New quantum algorithm surpasses the QPE norm
Osaka City University refines quantum computer-ready algorithm to measure the vertical ionization energies of atoms and molecules within 0.1 eV of precision.
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) OSAKA, Japan. Quantum computers have seen a lot attention recently as they are expected to solve certain problems that are outside the capabilities of normal computers. Primary to these problems is determining the electronic states of atoms and molecules so they can be used more effectively in a variety of industries - from lithium-ion battery designs to in silico technologies in drug development. A common way scientists have approached this problem is by calculating the total energies of the individual states of a molecule or atom and then determine the difference in energy between these states. In nature, many molecules grow in size and complexity, and the cost to calculate this constant flux is beyond the capability of any traditional computer or currently establish quantum algorithms. Therefore, theoretical predictions of the total energies have only been possible if molecules are not sizable and isolated from their natural environment.
"For quantum computers to be a reality, its algorithms must be robust enough to accurately predict the electronic states of atoms and molecules, as they exist in nature, " state Kenji Sugisaki and Takeji Takui from the Graduate School of Science, Osaka City University.
In December 2020, Sugisaki and Takui, together with their colleagues, led a team of researchers to develop a quantum algorithm they call Bayesian eXchange coupling parameter calculator with Broken-symmetry wave functions (BxB), that predicts the electronic states of atoms and molecules by directly calculating the energy differences. They noted that energy differences in atoms and molecules remain constant, regardless to how complex and large they get despite their total energies grow as the system size. "With BxB, we avoided the common practice of calculating the total energies and targeted the energy differences directly, keeping computing costs within polynomial time", they state. "Since then, our goal has been to improve the efficiency of our BxB software so it can predict the electronic sates of atoms and molecules with chemical precision."
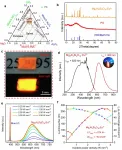
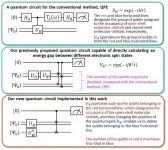
Using the computing costs of a well-known algorithm called Quantum Phase Estimation (QPE) as a benchmark, "we calculated the vertical ionization energies of small molecules such as CO, O2, CN, F2, H2O, NH3 within 0.1 electron volts (eV) of precision," states the team, using half the number of qubits, bringing the calculation cost on par with QPE.
Their findings will be published online in the March edition of The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
Ionization energy is one of the most fundamental physical properties of atoms and molecules and an important indicator for understanding the strength and properties of chemical bonds and reactions. In short, accurately predicting the ionization energy allows us to use chemicals beyond the current norm. In the past, it was necessary to calculate the energies of the neutral and ionized states, but with the BxB quantum algorithm, the ionization energy can be obtained in a single calculation without inspecting the individual total energies of the neutral and ionized states. "From numerical simulations of the quantum logic circuit in BxB, we found that the computational cost for reading out the ionization energy is constant regardless of the atomic number or the size of the molecule," the team states, "and that the ionization energy can be obtained with a high accuracy of 0.1 eV after modifying the length of the quantum logic circuit to be less than one tenth of QPE." (See image for modification details)
With the development of quantum computer hardware, Sugisaki and Takui, along with their team, are expecting the BxB quantum algorithm to perform high-precision energy calculations for large molecules that cannot be treated in real time with conventional computers.
INFORMATION:
We are Osaka City University - the oldest research university in Osaka. With 9 undergraduate faculties and 11 graduate schools all dedicated to making urban life better, energy cleaner, and people healthier and happier, we have won numerous awards and have produced 2 Nobel laureates. For more information, please visit our website at https://www.osaka-cu.ac.jp/en
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
High-power laser diode (LD) driven solid-state lighting can generate super-high luminance far exceeding the state-of-art light-emitting diodes (LEDs) source by factors of 2-10, enabling it particularly attractive for automotive headlamp, outdoor lighting, multimedia projectors, laser TVs and so on. Whereas, the thermal shock of laser is extreme, and under intense laser excitation, traditional LEDs phosphor would suffer from luminescence degradation or even failure due to the luminescence saturation. Aiming to overcome this deficiency, highly efficient and stable luminescence bulk phosphors including single crystal, polycrystalline ceramic phosphor and glass ceramic composite phosphor ...
2021-03-17
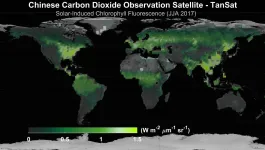
Solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) is emitted during plant photosynthesis. SIF results from vegetation chlorophyll giving off red and infrared light wavelengths when excited by solar radiation. Measuring SIF is important because it is closely related to the terrestrial gross primary productivity (GPP), which calculates the total amount of carbon dioxide fixed through photosynthesis in a given area. According to many laboratory and field experiments, studies show that SIF can effectively improve estimations of GPP, which is necessary for global carbon sink research and carbon mitigation strategies.
China has committed to carbon neutrality by 2060. Technological upgrades and energy structure adjustments through the next four decades will be vital to reducing carbon ...
2021-03-17
This is a landmark study in so far as being the first to raise the alarm that, despite early successes with Covid-19 vaccines, further research is warranted on a next generation of Covid-19 vaccines.
The results from this study, however, only indicate that the AstraZeneca vaccine does not have at least 60% efficacy against mild-moderate Covid-19 due to the B.1.351 (N501Y.V2) variant.
Based on a broader body of evidence, the World Health Organization recommends that this vaccine still be deployed in countries where the B.1.351 variant circulates, as it likely still protects against severe ...
2021-03-17
Researchers from Skoltech and their colleagues from Hadassah Medical Center have developed hybrid nanostructured particles that can be magnetically guided to the tumor, tracked by their fluorescence and pushed to release the drug on demand by ultrasound. This technology can help make cancer chemotherapy more targeted. The paper was published in the journal Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces.Current treatments for cancer include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation, and surgery, but these are often not selective enough to target just the tumor ...
2021-03-17
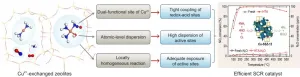
The diesel engine is the backbone of transportation due to its irreplaceability as the primary power source for the freight, navigation and marine engine industries and non-road engineering machinery for the foreseeable future. However, the control of contaminants from fuel combustion has become an urgent global concern. Nitrogen oxides are the primary pollutants from transportation and can contribute to the formation of haze, photochemical smog and acid rain. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with ammonia (NH3-SCR) technology has been successfully and commercially applied for controlling pollution from diesel vehicle exhaust. The development of ...
2021-03-17
Electronic organic materials offer promise to support alternative and green energy sources to meet escalating global energy demands and strict environmental regulations. A KAUST-led team has now developed electron-transporting, so-called n-type, organic semiconductors that could help generate electricity from waste heat released by industrial processes and homes.
Thermoelectric generators that can convert temperature changes or gradients into electricity are highly suited for harnessing waste heat. These readily scalable devices are environmentally friendly and do not have any moving parts, which makes them ...
2021-03-17
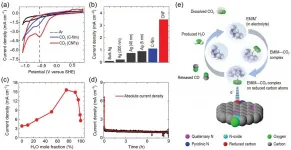
The use of fossil fuels as energy carriers and raw materials promotes the rapid development of the society. However, the excessive exploitation of fossil fuels gives rise to the energy crisis and undesirable environmental changes. In particular, a continuous increase of CO2 concentration in the atmosphere, which is > 400 ppm today and is estimated to triple by 2040, might result in a series of environmental issues, such as global warming, rising sea levels, and more extreme weather. Therefore, cutting CO2 emissions and developing abundant renewable energy are urgent needs and challenges for our society.
CO2 is not only one of the main greenhouse gases but also an abundant, nontoxic, nonflammable, and renewable C1 resource. Electrochemical conversion of CO2 is an attractive way to recycle ...
2021-03-17
According to a new study published in the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, the carbon footprint of personal protective equipment (PPE) provided to health and social care staff in England during the first six months of the COVID-19 pandemic was equivalent to flying from London to New York 244 times every day. The good news is that adopting a range of strategies including increased UK manufacture, reusing and recycling could reduce the environmental impact of PPE dramatically while maintaining the safety of staff and patients.
The study, by Brighton and Sussex Medical School and Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust, found that the 3 billion items of PPE used from ...
2021-03-17
Precision or invar alloys have been developed by scientists for many centuries. These iron and nickel-based alloys are capable of keeping their size unchanged within a given range of temperatures. Because of this, they are used in the manufacture of precision gages, standards of length, details for mechanical dial plates, and similar devices. However, invar alloys lack many other useful physical characteristics, and this limits their use in other areas, for example, those that require high thermal conductivity of materials. Therefore, scientists have long been trying to create a unique composite material based on other metals ...
2021-03-17
Connections are crucial. Bacteria may be most dangerous when they connect - banding together to build fortress-like structures known as biofilms that afford them resistance to antibiotics. But a biomolecular scientist in Israel and a microbiologist in California have forged their own connections that could lead to new protocols for laying siege to biofilm-protected colonies. Their research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), USA.
This interdisciplinary collaboration began with a lecture given at the Weizmann Institute of Science in the Life Sciences Colloquium. Prof. Dianne Newman of the California Institute of Technology was the speaker, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New quantum algorithm surpasses the QPE norm
Osaka City University refines quantum computer-ready algorithm to measure the vertical ionization energies of atoms and molecules within 0.1 eV of precision.