of the University of Manchester, in the framework of the European Graphene Flagship project. This nanomaterial has demonstrated the ability to interact with the functions of the nervous system in vertebrates in a very specific manner, interrupting the building up of a pathological process that leads ...
2021-03-10
Healthcare personnel who were infected with COVID-19 had stronger risk factors outside the workplace than in their hospital or healthcare setting. That is the finding of a new study published today in JAMA Network Open conducted by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers, colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and three other universities.
The study examined survey data from nearly 25,000 healthcare providers in Baltimore, Atlanta, and Chicago including at University of Maryland Medical System (UMMS) hospitals. They found that having a known exposure to someone who tested positive for COVID-19 in the community was the strongest risk factor for testing ...
2021-03-10
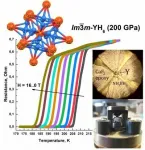
An international team led by Artem R. Oganov, a Professor at Skoltech and MISIS, and Dr. Ivan Troyan from the Institute of Crystallography of RAS performed theoretical and experimental research on a new high-temperature superconductor, yttrium hydride (YH6). Their findings were published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Yttrium hydrides rank among the three highest-temperature superconductors known to date. The leader among the three is a material with an unknown S-C-H composition and superconductivity at 288 K, which is followed by lanthanum hydride, LaH10, superconducting at temperatures up to 259 K), and, finally, yttrium hydrides, YH6 and YH9, with maximum superconductivity temperatures of 224 K and 243 K, respectively. The superconductivity of YH6 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists develop new magnetic nanomaterial for ?ounterfeit money prevention