(Press-News.org) March 18, 2021 -- A study conducted at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health reports a high global prevalence of both depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic and shows how implementation of mitigation strategies including public transportation and school closures, and stay-at-home orders impacted such disorders. The results are published in Psychological Medicine.
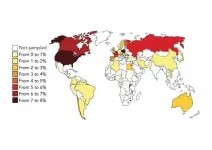
"Our research found an elevated global prevalence of these mental health issues during COVID-19 and also revealed there was a wide variance in each at the region- and country-level," said, João Castaldelli-Maia, MD, PhD, NIDA-INVEST Postdoctoral Fellow in the Department of Epidemiology, and lead author. In particular, Asia (most studies came from China) presented lower levels of both anxiety and depression, compared to the other regions of the world. Closure of public transportation increased levels of anxiety, whether it was two weeks or four weeks past the passage of closure enactment, especially in Europe."
Using an end date of July 29th, 2020, the researchers analyzed data from Pubmed, MEDLINE, Web of Science, and medRxiv, among other databases, for depression and anxiety prevalence. They also reviewed the Oxford Covid-19 Government Response Tracker for the containment and closure policies indexes; and the Global Burden of Disease Study for previous levels of depression and anxiety. The WHO database which includes COVID literature for studies published by the same date was also used.
In total, 226,638 individuals were assessed within 60 included studies. Global prevalence of both depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic were 24 percent and 21 percent, respectively. Asia with rates of 18 percent for each, and China especially, had the lowest prevalence of both disorders. Regarding the impact of mitigation strategies on mental health -- whether it was public transportation closures, school closings, workplace closures, cancellation of public events, or restrictions on gathering -- only public transportation closures increased prevalence of anxiety, especially in Europe.
Castaldelli-Maia and colleagues found a 21 percent global prevalence of anxiety. Asia had lower levels of anxiety (18 percent) compared to other regions of the world (29 percent). In this case, Europe did not differ from Asia and other regions of the world. Again, a subgroup analysis at the country-level showed that China had a lower prevalence of anxiety at 15.5 percent compared to all other countries at 26 percent.
"Our study confirms how critical it is to investigate levels of mental health disorders and the possible impacts of social distancing measures on mental health outcomes, according to Silvia Martins, MD, PhD, associate professor of Epidemiology at Columbia Mailman School, and senior author. "Mental health concerns should not be viewed only as a delayed consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, but also as a concurrent epidemic."
Within the subgroup of Asian countries, estimates of depression prevalence ranged from 15 percent to 20 percent. When comparing the prevalence of depression in the pre-and post-COVID-19 eras, the estimates ranging from 1.3-3.4 percent, are demonstrably larger after the initiation of COVID-19.
Depression was observed among 26 percent of the population in Europe, and among 39 percent in other non-Asia regions of the world. A further analysis showed that China had a lower prevalence of depression, 16 percent compared with 29 percent in other countries.
Similarly, the prevalence of anxiety, as reported in the subgroup of Asian countries is higher post-COVID-19. Rates of anxiety prior to COVID-19 ranged from 2.1 to 4.1 percent vs. 18 percent in the present study. Increases in anxiety can be observed in countries outside Asia and Europe (3 to 7 percent vs. 29 percent).
"The lower levels of depression and anxiety that we found in Asian countries could be culture-dependent," observes Martins.
The effect of public transportation closures on anxiety levels points to the importance of these systems to global populations, particularly the results in Europe but not in Asia. "These findings could be linked to the fact that Europe has a more effective and implemented public transport network on average, making Europeans depending more on public transportation than people in Asian countries," noted Martins.
"The COVID-19 pandemic, and the resulting physical distancing measures to mitigate viral spread, has certainly impacted population mental health worldwide, and the high prevalence of mental health disorders is a considerable concern during the COVID era," said Castaldelli-Maia. "These results have important implications for policymakers and show the urgent need for the healthcare sector to increase support now for prevention and early intervention of depression and anxiety."
INFORMATION:
Megan Marziali and Ziyin Lu, Columbia Mailman School, are co-authors.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the seventh largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master's and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit http://www.mailman.columbia.edu.
Our knowledge of Alzheimer's disease has grown rapidly in the past few decades but it has proven difficult to translate fundamental discoveries about the disease into new treatments. Now researchers at the California National Primate Research Center at the University of California, Davis, have developed a model of the early stages of Alzheimer's disease in rhesus macaques. The macaque model, published March 18 in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association could allow better testing of new treatments.
The model was developed by Professor John Morrison's laboratory ...
IN BRIEF:
It's a first: approximately 100 scientists in 42 countries joined forces to learn about the incidence of parental burnout.
They found that Western countries are the most affected by parental burnout.
The cause? The often individualistic culture of Western countries. This international study, published in Affective Science, shows how culture, rather than socio-economic factors, plays a predominant role in parental burnout.
The individualism is more pronounced during health crises.
Does the incidence of parental burnout depend on a country's culture? This question was at the heart of the first international study on the subject for which hundreds of scientists in 42 countries mobilised. In other words, the global scientific ...
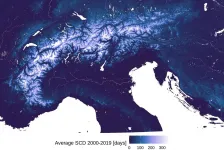
The results, published in the renowned scientific journal The Cryosphere, have made it possible to reliably describe snow trends at up to 2000 metres above sea level. Higher than that, there are too few measuring stations to be able to extract reliable information for the entire Alpine region. This consistent data set spans five decades and was created through the collaboration of more than 30 scientists from each of the Alpine states. The results and data collected represent a valuable aid for future studies, especially those which centre on climate change.
"This ...
Bottlenose dolphins learn to cope with coastal construction activities. That is the conclusion of a study published in END ...
A large gathering of fish tempts harbour porpoises to search for food around oil and gas platforms, even though the noise from these industrial plants normally to scare the whales away. Decommissioned platforms may therefore serve as artificial reefs in the North Sea.
Harbour porpoises are one of the smallest of all whales and the only whale that with certainty breeds in Danish waters. The harbour porpoise was protected in 1967 in Danish Waters, and researchers from Aarhus University, Denmark, have previously shown that underwater noise from ships, and seismic surveys of the seabed scare the porpoises away.
A brand new study now shows that in some parts of the year there are ...
A new study in Behavioral Ecology, published by Oxford University Press, finds that women are less likely to procreate in urban areas that have a higher percentage of females than males in the population.
Although the majority modern cities have more women than men and thus suffer from lower fertility rates, the effects of female-biased sex ratios - having more women than men in a population - is less studied than male-biased ratios. Researchers here analyzed how female-biased sex ratios are linked to marriages, reproductive histories, dispersal, and the effects of urbanization on society.
The research team from University of Turku, University of Helsinki and Pennsylvania ...
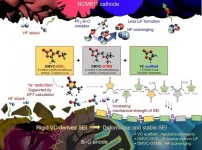
A joint research team, affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a novel electrolyte additive that could enable a long lifespan and fast chargeability of high-energy-density lithium-ion batteries (LIBs).
Published in the February 2021 issue of Nature Communications, this research has been carried out by Professor Nam-Soon Choi and Professor Sang Kyu Kwak in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Sung You Hong in the Department of Chemistry at UNIST. It has also been participated by Professor Jaephil Cho in the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST.
As the demand for large-capacity batteries (i.e., EV batteries) increases, efforts are actively underway to replace the conventional lithium-ion ...
Researchers from the University of Helsinki's Finnish Museum of Natural History Luomus and the National Museums of Kenya have discovered four lichen species new to science in the rainforests of the Taita Hills in southeast Kenya.
Micarea pumila, M. stellaris, M. taitensis and M. versicolor are small lichens that grow on bark of trees and on decaying wood. The species were described based on morphological features and DNA-characters.
"Species that belong to the Micarea genus are known all over the world, including Finland. However, the Micarea species recently described from the Taita ...
Researchers from Arizona State University, New York University, and Northwestern University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how marketers can fuel positive WOM without using explicit incentives.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "How Marketing Perks Influence Word of Mouth" and is authored by Monika Lisjak, Andrea Bonezzi, and Derek Rucker.
Word-of-mouth (WOM) is arguably the most influential means of persuasion and can be a critical driver of a company's growth. For this reason, many companies offer consumers incentives to encourage them to generate WOM. Classic examples of this practice are referral and seeding programs, whereby a company literally "pays" ...
A study from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, has yielded new answers to fundamental questions about the relationship between the size of an atom and its other properties, such as electronegativity and energy. The results pave the way for advances in future material development. For the first time, it is now possible under certain conditions to devise exact equations for such relationships.
"Knowledge of the size of atoms and their properties is vital for explaining chemical reactivity, structure and the properties of molecules and materials of all kinds. This is fundamental research that is necessary for us to make important advances," explains Martin Rahm, the main author of the study and research leader from ...