Semiconductor nanogrooves enhanced broad spectral band mmW and THz detection
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) Millimetre and terahertz wave detectors have a wide range of applications in areas such as communications, security, biological diagnosis, spectroscopy, and remote sensing. They are the components that can transform light information loaded by long-wavelength millimetre and terahertz waves into electrical signals. High-performance room-temperature detectors with high sensitivity, fast response, broad spectral bandwidth, and possibility to be extended to large format arrays are always pursued. They are the building blocks for a wide range of millimetre and terahertz wave related systems, including communication network, deep space exploration equipment, security screening system, spectroscopy system, and material composition inspection. However, conventional efficient photoexcitation in optoelectronic semiconductors seems not applicable due to small quantum energy of millimetre and terahertz waves and strong background thermal disturbances. Although Golay cells, pyroelectrics, bolometers, and Schottky barrier diodes (SBDs) are in widespread use, they suffer from poor noise equivalent power (NEP) (only 10-9-10-10 W Hz-1/2 level for Golay cells and pyroelectrics), slow response (ms level for Golay cells, pyroelectrics), or narrow spectral bandwidth (multiple modules for SBDs to achieve broad spectral bandwidth).
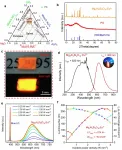
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, Professor Dao Hua Zhang and Presidential Postdoctoral Fellow Jinchao Tong from the School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore and co-workers reported millimetre and terahertz wave detectors based on epitaxially grown InSb/AlInSb/GaSb/GaAs by molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE) with nanogroove array for enhancement. The InSb films in such a novel structure possess high electron mobility and negative permittivity in a broad millimetre and terahertz wave band, and further, it is suitable for fabrication of large format arrays. A broad spectral bandwidth planar equiangular spiral antenna is designed to efficiently couple millimetre and terahertz waves. A nanogroove array is fabricated in the InSb layer, which can arouse strong excitation of millimetre and terahertz wave surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), especially at the InSb-air interfaces, leading to a general improvement of 50-100% for detection performance. A NEP of 2.2×10-14 W Hz-1/2 or a detectivity (D*) of 2.7×1012 cm Hz1/2 W-1 is achieved at 1.75 mm (0.171 THz) at room temperature. The device also shows a broad spectral band detection from 0.9 mm (0.330 THz) to 9.4 mm (0.032 THz) and a fast response speed of 3.5 μs. By moderately decreasing the temperature to the thermoelectric cooling of 200 K, the corresponding NEP, D* and response speed can be further improved to 3.8×10-15 W Hz-1/2, 1.6×1013 cm Hz1/2 W-1 and 780 ns, respectively.
The detection of the detector is based millimetre and terahertz wave SPPs induced nonequilibrium electrons. Under external bias, unidirectional drift of these carriers will form photocurrent. The newly developed detector has a few advantages compared to current technologies. High sensitivity: the achieved NEP is 2-3 order superior to state-of-the-art. Uncooled operation: no cooling technology is required for its normal operation. Broad spectral band detection: A single detector can performance detection in 0.9-9.4 mm. Easy to be extended: this detector is based on wafer-scale InSb. Fast response speed: the detector has a response speed of μs level at room temperature. Simple configuration: the detector is based on very simple two-terminal structure.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
Singapore, 17 March 2021 - Healthy and cancer cells can look similar under a microscope. One way of differentiating them is by examining the level of acidity, or pH level, inside the cells.
Tapping on this distinguishing characteristic, a research team from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has developed a technique that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to determine whether a single cell is healthy or cancerous by analysing its pH. Each cancer test can be completed in under 35 minutes, and single cells can be classified with an accuracy rate of more than 95 per cent.
The research, led by Professor Lim Chwee Teck, Director of the Institute for Health Innovation ...
2021-03-17
A 2020 explosion in Lebanon's port city of Beirut led to a southward-bound, high-velocity atmospheric wave that rivaled ones generated by volcanic eruptions.
Just after 6 p.m. local time (15.00 UTC) on August 4, 2020, more than 2,750 tons worth of unsafely stored ammonium nitrate exploded in Lebanon's port city of Beirut, killing around 200 people, making more than 300,000 temporarily homeless, and leaving a 140-metre-diameter crater in its wake. The blast is considered one of the most powerful non-nuclear, man-made explosions in human history.
Now, calculations by Hokkaido University scientists in Japan have found that the atmospheric ...
2021-03-17
PHILADEPHIA - Since the 1990s the rate of spinal fusion to treat lower back pain has been on the rise. A new prospective clinical study published in the journal Neurosurgery, the official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons, found that lumbar fusions were three times more likely to be effective and obtain better patient outcomes, when guidelines for fusion were followed. The results suggest that when surgeons operate outside of what the evidence based literature suggests, patients may not have significant improvements in their quality of life and could have increased pain or other limitations.
"Unfortunately, we don't know how many lumbar fusion surgeries are ...
2021-03-17
Philadelphia, March 17, 2021 - Researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) affiliated with the CHOP Epilepsy Neurogenetics Initiative (ENGIN) have compiled a complete genetic and clinical analysis of more than 400 individuals with SCN2A-related disorder, which has been linked to a variety of neurodevelopmental disorders, including epilepsy and autism. By linking clinical features to genetic abnormalities in a standardized format, the researchers hope their findings lead to improved identification and clinical intervention.
The study was published ...
2021-03-17
A groundbreaking study has given new insights into how copper deposit-forming fluids are transported naturally from their source deep underground towards the Earth's surface.
A team of geologists, led by Lawrence Carter from the University of Exeter's Camborne School of Mines, has published a new theory for how porphyry copper deposits form.
Porphyry deposits provide around 75 per cent of the world's copper which is in increasing demand for electric vehicles, power infrastructure and green technologies such as wind turbines. They originally develop several kilometres below the Earth's surface above large magma chambers. Not only are porphyry deposits rare but most large near-surface examples have already been ...
2021-03-17
A world-first 'flow model' devised by Australian researchers could drastically slash public transport commuter times during peak periods on some of the busiest roads in major cities, new research shows.
When this flow model was implemented to improve the worst traffic bottlenecks across Melbourne, commuters saved close to 2000 hours of travel time during a single morning peak period (7am-9am) and approximately 11,000 hours of passenger travel time during a normal weekday.
Ameliorating major traffic bottlenecks also contributed to a more than 23 per cent improvement in reliability of Melbourne's public transport network, ...
2021-03-17
OSAKA, Japan. Quantum computers have seen a lot attention recently as they are expected to solve certain problems that are outside the capabilities of normal computers. Primary to these problems is determining the electronic states of atoms and molecules so they can be used more effectively in a variety of industries - from lithium-ion battery designs to in silico technologies in drug development. A common way scientists have approached this problem is by calculating the total energies of the individual states of a molecule or atom and then determine the difference in energy between these states. In nature, many molecules grow in size and complexity, and the cost to calculate this constant flux is beyond the capability of any traditional ...
2021-03-17
High-power laser diode (LD) driven solid-state lighting can generate super-high luminance far exceeding the state-of-art light-emitting diodes (LEDs) source by factors of 2-10, enabling it particularly attractive for automotive headlamp, outdoor lighting, multimedia projectors, laser TVs and so on. Whereas, the thermal shock of laser is extreme, and under intense laser excitation, traditional LEDs phosphor would suffer from luminescence degradation or even failure due to the luminescence saturation. Aiming to overcome this deficiency, highly efficient and stable luminescence bulk phosphors including single crystal, polycrystalline ceramic phosphor and glass ceramic composite phosphor ...
2021-03-17
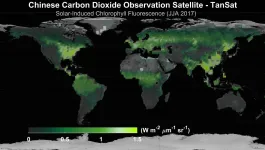
Solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) is emitted during plant photosynthesis. SIF results from vegetation chlorophyll giving off red and infrared light wavelengths when excited by solar radiation. Measuring SIF is important because it is closely related to the terrestrial gross primary productivity (GPP), which calculates the total amount of carbon dioxide fixed through photosynthesis in a given area. According to many laboratory and field experiments, studies show that SIF can effectively improve estimations of GPP, which is necessary for global carbon sink research and carbon mitigation strategies.
China has committed to carbon neutrality by 2060. Technological upgrades and energy structure adjustments through the next four decades will be vital to reducing carbon ...
2021-03-17
This is a landmark study in so far as being the first to raise the alarm that, despite early successes with Covid-19 vaccines, further research is warranted on a next generation of Covid-19 vaccines.
The results from this study, however, only indicate that the AstraZeneca vaccine does not have at least 60% efficacy against mild-moderate Covid-19 due to the B.1.351 (N501Y.V2) variant.
Based on a broader body of evidence, the World Health Organization recommends that this vaccine still be deployed in countries where the B.1.351 variant circulates, as it likely still protects against severe ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Semiconductor nanogrooves enhanced broad spectral band mmW and THz detection