Certain mouthwashes might stop COVID-19 virus transmission
A Rutgers study shows two types of mouthwash disrupt SARS-CoV-2 in laboratory
2021-03-17
(Press-News.org) Researchers at Rutgers School of Dental Medicine have found evidence that two types of mouthwash disrupt the COVID-19 virus under laboratory conditions, preventing it from replicating in a human cell.
The study, published in the journal Pathogens, found that Listerine and the prescription mouthwash Chlorhexidine disrupted the virus within seconds after being diluted to concentrations that would mimic actual use. Further studies are needed to test real-life efficacy in humans.
The study was conducted in a lab using concentrations of the mouthwash and the time it would take to contact tissues to replicate conditions found in the mouth, said Daniel H. Fine, the paper's senior author and chair of the school's Department of Oral Biology.
The study found two other mouthwashes showed promise in potentially providing some protection in preventing viral transmission: Betadine, which contains povidone iodine, and Peroxal, which contains hydrogen peroxide. However, only Listerine and Chlorhexidine disrupted the virus with little impact on skin cells inside the mouth that provide a protective barrier against the virus.
"Both Povidone iodine and Peroxal caused significant skin cell death in our studies, while both Listerine and Chlorhexidine had minimal skin cell killing at concentrations that simulated what would be found in daily use," said Fine.
The team studied the efficacy of mouthwash potential for preventing viral transmission to better understand how dental providers can be protected from aerosols exhaled by patients. "As dentists, we're right there in a patient's face. We wanted to know if there's something that might lower the viral load,'' said coauthor Eileen Hoskin, an assistant professor at Rutgers School of Dental Medicine.
Fine cautions the public against relying on mouthwash as a way to slow the spread until it is proven in clinical trials on humans.
"The ultimate goal would be to determine whether rinsing two or three times a day with an antiseptic agent with active anti-viral activity would have the potential to reduce the ability to transmit the disease. But this needs to be investigated in a real-world situation,'' he said.
Previous research has shown various types of antiseptic mouthwashes can disrupt the novel coronavirus and temporarily prevent transmission, but this was one of the first studies that examined antiseptic rinse concentrations, time of contact and the skin-cell killing properties that simulated oral conditions. The study was conducted by a team of dental school scientists and virologist at the Public Health Research Institute.
"Since the SARS CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19 enters primarily through the oral and nasal cavity, oral biologists should be included in these studies because they have an in-depth understanding of oral infectious diseases," said Fine.
INFORMATION:
Other Rutgers authors included Theresa Chang and Chuan Xu at the Public Health Research Institute based at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School and Kenneth Markowitz and Carla Cugini at Rutgers School of Dental Medicine.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-17
A study published March 16 in JAMA (the Journal of the American Medical Association) confirms that neither vitamin D nor the omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil prevent the development of atrial fibrillation (AF), a potentially serious heart rhythm disturbance. The newly published research follows a presentation made by Christine Albert, MD, MPH, at the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions last year.
In their JAMA analysis, Albert and her research team also examined whether vitamin D or omega-3 fatty acids might have an impact on paroxysmal versus persistent atrial ...
2021-03-17
Millimetre and terahertz wave detectors have a wide range of applications in areas such as communications, security, biological diagnosis, spectroscopy, and remote sensing. They are the components that can transform light information loaded by long-wavelength millimetre and terahertz waves into electrical signals. High-performance room-temperature detectors with high sensitivity, fast response, broad spectral bandwidth, and possibility to be extended to large format arrays are always pursued. They are the building blocks for a wide range of millimetre ...
2021-03-17
Singapore, 17 March 2021 - Healthy and cancer cells can look similar under a microscope. One way of differentiating them is by examining the level of acidity, or pH level, inside the cells.
Tapping on this distinguishing characteristic, a research team from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has developed a technique that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to determine whether a single cell is healthy or cancerous by analysing its pH. Each cancer test can be completed in under 35 minutes, and single cells can be classified with an accuracy rate of more than 95 per cent.
The research, led by Professor Lim Chwee Teck, Director of the Institute for Health Innovation ...
2021-03-17
A 2020 explosion in Lebanon's port city of Beirut led to a southward-bound, high-velocity atmospheric wave that rivaled ones generated by volcanic eruptions.
Just after 6 p.m. local time (15.00 UTC) on August 4, 2020, more than 2,750 tons worth of unsafely stored ammonium nitrate exploded in Lebanon's port city of Beirut, killing around 200 people, making more than 300,000 temporarily homeless, and leaving a 140-metre-diameter crater in its wake. The blast is considered one of the most powerful non-nuclear, man-made explosions in human history.
Now, calculations by Hokkaido University scientists in Japan have found that the atmospheric ...
2021-03-17
PHILADEPHIA - Since the 1990s the rate of spinal fusion to treat lower back pain has been on the rise. A new prospective clinical study published in the journal Neurosurgery, the official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons, found that lumbar fusions were three times more likely to be effective and obtain better patient outcomes, when guidelines for fusion were followed. The results suggest that when surgeons operate outside of what the evidence based literature suggests, patients may not have significant improvements in their quality of life and could have increased pain or other limitations.
"Unfortunately, we don't know how many lumbar fusion surgeries are ...
2021-03-17
Philadelphia, March 17, 2021 - Researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) affiliated with the CHOP Epilepsy Neurogenetics Initiative (ENGIN) have compiled a complete genetic and clinical analysis of more than 400 individuals with SCN2A-related disorder, which has been linked to a variety of neurodevelopmental disorders, including epilepsy and autism. By linking clinical features to genetic abnormalities in a standardized format, the researchers hope their findings lead to improved identification and clinical intervention.
The study was published ...
2021-03-17
A groundbreaking study has given new insights into how copper deposit-forming fluids are transported naturally from their source deep underground towards the Earth's surface.
A team of geologists, led by Lawrence Carter from the University of Exeter's Camborne School of Mines, has published a new theory for how porphyry copper deposits form.
Porphyry deposits provide around 75 per cent of the world's copper which is in increasing demand for electric vehicles, power infrastructure and green technologies such as wind turbines. They originally develop several kilometres below the Earth's surface above large magma chambers. Not only are porphyry deposits rare but most large near-surface examples have already been ...
2021-03-17
A world-first 'flow model' devised by Australian researchers could drastically slash public transport commuter times during peak periods on some of the busiest roads in major cities, new research shows.
When this flow model was implemented to improve the worst traffic bottlenecks across Melbourne, commuters saved close to 2000 hours of travel time during a single morning peak period (7am-9am) and approximately 11,000 hours of passenger travel time during a normal weekday.
Ameliorating major traffic bottlenecks also contributed to a more than 23 per cent improvement in reliability of Melbourne's public transport network, ...
2021-03-17
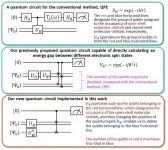
OSAKA, Japan. Quantum computers have seen a lot attention recently as they are expected to solve certain problems that are outside the capabilities of normal computers. Primary to these problems is determining the electronic states of atoms and molecules so they can be used more effectively in a variety of industries - from lithium-ion battery designs to in silico technologies in drug development. A common way scientists have approached this problem is by calculating the total energies of the individual states of a molecule or atom and then determine the difference in energy between these states. In nature, many molecules grow in size and complexity, and the cost to calculate this constant flux is beyond the capability of any traditional ...
2021-03-17
High-power laser diode (LD) driven solid-state lighting can generate super-high luminance far exceeding the state-of-art light-emitting diodes (LEDs) source by factors of 2-10, enabling it particularly attractive for automotive headlamp, outdoor lighting, multimedia projectors, laser TVs and so on. Whereas, the thermal shock of laser is extreme, and under intense laser excitation, traditional LEDs phosphor would suffer from luminescence degradation or even failure due to the luminescence saturation. Aiming to overcome this deficiency, highly efficient and stable luminescence bulk phosphors including single crystal, polycrystalline ceramic phosphor and glass ceramic composite phosphor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Certain mouthwashes might stop COVID-19 virus transmission
A Rutgers study shows two types of mouthwash disrupt SARS-CoV-2 in laboratory