INFORMATION:
New aluminum and samarium hexaboride-based composite material with near-zero expansion
Scientists developed a new aluminum and samarium hexaboride-based composite material with near-zero expansion
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) Precision or invar alloys have been developed by scientists for many centuries. These iron and nickel-based alloys are capable of keeping their size unchanged within a given range of temperatures. Because of this, they are used in the manufacture of precision gages, standards of length, details for mechanical dial plates, and similar devices. However, invar alloys lack many other useful physical characteristics, and this limits their use in other areas, for example, those that require high thermal conductivity of materials. Therefore, scientists have long been trying to create a unique composite material based on other metals that would combine thermal expansion typical for invar alloys with additional physical properties.
A team of researchers from BFU suggested their approach to this issue. To develop a new composite material, they used a traditional method based on the reduction of heat expansion of functional materials. In the course of this technique, ceramic or other particles are added to the initial metal. Compared to the metal, the particles have considerably lower heat expansion. This time, the scientists added an intermediary valence compound to the mix. Unlike integral valence elements, such compounds can have anomalous properties: for example, some of them can shrink when heated. Moreover, the level of such shrinkage can be regulated. Composites based on a metal and an intermediate valence system allow one to manage their thermal expansion and to bring it down to almost zero. This considerably widens the range of their applications.
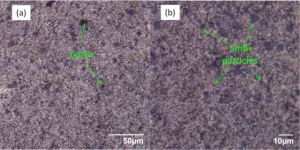
In their study, the team used aluminum and samarium hexaboride. Although these substances are widely known, it was the first time they were combined together. To obtain the composite, the components in powder form were hot-pressed. After that, the team studied the result with an optical microscope and used X-ray tomography to diagnose the internal structure of the sample without additional polishing and finishing. Using layer-by-layer scanning, the scientists developed a 3D model of the new substance and found out that samarium hexaboride particles were evenly distributed in aluminum. This confirmed that the composite was fit for further studies. To measure its heat expansion, the team used capacitive dilatometry within the temperature range of 10-210 ?. The sample had zero heat expansion at 45 ? and demonstrated invar behavior up to 60 K.
"Our work is the first in its field, and we are not ready to consider scaling to the industrial level yet. Currently, we are focused on specific problems that require unique solutions. The issue of reducing the heat expansion of functional materials by means of adding small particles of low or zero expansion substances has been relevant in the instrument-making industry, radio electronics, aviation, and space industry, as well as in laser and cryogen technologies for many years," said Dmitry Serebrennikov, a Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, and a research associate at the Laboratory for Strongly Correlated Electron Systems, Science and Research Center "Functional Nanomaterials" at BFU.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Evolved to stop bacteria, designed for stability
2021-03-17
Connections are crucial. Bacteria may be most dangerous when they connect - banding together to build fortress-like structures known as biofilms that afford them resistance to antibiotics. But a biomolecular scientist in Israel and a microbiologist in California have forged their own connections that could lead to new protocols for laying siege to biofilm-protected colonies. Their research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), USA.
This interdisciplinary collaboration began with a lecture given at the Weizmann Institute of Science in the Life Sciences Colloquium. Prof. Dianne Newman of the California Institute of Technology was the speaker, ...
Simple blood test could replace surgery for some brain tumour patients
2021-03-17
A research breakthrough shows that a simple blood test could reduce, or in some cases replace, the need for intrusive surgery when determining the best course of treatment for patients with a specific type of brain tumour.
Researchers at the Brain Tumour Research Centre of Excellence at the University of Plymouth have discovered a biomarker which helps to distinguish whether meningioma - the most common form of adult primary brain tumour - is grade I or grade II.
The grading is significant because lower grade tumours can sometimes remain dormant for long periods, not requiring high risk surgery or harsh treatments such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Tumours classified as grade II can progress to become cancerous and more aggressive treatment may be needed in order ...
Pressure sensors could ensure a proper helmet fit to help protect the brain
2021-03-17
Many athletes, from football players to equestrians, rely on helmets to protect their heads from impacts or falls. However, a loose or improperly fitted helmet could leave them vulnerable to traumatic brain injuries (TBIs), a leading cause of death or disability in the U.S. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Sensors have developed a highly sensitive pressure sensor cap that, when worn under a helmet, could help reveal whether the headgear is a perfect fit.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1.6 to 3.8 million sports- and recreation-related TBIs occur each year in the U.S. Field data suggest that loose or improperly fitted helmets can contribute ...
Socioeconomic factors play key role in COVID-19 impact on Blacks, Hispanics
2021-03-17
March 17, 2021-- A new study published online in the Annals of the American Thoracic Society reveals how socioeconomic factors partially explain the increased odds that Black and Hispanic Americans have of testing positive for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
In "Association of Race and Ethnicity With COVID-19 Test Positivity and Hospitalization Is Mediated by Socioeconomic Factors," Hayley B. Gershengorn, MD, associate professor, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and co-authors ...
Scientists shrink pancreatic tumors by starving their cellular 'neighbors'
2021-03-17
Scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute demonstrated for the first time that blocking "cell drinking," or macropinocytosis, in the thick tissue surrounding a pancreatic tumor slowed tumor growth--providing more evidence that macropinocytosis is a driver of pancreatic cancer growth and is an important therapeutic target. The study was published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
"Now that we know that macropinocytosis is 'revved up' in both pancreatic cancer cells and the surrounding fibrotic tissue, blocking the process might provide a 'double whammy' to pancreatic tumors," ...
New software improves accuracy of factories' mass-produced 3D-printed parts
2021-03-17
Researchers at University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign developed software to improve the accuracy of 3D-printed parts, seeking to reduce costs and waste for companies using additive manufacturing to mass produce parts in factories.
"Additive manufacturing is incredibly exciting and offers tremendous benefits, but consistency and accuracy on mass-produced 3D-printed parts can be an issue. As with any production technology, parts built should be as close to identical as possible, whether it is 10 parts or 10 million," said Professor Bill King, Andersen Chair in the Department of Mechanical Science and Engineering and leader of the project.
The team's ...
More than one in 10 patients with lung cancer do not know what type they have
2021-03-17
- The increasing complexity of treatments for lung cancer and language differences can make it difficult for patients to communicate with their medical teams
- Risks of jeopardising the treatment and care journey as well as recent progress in patient empowerment.
Lugano, Switzerland; Denver, CO, USA, 17 March 2021 - More than one in 10 patients with lung cancer do not know what type of tumour they have, according to data from a 17-country study carried out by the Global Lung Cancer Coalition (GLCC) to be presented at the European Lung Cancer Conference (ELCC) ...
When volcanoes go metal
2021-03-17
What would a volcano - and its lava flows - look like on a planetary body made primarily of metal? A pilot study from North Carolina State University offers insights into ferrovolcanism that could help scientists interpret landscape features on other worlds.
Volcanoes form when magma, which consists of the partially molten solids beneath a planet's surface, erupts. On Earth, that magma is mostly molten rock, composed largely of silica. But not every planetary body is made of rock - some can be primarily icy or even metallic.
"Cryovolcanism is volcanic activity on icy worlds, and we've seen it happen on Saturn's moon Enceladus," says Arianna Soldati, assistant professor of marine, earth and atmospheric sciences at NC State and lead author of a paper describing the ...
Serious vision impairment declines among older Americans between 2008 and 2017
2021-03-17
TORONTO, ON - American adults 65 years old and older have better vision than that age group did nearly a decade ago, according to a recent study published in the journal Ophthalmic Epidemiology.
In 2008, 8.3% of those aged 65 and older in the US reported serious vision impairment. In 2017 that number decreased to 6.6% for the 65-plus cohort. Put another way: if vision impairment rates had remained at 2008 levels, an additional 848,000 older Americans would have suffered serious vision impairment in 2017.
"The implications of a reduction in vision impairment are significant," ...
Cancer mutations insight could boost detection and personalize treatments
2021-03-17
Cancer develops when changes occur with one or more genes in our cells. A change in a gene is called a fault or a mutation.
The inherited gene mutations found in this study, are passed from parent to child and are common in the population. However, each one individually does not significantly raise cancer risk.
Instead, these mutations collectively act to raise the risk of cancer developing. They do not directly cause cancer, instead they most likely interact with many other risk factors or random mutations that accumulate over a person's lifetime.
Cancers caused by inherited faulty genes were previously thought to be very rare, compared with mutations that happen by chance as we ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] New aluminum and samarium hexaboride-based composite material with near-zero expansionScientists developed a new aluminum and samarium hexaboride-based composite material with near-zero expansion