Escape from mongoose: frog's novel strategy
Invasive mongooses altered leg length and endurance of endangered island frogs
2021-03-18
(Press-News.org) Biodiversity is increasingly ruined by humanity's many impacts, a major aspect of which is biological invasion. Although there are a lot of studies reporting that invasive predators decrease the population size of native species, only a few studies have reported impact on phenotypic traits such as morphology and performance of native species. Particularly island ecosystem is very sensitive to invasive predators because strong predators such as mammalian predators are not in such environment.
Researchers at Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT) analyzed predators' effect on frogs in a Japanese island and their findings were reported in Biological Invasions on January 3rd.
Mongooses were introduced many areas worldwide and damaged native ecosystem seriously. In 1979, these were brought to Amami Island in Japan. As a result, Amami tip-nosed frog, which is a relatively large forest species, is one of the species at risk of extinction in near future due to the invasive mongoose.
"We hypothesized the strong predation pressure of mongoose drove rapid change in morphology and performance of the native frog," said Hirotaka Komine, first author of the paper, assistant professor (when this research was done) at TUAT.
"We recorded hind limb length and two types of performance traits: burst movement ability (evaluated based on jump distance) and endurance (evaluated based on number of jumps), " said Komine. For jump distance, the researchers measured the distance of the first jump after the frog was released. For the number of jumps, they analysed the number of jumps in the net upon capture until the frog was exhausted (i.e., stopped jumping). "We then estimated the relationship between hind limb length and explanatory variables (proxy of mongoose impact, sex, year), and the relationship between performance traits and the explanatory variables using a spatial regression model, " Komine explains.
Interestingly, the results showed that the hind limb length of the frog was longer under the strong predation effect of the mongoose, which may have acted as a selective agent to induce rapid morphological responses. The endurance, but not the burst movement ability, of the frog was higher under the strong effect of predation by the mongoose. "Our results suggest that endurance was a specific target of natural selection and that the performance of the native prey changed in response to the new predation type," said Komine.
When their research was carried out it was at least 7 years after the mongooses were mostly removed and population size of the native frog recovered owing to the eradication project run by the Ministry of the Environment of Japan. Therefore, apparently their result suggested that impact of invasive mongooses on phenotypic traits of native frog remained even after the invasive predator mostly removed.
"Island ecosystem is often unique in terms of behavior, morphology, and performance, reflecting its evolutionary uniqueness. Hence, the recovery of traits in native species after the removal of invasive species may be a useful measure of the success of eradication projects," concludes Komine.
INFORMATION:
More information about Dr Komine, please visit https://researchmap.jp/hkomine?lang=en
About Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (TUAT):
TUAT is a distinguished university in Japan dedicated to science and technology. TUAT focuses on agriculture and engineering that form the foundation of industry, and promotes education and research fields that incorporate them. Boasting a history of over 140 years since our founding in 1874, TUAT continues to boldly take on new challenges and steadily promote fields. With high ethics, TUAT fulfills social responsibility in the capacity of transmitting science and technology information towards the construction of a sustainable society where both human beings and nature can thrive in a symbiotic relationship. For more information, please visit http://www.tuat.ac.jp/en/.
Original publication:
Komine, H. *, Iwai, N. & Kaji, K. Rapid responses in morphology and performance of native frogs induced by predation pressure from invasive mongooses. Biol Invasions (2021).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-020-02440-0
*: corresponding author
Contact:
Hirotaka Komine, Ph.D.
komitorihiro@gmail.com
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-18
If you reach for water when a muscle cramp strikes, you might want to think again. New research from Edith Cowan University (ECU) has revealed drinking electrolytes instead of pure water can help prevent muscle cramps.
The study, published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, found that people who drank electrolyte enhanced water during and after exercise were less susceptible to muscle cramps than those who drank pure water.
Muscle cramps are a common painful condition affecting many people, including around 39 per cent of marathon runners, 52 per cent of rugby players and 60 per cent of cyclists. ...
2021-03-18
Scientists are learning that a lesser-studied region on the pandemic coronavirus is recognized by COVID-19 infection-fighting antibodies. These antibodies were identified in blood samples from previously infected patients, and were found to potently prevent the virus from infecting cells.
The coronavirus spike protein is the key that unlocks the door to the cell, and antibodies bind to the spike protein to jam this function. Much attention has been given to studying antibodies that target the receptor-binding domain on the coronavirus spike protein. (The receptor-binding domain of the spike is responsible for triggering the merging of the ...
2021-03-18
Anemia, a condition characterized by the lack of healthy red blood cells in the body, is common in patients with chronic kidney disease who need to undergo routine hemodialysis (a process that helps to "clean" the blood when the kidneys don't function well). Thus, red blood cell-stimulating agents (called "erythropoiesis-stimulating agents" or ESAs) and iron supplements (ISs) are administered as part of this process. But, complications can arise if the patients have an altered iron metabolism or poor response to medications. Moreover, the medications tend to be expensive and impose a heavy financial burden on public health. Thus, with such patients currently ...
2021-03-18
Malting, the processing of cereal grains into malt, generates rootlets as a side-stream product, which is currently mostly utilised as animal feed. However, this leftover material has not only a high protein content, but also high amounts of phytochemicals, which makes it a highly potential source of development for the food industry, according to a recent study from the University of Eastern Finland, published in npj Science of Food.
Germination increased the amount of phytochemicals
The study utilised metabolomics to analyse samples from grains of four cereals typically used in malting: barley, rye, wheat, and oats. The researchers were particularly interested in phytochemicals, which are bioactive compounds ...
2021-03-18
Leesburg, VA, March 18, 2021--According to ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) showed concordance with MRI in women with newly diagnosed breast cancer and breast augmentation.
Noting that CEM has not been investigated in women with breast augmentation, Molly Carnahan and her Mayo Clinic team in Phoenix, AZ, concluded, "the findings suggest a possible role of CEM for staging in women with breast augmentation and contraindication or limited access to MRI."
From an institutional database of 2,215 women who underwent ...
2021-03-18
The immense diversity in the living world and how it came into being has always been a subject of human enquiry. After centuries of playing detective in search of the basis of the parities and disparities that we see among living beings around us, the past century stood witness to some marvellous discoveries in biology and today the Central Dogma of life has been disclosed to us: DNA makes RNA and RNA makes protein (a facile view of a much more complex sequence of events). Together with contributing environmental factors, proteome(s) (total protein content of a cell) collectively influence 'traits' or characteristics of organisms that vary among individuals of a population. In a population, individuals with traits better suited to their environment have a higher chance at survival ...
2021-03-18
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. - The triggers and causes of a severe scarring disease of the lungs -- idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, or IPF -- remain unclear.
Now research published in Science Translational Medicine shows how cadmium and carbon black can trigger lung macrophages to produce a modified protein, citrullinated vimentin, or cit vim, which leads to lung fibrosis. Researchers from the University of Alabama at Birmingham and three other American universities also describe a sequence of mechanistic steps in lung macrophages and lung fibroblasts that leads to the lung scarring.
One of the enzymes involved in these steps -- peptidylarginine deiminase 2, or PAD2 -- may be a promising target to attenuate cadmium/carbon black-induced ...
2021-03-18
March 18, 2021 -- A study conducted at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health reports a high global prevalence of both depression and anxiety during the COVID-19 pandemic and shows how implementation of mitigation strategies including public transportation and school closures, and stay-at-home orders impacted such disorders. The results are published in Psychological Medicine.
"Our research found an elevated global prevalence of these mental health issues during COVID-19 and also revealed there was a wide variance in each at the region- and country-level," said, João Castaldelli-Maia, MD, PhD, NIDA-INVEST Postdoctoral Fellow in the Department of Epidemiology, and ...
2021-03-18
Our knowledge of Alzheimer's disease has grown rapidly in the past few decades but it has proven difficult to translate fundamental discoveries about the disease into new treatments. Now researchers at the California National Primate Research Center at the University of California, Davis, have developed a model of the early stages of Alzheimer's disease in rhesus macaques. The macaque model, published March 18 in the journal Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association could allow better testing of new treatments.
The model was developed by Professor John Morrison's laboratory ...
2021-03-18
IN BRIEF:
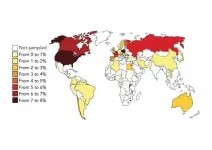
It's a first: approximately 100 scientists in 42 countries joined forces to learn about the incidence of parental burnout.
They found that Western countries are the most affected by parental burnout.
The cause? The often individualistic culture of Western countries. This international study, published in Affective Science, shows how culture, rather than socio-economic factors, plays a predominant role in parental burnout.
The individualism is more pronounced during health crises.
Does the incidence of parental burnout depend on a country's culture? This question was at the heart of the first international study on the subject for which hundreds of scientists in 42 countries mobilised. In other words, the global scientific ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Escape from mongoose: frog's novel strategy
Invasive mongooses altered leg length and endurance of endangered island frogs