(Press-News.org) Females who are fit and healthy tend to burn more fat when they exercise than men, according to new research from a team of sports nutritionists.
The research, comprising two new studies from academics led by the University of Bath's Centre for Nutrition, Exercise & Metabolism, analysed the factors that most influenced individuals' capacity to burn body fat when undertaking endurance sports.
How the body burns fat is important to all of us for good metabolic health, insulin sensitivity and in reducing the risk of developing Type II diabetes. But, for endurance sport competitions, such as running or cycling, how the body burns fat can make the difference between success and failure.
Previous research from the same team has shown how, for endurance athletes competing in distance events, the body's carbohydrate stores deplenish quickly when exercising. This means that that an athletes' ability to tap into their fat reserves to fuel them on becomes essential to their performance.
The first study, published in the International Journal of Sport Nutrition & Exercise Medicine, involved 73 healthy adults aged 19-63 (41 men; 32 women). It tested the lifestyle and biological factors for optimal fat burning by asking participants to take part in a cycling fitness test and measuring key indicators.
Their results found that females and those who were physically fitter, right across the age ranges, burnt fat more efficiently when exercising.
The second related paper, published in the journal Experimental Physiology, took this a stage further to explore what molecular factors in our muscles and fat tissue determine how fat is burnt. This experiment involved the researchers taking fat and muscle biopsies from participants to analyse how differences in the proteins in fat and muscle tissue might affect their ability to burn fat.
It found that the proteins in muscle that are involved in breaking down stored fat into the smaller fatty acids, and proteins involved in transporting those fatty acids into the mitochondria in muscle (the powerhouse of the cells) consistently correlated with a greater ability to burn fat. The molecular factors explored did not explain why females burned more fat than males, however.
Lead author on both papers, Ollie Chrzanowski-Smith from the University of Bath explains: "Our study found that females typically have a greater reliance upon fat as a fuel source during exercise than males. Understanding the mechanisms behind these sex differences in fuel use may help explain why being female seems to confer a metabolic advantage for insulin sensitivity, an important marker of metabolic health."
The researchers note that the ability to burn fat as a fuel appears to protect against future weight gain, ensuring good weight management. However, they caution that the body's ability to burn fat should not be equated with an ability to lose weight. Losing weight is primarily produced by an energy deficit (ie. consuming fewer calories than we expend). For weight loss, in particular where individuals might be overweight, they stress the importance of diet and exercise.
Dr Javier Gonzalez, also from the University of Bath's Department for Health, added: "Weight management is mainly about energy balance, so to lose weight we need to eat fewer calories than we expend through our resting metabolism and physical activity. However, people with a higher ability to burn fat as a fuel seem to be somewhat protected against future weight gain, which might be related to how fat burning affects food intake and energy expenditure.
"Ultimately, a greater capacity to burn fat as a fuel has potential benefits for endurance athletes, by delaying the timepoint when they run out of precious carbohydrate stores."
INFORMATION:
To access the studies, both funded by the University of Bath, see:
- Determinants of Peak Fat Oxidation Rates During Cycling in Healthy Men and Women,
https://doi.org/10.1123/ijsnem.2020-0262.
- Resting skeletal muscle ATGL and CPT1b are associated with peak fat oxidation rates in men and women but do not explain observed sex?differences,
https://doi.org/10.1113/EP089431.
Research led by the Cavendish Laboratory at the University of Cambridge has identified a material that could help tackle speed and energy, the two biggest challenges for computers of the future.
Research in the field of light-based computing - using light instead of electricity for computation to go beyond the limits of today's computers - is moving fast, but barriers remain in developing optical switching, the process by which light would be easily turned 'on' and 'off', reflecting or transmitting light on-demand.
The study, published in Nature Communications, shows that a material known as Ta2NiSe5 could switch between a window and a mirror in a quadrillionth of a second when struck by a short laser pulse, paving the way for the development ...
The bacterial equivalent of a traffic jam causes multilayered biofilms to form in the presence of antibiotics, shows a study published today in eLife.
The study reveals how the collective behaviour of bacterial colonies may contribute to the emergence of antibiotic resistance. These insights could pave the way to new approaches for treating bacterial infections that help thwart the emergence of resistance.
Bacteria can acquire resistance to antibiotics through genetic mutations. But they can also defend themselves via collective behaviours such as joining together ...
The inclusion of a special new perovskite layer has enabled scientists to create a "spin-polarized LED" without needing a magnetic field or extremely low temperatures, potentially clearing the path to a raft of novel technologies.
Details of the research conducted at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the University of Utah appear in the journal Science.
Researchers at NREL and around the world have been investigating the use of perovskite semiconductors for solar cells that have proven to be highly efficient at converting sunlight to electricity. Since a solar cell is one of the most demanding applications of any semiconductor, scientists are discovering other uses exist as well.
"We are exploring the fundamental properties of metal-halide ...
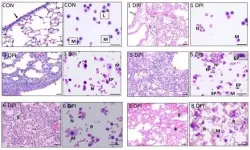
Philadelphia, March 16, 2021 - A significant proportion of hospitalized patients with influenza develop complications of acute respiratory distress syndrome, driven by virus-induced cytopathic effects as well as exaggerated host immune response. Reporting in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, investigators have found that treatment with an immune receptor blocker in combination with an antiviral agent markedly improves survival of mice infected with lethal influenza and reduces lung pathology in swine-influenza-infected piglets. Their research also provides insights into the optimal timing of treatment to prevent acute lung injury.
Previously, the investigators found ...
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a new intravascular imaging technique that could one day be used to detect coronary plaques that are likely to lead to a heart attack. Heart attacks are often triggered when an unstable plaque ruptures and then blocks a major artery that carries blood and oxygen to the heart.
"If unstable coronary plaques could be detected before they rupture, pharmacological or other treatments could be initiated early to prevent heart attacks and save lives," said research team leader Seemantini Nadkarni from the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital. "Our new imaging technique represents a major step toward achieving this."
In The Optical Society (OSA) journal Biomedical ...
MADISON, Wis. -- Millions of people are administered general anesthesia each year in the United States alone, but it's not always easy to tell whether they are actually unconscious.
A small proportion of those patients regain some awareness during medical procedures, but a new study of the brain activity that represents consciousness could prevent that potential trauma. It may also help both people in comas and scientists struggling to define which parts of the brain can claim to be key to the conscious mind.
"What has been shown for 100 years in an unconscious state like sleep are these slow ...
Low doses of propylparaben - a chemical preservative found in food, drugs and cosmetics - can alter pregnancy-related changes in the breast in ways that may lessen the protection against breast cancer that pregnancy hormones normally convey, according to University of Massachusetts Amherst research.
The findings, published March 16 in the journal Endocrinology, suggest that propylparaben is an endocrine-disrupting chemical that interferes with the actions of hormones, says environmental health scientist Laura Vandenberg, the study's senior author. Endocrine ...
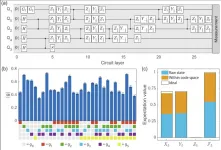
Universal fault-tolerant quantum computing relies on the implementation of quantum error correction. An essential milestone is the achievement of error-corrected logical qubits that genuinely benefit from error correction, outperforming simple physical qubits. Although tremendous efforts have been devoted to demonstrate quantum error correcting codes with different quantum hardware, previous realizations are limited to be against certain types of errors or to prepare special logical states. It remains one of the greatest and also notoriously difficult challenges to realize a universal quantum error correcting code for more than a decade.
In a new research article published in the ...
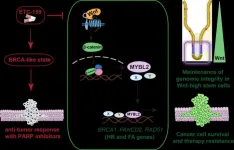
SINGAPORE, 16 March 2021 - ETC-159, a made-in-Singapore anti-cancer drug that is currently in early phase clinical trials for use in a subset of colorectal and gynaecological cancers, could also prevent some tumours from resisting therapies by blocking a key DNA repair mechanism, researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) in Singapore reported in the journal EMBO Molecular Medicine.
Among the many therapies used to treat cancers, inhibitors of the enzyme poly (ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) prevent cancer cells from repairing naturally occurring DNA damage, including unwanted/harmful breaks in the DNA. When too many breaks accumulate, the cell dies.
"Some cancers have an overactive Wnt signalling pathway that may make them ...
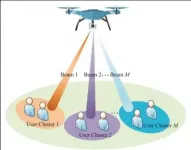
Non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) and millimeter-wave (mmWave) are two crucial techniques of 5G to meet the explosive capacity demands. On the other hand, UAVs deployed as aerial base stations are potential to provide ubiquitous coverage and satisfy users' multifarious requirements due to their flexibility and mobility. Nevertheless, the finite onboard energy is a fundamental limit of UAVs, which can deter the performance of UAV communication networks. Therefore, the researchers Xiaowei PANG and Nan ZHAO from Dalian University of Technology, Jie TANG and Xiuyin ZHANG from South China University of Technology, and Yi QIAN from University of Nebraska-Lincoln have focused on designing energy-efficient ...