'Hunger hormone' ghrelin affects monetary decision making
High ghrelin levels in healthy females predict more impulsive choices, researchers say
2021-03-20
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON--Higher levels of the stomach-derived hormone ghrelin, which stimulates appetite, predict a greater preference for smaller immediate monetary rewards over larger delayed financial rewards, a new study finds. The study results will be presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting.
This research presents novel evidence in humans that ghrelin, the so-called "hunger hormone," affects monetary decision making, said co-investigator Franziska Plessow, Ph.D., assistant professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston. She said recent research findings in rodents suggested that ghrelin may play a part in impulsive choices and behaviors.
"Our results indicate that ghrelin might play a broader role than previously acknowledged in human reward-related behavior and decision making, such as monetary choices," Plessow said. "This will hopefully inspire future research into its role in food-independent human perception and behavior."
Ghrelin signals the brain for the need to eat and may modulate brain pathways that control reward processing. Levels of ghrelin fluctuate throughout the day, depending on food intake and individual metabolism.
This study included 84 female participants ages 10 to 22 years: 50 with a low-weight eating disorder, such as anorexia nervosa, and 34 healthy control participants. Plessow's research team tested blood levels of total ghrelin before and after a standardized meal that was the same for all participants, who had fasted beforehand. After the meal, participants took a test of hypothetical financial decisions, called the delay discounting task. They were asked to make a series of choices to indicate their preference for a smaller immediate monetary reward or a larger delayed amount of money, for instance, $20 today or $80 in 14 days.
Healthy girls and young women with higher ghrelin levels were more likely to choose the immediate but smaller monetary reward rather than waiting for a larger amount of money, the researchers reported. This preference indicates more impulsive choices, Plessow said.
The relationship between ghrelin level and monetary choices was absent in age-matched participants with a low-weight eating disorder. People with this eating disorder are known to have ghrelin resistance, and Plessow said their finding might be another indicator of a disconnect between ghrelin signaling and behavior in this population.
The study received funding from the National Institutes of Health and a Charles A. King Trust Research Fellowship Award to Plessow. Naila Shiraliyeva, M.D., a research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital, will present the study findings at the meeting.
INFORMATION:
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world's oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at http://www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-20
WASHINGTON--Nearly one in five U.S. children and teenagers has obesity, and statistics show a higher prevalence of obesity in certain ethnicities, such as Hispanics and Blacks. Now results of a study being presented at ENDO 2021, the Endocrine Society's annual meeting, suggest that Spanish as a family's primary language is a predictor of childhood obesity, regardless of ethnicity.
The prevalence of obesity among children and teens from Spanish-speaking households in the nation was 24.4 percent, approximately 50 percent higher than those from English-speaking households, according to results of a new analysis of the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. This survey examines a nationally representative sample ...
2021-03-20
Tokyo, Japan - Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have devised and implemented a simplified algorithm for turning freely drawn lines into holograms on a standard desktop CPU. They dramatically cut down the computational cost and power consumption of algorithms that require dedicated hardware. It is fast enough to convert writing into lines in real-time, and makes crisp, clear images that meet industry standards. Potential applications include hand-written remote instructions superimposed on landscapes and workbenches.
Flying cars, robots, spaceships...whatever sci-fi future you can imagine, there is always a common feature: holograms. ...
2021-03-20
Researchers from Columbia University and Temple University published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that examines how choice architecture can reduce socioeconomic disparities.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "Do Nudges Reduce Disparities? Choice Architecture Compensates for Low Consumer Knowledge" and is authored by Kellen Mrkva, Nathaniel Posner, Crystal Reeck, and Eric Johnson.
As Mrkva explains, "Our research demonstrates that people with low socioeconomic status (SES), low numerical ability, and low knowledge are most impacted by nudges. As a result, 'good nudges,' designed to encourage ...
2021-03-19
It's estimated that an average-sized wastewater treatment plant serving roughly 400,000 residents will discharge up to 2,000,000 microplastic particles into the environment each day. Yet, researchers are still learning the environmental and human health impact of these ultra-fine plastic particles, less than 5 millimeters in length, found in everything from cosmetics, toothpaste and clothing microfibers, to our food, air and drinking water.
Now, researchers at New Jersey Institute of Technology have shown that ubiquitous microplastics can become 'hubs' for antibiotic-resistant bacteria ...
2021-03-19
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Low representation of minority groups in public genomic databases may affect therapy selection for Black patients with cancer, according to new Mayo Clinic research published in npj Precision Oncology.
The researchers investigated the use of genomic databases and found that tumor mutation burden was significantly inflated in Black patients compared to White patients.
As a result of the study, clinicians who are using public genomic databases need to be aware of the potential for inflated tumor mutation burden values and how that may affect therapy selection and outcomes, especially for patients from underrepresented groups.
Clinicians use biomarkers, which are indicators of a disease or condition, to determine ...
2021-03-19
BOSTON - Researchers have used a genetic engineering strategy to dramatically reduce levels of tau--a key protein that accumulates and becomes tangled in the brain during the development of Alzheimer's disease--in an animal model of the condition. The results, which come from investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Sangamo Therapeutics Inc., could lead to a potentially promising treatment for patients with this devastating illness.
As described in Science Advances, the strategy involves a gene regulation technology called zinc finger protein transcription ...
2021-03-19
A team of scientists, led by researchers at Northwestern University, Shirley Ryan AbilityLab and the University of Illinois at Chicago (UIC), has developed novel technology promising to increase understanding of how brains develop, and offer answers on repairing brains in the wake of neurotrauma and neurodegenerative diseases.
Their research is the first to combine the most sophisticated 3-D bioelectronic systems with highly advanced 3-D human neural cultures. The goal is to enable precise studies of how human brain circuits develop and repair themselves in vitro. The study is the cover story for ...
2021-03-19
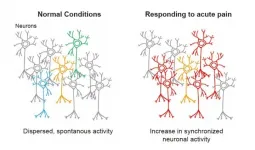
In a world first, a cross-institutional research collaboration has used a two-photon microscope (*1) with a combination of calcium imaging (*2) and holographic stimulation (*3) to reveal that the functional connectivity between neurons located in the primary somatosensory cortex is increased in response to acute pain.
Pain occurs as a result of injury, such as peripheral neuron damage or inflammation stemming from peripheral tissue violation. Research findings have been published on the involvement of central nervous system abnormalities in the onset of pain and sustained pain. The primary somatosensory cortex ...
2021-03-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Most stroke victims don't receive treatment fast enough to prevent brain damage. Scientists at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, College of Engineering and College of Medicine have developed technology to "retrain" cells to help repair damaged brain tissue. It's an advancement that may someday help patients regain speech, cognition and motor function, even when administered days after an ischemic stroke.
Engineering and medical researchers use a process created by Ohio State called tissue nanotransfection (TNT) to introduce genetic material into cells. This allows them to reprogram skin cells to become something ...
2021-03-19
New York, NY--March 19, 2020--Columbia Engineering researchers, working with Brookhaven National Laboratory, report today that they have built designed nanoparticle-based 3D materials that can withstand a vacuum, high temperatures, high pressure, and high radiation. This new fabrication process results in robust and fully engineered nanoscale frameworks that not only can accommodate a variety of functional nanoparticle types but also can be quickly processed with conventional nanofabrication methods.
"These self-assembled nanoparticles-based materials are so resilient that they could fly in space," says Oleg Gang, professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Hunger hormone' ghrelin affects monetary decision making
High ghrelin levels in healthy females predict more impulsive choices, researchers say