(Press-News.org) March 12, 2021 - Financial strains like debt or unemployment are significant risk factors for becoming homeless, and even help to explain increased risk of homelessness associated with severe mental illness, reports a study in a supplement to the April issue of Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
The findings "suggest that adding financial well-being as a focus of homelessness prevention efforts seems promising, both at the individual and community level," according to the new research, led by Eric Elbogen, PhD, of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) National Center on Homelessness and Duke University School of Medicine. The study appears as part of a special issue on "Multimorbidity and social drivers of homelessness and health," produced in partnership between the VA National Center on Homelessness and the American Public Health Association Caucus on Homelessness.
Financial strain is a mediator of the link between homelessness and mental illness
Using data on nearly 35,000 participants in a nationally representative longitudinal survey, Dr. Elbogen and colleagues analyzed financial strain as a predictor of homelessness, on its own and in combination with mental illness. Responses to a 2001-02 survey were analyzed to identify factors associated with homelessness at a follow-up survey in 2004-05.
All types of financial strain analyzed - financial crises and debt, lower income, and unemployment - were associated with an increased risk of future homelessness. As expected, severe mental illness - psychotic, bipolar, or depressive disorder - was directly related to an increased risk of homelessness.
In addition, there was a significant "mediating effect" of financial strain, which explained 39 percent of the link between homelessness and mental illness. Homelessness risk was lowest for participants with none of the four types of financial strain, whether or not they had severe mental illness.
"Conversely, participants with all four financial strain variables had significantly higher risk of homelessness," Dr. Elbogen and coauthors write. The risk of becoming homeless increased with each additional type of financial strain, independent of mental illness.
The findings offer a "fresh perspective" on homelessness prevention efforts, the researchers write. "[I]nterventions could be proactively targeted at improving an individual's financial literacy and well-being such that they could prevent situations that may contribute to future homelessness."
The finding that financial strain accounts for part of the impact of severe mental illness "suggests that addressing mental illness without consideration of financial strain may not lead to optimal reduction in homelessness risk," Dr. Elbogen and colleagues add. The study supports efforts to help homeless individuals grow financially through employment, increased financial knowledge, and money management skills - as offered in effective interventions such as Housing First and VA homeless programs.
The special supplement to Medical Care focuses "on the intersection of homelessness, medical illnesses, and related social factors," according to an introductory guest editorial by Jack Tsai, PhD, of the VA National Center on Homelessness and University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston and colleagues. A key focus is on the rising rates of multimorbidity - having multiple medical, mental health, and substance use disorders - amid the ongoing obesity crisis in an aging population.
The supplement includes nine original papers examining special populations such as homeless youth, older adults, and veterans, along with medical and behavioral health conditions such as tuberculosis, HIV, and opioid use disorder. It also presents two editorials commenting on the history of homelessness and its association with suicide. Dr. Tsai and colleagues write: "This special issue illustrates the complex realities of homelessness but also the progress that has been made and the continued efforts and gaps in knowledge that need work."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Financial Strain, Mental Illness, and Homelessness: Results from a National Longitudinal Study."
DOI: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000001453
About Medical Care
Rated as one of the top ten journals in health care administration, Medical Care is devoted to all aspects of the administration and delivery of health care. This scholarly journal publishes original, peer-reviewed papers documenting the most current developments in the rapidly changing field of health care. Medical Care provides timely reports on the findings of original investigations into issues related to the research, planning, organization, financing, provision, and evaluation of health services. In addition, numerous special supplementary issues that focus on specialized topics are produced with each volume. Medical Care is the official journal of the Medical Care Section of the American Public Health Association.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (WKL) is a global leader in professional information, software solutions, and services for the clinicians, nurses, accountants, lawyers, and tax, finance, audit, risk, compliance, and regulatory sectors. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with advanced technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2019 annual revenues of €4.6 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers and students with advanced clinical decision support, learning and research and clinical intelligence. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter @WKHealth.
For more information, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
Mantle cell lymphoma is a malignant disease in which intensive treatment can prolong life. In a new study, scientists from Uppsala University and other Swedish universities show that people with mantle cell lymphoma who were unmarried, and those who had low educational attainment, were less often treated with a stem-cell transplantation, which may result in poorer survival. The findings have been published in the scientific journal Blood Advances.
Patients diagnosed with a mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) where the disease has spread receive intensive treatment with cytotoxic drugs and stem-cell transplantation. In a new study, researchers looked at which people are more likely to be offered transplants, and compared survival between those ...
WINSTON-SALEM, NC - March 12, 2021 - The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine is investigating how cats with chronic kidney disease could someday help inform treatment for humans.
In humans, treatment for chronic kidney disease -- a condition in which the kidneys are damaged and cannot filter blood as well as they should -- focuses on slowing the progression of the organ damage. The condition can progress to end-stage kidney failure, which is fatal without dialysis or a kidney transplant. An estimated 37 million people in the US suffer from chronic kidney disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
The American Veterinary Medical Association estimates there are about 58 million ...
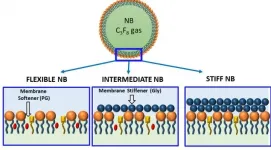
If you were given "ultrasound" in a word association game, "sound wave" might easily come to mind. But in recent years, a new term has surfaced: bubbles. Those ephemeral, globular shapes are proving useful in improving medical imaging, disease detection and targeted drug delivery. There's just one glitch: bubbles fizzle out soon after injection into the bloodstream.
Now, after 10 years' work, a multidisciplinary research team has built a better bubble. Their new formulations have resulted in nanoscale bubbles with customizable outer shells -- so small and durable that they can travel to and penetrate some of the ...
(BOSTON) -- There is a great need to generate various types of cells for use in new therapies to replace tissues that are lost due to disease or injuries, or for studies outside the human body to improve our understanding of how organs and tissues function in health and disease. Many of these efforts start with human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) that, in theory, have the capacity to differentiate into virtually any cell type in the right culture conditions. The 2012 Nobel Prize awarded to Shinya Yamanaka recognized his discovery of a strategy that can reprogram adult cells to become iPSCs ...
Arlington, Va. (March 12, 2021)--A new supplement offering guidance on severe COVID-19 management in resource-limited settings is now available on the American Journal of Tropical Medicine (AJTMH) website. Pragmatic Recommendations for the Management of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in Low- and Middle-Income Countries was coordinated by a COVID-LMIC Task Force headed by Alfred Papali, MD, of Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC, and Marcus Schultz, MD, PhD, of Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand; University of Oxford, United Kingdom; and Amsterdam University Medical Centers, The Netherlands. ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - University at Buffalo computer scientists have developed a tool that automatically identifies deepfake photos by analyzing light reflections in the eyes.
The tool proved 94% effective in experiments described in a paper accepted at the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing to be held in June in Toronto, Canada.
"The cornea is almost like a perfect semisphere and is very reflective," says the paper's lead author, Siwei Lyu, PhD, SUNY Empire Innovation Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering. "So, anything that is coming to the eye with a light emitting from those sources will have an image on ...
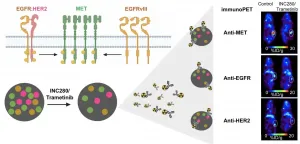
Reston, VA--Immuno-positron emission tomography (PET) imaging can provide early insight into a tumor's response to targeted therapy, allowing physicians to select the most effective treatment for patients who have cancer. The new research was published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
The research showed that immuno-PET successfully visualizes changes in different cancer receptors (receptor tyrosine kinases, or RTKs) within tumors during targeted therapies. This gives physicians a tool that can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment soon after its administration.
"When healthy cells turn into cancer cells, there is a disruption in the RTK signaling. This makes RTKs a valuable therapeutic and ...
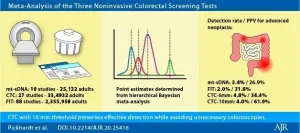
Leesburg, VA, March 12, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), compared with multi-target stool-DNA (mt-sDNA) and fecal immunochemical test (FIT), CT colonography (CTC) with 10 mm threshold most effectively targets advanced neoplasia (AN)--preserving detection while decreasing unnecessary colonoscopies.
"CTC performed with a polyp size threshold for colonoscopy referral set at 10 mm represents the most effective and efficient non-invasive screening test for colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention and detection," clarified first author Perry J. Pickhardt from the department of radiology ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Did you ever wonder how social networking applications like Facebook and LinkedIn make recommendations on the people you should friend or pages you should follow?
Behind the scenes are machine learning models that classify nodes based on the data they contain about users -- for example, their level of education, location or political affiliation. The models then use these classifications to recommend people and pages to each user. But there is significant bias in the recommendations made by these models -- known as graph neural networks (GNNs) ...
A new study by UC Davis MIND Institute researchers suggests that executive control differences in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be the result of a unique approach, rather than an impairment.
Executive control difficulties are common in individuals with autism and are associated with challenges completing tasks and managing time. The study, published in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, sought to tease out whether these difficulties represent a disruption in proactive executive control (engaged and maintained before a ...