Real "doodles of light" in real-time mark leap for holograms at home
Fast line-based algorithm turns hand-writing into holograms using standard CPUs
2021-03-20
(Press-News.org) Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have devised and implemented a simplified algorithm for turning freely drawn lines into holograms on a standard desktop CPU. They dramatically cut down the computational cost and power consumption of algorithms that require dedicated hardware. It is fast enough to convert writing into lines in real-time, and makes crisp, clear images that meet industry standards. Potential applications include hand-written remote instructions superimposed on landscapes and workbenches.
Flying cars, robots, spaceships...whatever sci-fi future you can imagine, there is always a common feature: holograms. But holography isn't just about aesthetics. Its potential applications include important enhancements to vital, practical tasks, like remote instructions for surgical procedures, electronic assembly on circuit boards, or directions projected on landscapes for navigation. Making holograms available in a wide range of settings is vital to bringing this technology out of the lab and into our daily lives.
One of the major drawbacks of this state-of-the-art technology is the computational load of hologram generation. The kind of quality we've come to expect in our 2D displays is prohibitive in 3D, requiring supercomputing levels of number crunching to achieve. There is also the issue of power consumption. More widely available hardware like GPUs in gaming rigs might be able to overcome some of these issues with raw power, but the amount of electricity they use is a major impediment to mobile applications. Despite improvements to available hardware, the solution is not something we can expect from brute-force.
A key solution is to limit the kind of images that are projected. Now, a team led by Assistant Professor Takashi Nishitsuji have proposed and implemented a solution with unprecedented performance. They specifically chose to exclusively draw lines in 3D space. Though this may sound drastic at first, the number of things you can do is still impressive. In a particularly elegant implementation, they connected a tablet to a PC and conventional hologram generation hardware i.e. a laser and a spatial light modulator. Their algorithm is fast enough that handwriting on the tablet could be converted to images in the air in real-time. The PC they used was a standard desktop with no GPU, significantly expanding where it might be implemented. Though the images were slightly inferior in quality to other, more computationally intensive methods, the sharpness of the writing comfortably met industry standards.
All this means that holograms might soon be arriving in our homes or workplaces. The team is especially focused on implementations in heads-up displays (HUDs) in helmets and cars, where navigation instructions might be displayed on the landscape instead of voice instructions or distracting screens. The light computational load of the algorithm significantly expands the horizons for this promising technology; that sci-fi "future" might not be the future for much longer.
INFORMATION:
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (20K19810, 19H01097), the Inoue Foundation for Science, the Takayanagi Kenjiro Foundation and Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (12ZQ220N, VS07820N).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-20
Researchers from Columbia University and Temple University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how choice architecture can reduce socioeconomic disparities.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Do Nudges Reduce Disparities? Choice Architecture Compensates for Low Consumer Knowledge" and is authored by Kellen Mrkva, Nathaniel Posner, Crystal Reeck, and Eric Johnson.
As Mrkva explains, "Our research demonstrates that people with low socioeconomic status (SES), low numerical ability, and low knowledge are most impacted by nudges. As a result, 'good nudges,' designed to encourage ...
2021-03-19
It's estimated that an average-sized wastewater treatment plant serving roughly 400,000 residents will discharge up to 2,000,000 microplastic particles into the environment each day. Yet, researchers are still learning the environmental and human health impact of these ultra-fine plastic particles, less than 5 millimeters in length, found in everything from cosmetics, toothpaste and clothing microfibers, to our food, air and drinking water.
Now, researchers at New Jersey Institute of Technology have shown that ubiquitous microplastics can become 'hubs' for antibiotic-resistant bacteria ...
2021-03-19
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Low representation of minority groups in public genomic databases may affect therapy selection for Black patients with cancer, according to new Mayo Clinic research published in npj Precision Oncology.
The researchers investigated the use of genomic databases and found that tumor mutation burden was significantly inflated in Black patients compared to White patients.
As a result of the study, clinicians who are using public genomic databases need to be aware of the potential for inflated tumor mutation burden values and how that may affect therapy selection and outcomes, especially for patients from underrepresented groups.
Clinicians use biomarkers, which are indicators of a disease or condition, to determine ...
2021-03-19
BOSTON - Researchers have used a genetic engineering strategy to dramatically reduce levels of tau--a key protein that accumulates and becomes tangled in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease--in an animal model of the condition. The results, which come from investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Sangamo Therapeutics Inc., could lead to a potentially promising treatment for patients with this devastating illness.
As described in Science Advances, the strategy involves a gene regulation technology called zinc finger protein transcription ...
2021-03-19
A team of scientists, led by researchers at Northwestern University, Shirley Ryan AbilityLab and the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), has developed novel technology promising to increase understanding of how brains develop, and offer answers on repairing brains in the wake of neurotrauma and neurodegenerative diseases.
Their research is the first to combine the most sophisticated 3-D bioelectronic systems with highly advanced 3-D human neural cultures. The goal is to enable precise studies of how human brain circuits develop and repair themselves in vitro. The study is the cover story for ...
2021-03-19
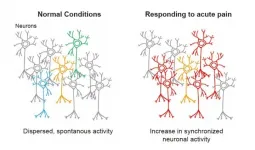
In a world first, a cross-institutional research collaboration has used a two-photon microscope (*1) with a combination of calcium imaging (*2) and holographic stimulation (*3) to reveal that the functional connectivity between neurons located in the primary somatosensory cortex is increased in response to acute pain.
Pain occurs as a result of injury, such as peripheral neuron damage or inflammation stemming from peripheral tissue violation. Research findings have been published on the involvement of central nervous system abnormalities in the onset of pain and sustained pain. The primary somatosensory cortex ...
2021-03-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Most stroke victims don't receive treatment fast enough to prevent brain damage. Scientists at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, College of Engineering and College of Medicine have developed technology to "retrain" cells to help repair damaged brain tissue. It's an advancement that may someday help patients regain speech, cognition and motor function, even when administered days after an ischemic stroke.
Engineering and medical researchers use a process created by Ohio State called tissue nanotransfection (TNT) to introduce genetic material into cells. This allows them to reprogram skin cells to become something ...
2021-03-19
New York, NY--March 19, 2020--Columbia Engineering researchers, working with Brookhaven National Laboratory, report today that they have built designed nanoparticle-based 3D materials that can withstand a vacuum, high temperatures, high pressure, and high radiation. This new fabrication process results in robust and fully engineered nanoscale frameworks that not only can accommodate a variety of functional nanoparticle types but also can be quickly processed with conventional nanofabrication methods.
"These self-assembled nanoparticles-based materials are so resilient that they could fly in space," says Oleg Gang, professor ...
2021-03-19
PITTSBURGH, March 19, 2021 - Non-circulating memory T cells, whose main function is to provide local protection against re-infection, contribute to chronic transplant rejection, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine researchers reveal in a paper published today in Science Immunology.
The scientists show that these "tissue-resident memory T cells" are harmful in situations where antigens that the cells recognize are present in the body for a long time, such as in cases of an organ or tissue transplant. This finding is an important step toward improving therapies to help prevent organ rejection in transplant recipients.
"Tissue-resident memory T cells serve an important surveillance function," said co-senior author Martin Oberbarnscheidt, ...
2021-03-19
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Many viruses infect their hosts through mucosal surfaces such as the lining of the respiratory tract. MIT researchers have now developed a vaccination strategy that can create an army of T cells that are ready and waiting at those surfaces, offering a quicker response to viral invaders.
The researchers showed that they could induce a strong memory T cell response in the lungs of mice by giving them a vaccine modified to bind to a protein naturally present in mucus. This can help ferry the vaccine across mucosal barriers, such as the lining of the lungs.
"In this paper, we specifically focused on T cell responses that would be useful against viruses or cancer, and our idea was to use this protein, albumin, as sort of a Trojan horse to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Real "doodles of light" in real-time mark leap for holograms at home
Fast line-based algorithm turns hand-writing into holograms using standard CPUs