Cyber security experts launch guidelines to help police crackdown on organised crime
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) The white paper, published today (March 22) by REPHRAIN, the National Research Centre on Privacy, Harm Reduction and Adversarial Influence Online in collaboration with the Dutch National Police, offers a solution to big data problems that tend to hamper police probes into this type of law-breaking.
The practice of attribution - who did what - is becoming increasingly complex as organised crimes incorporate deception, deletion and encryption in today's Information Age. Even when law enforcement are able to retrieve evidence via digital forensics, the complexities of the collected data mean it cannot be easily processed into factual police reports.
A frequently proposed solution is the introduction of 'smart' data science technologies to support criminal investigations. However, the transition to data scientific investigations requires legal, organisational and technical harmonisation with other public partners including a shared language of data scientific operations.
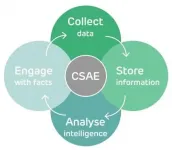
A Practitioner-in-Residence at REPHRAIN, together with partners at the Dutch National Police, have put together guiding principles and best practices for data scientific investigations of organised crime. These have been developed and put into practice by operational experts over several years, while connecting to existing law enforcement and industry standards. The associated framework is called CSAE (pronounced as 'see-say'), a comprehensive framework that consists of a business process, methodology, policy agenda and public interest philosophy for data scientific operations. It stands for Collect, Store, Analyse and Engage.
CSAE is a living document and will continue to be updated and improved when the academic world, industry and law enforcement provide feedback on concepts and implementation. As CSAE is put into greater practice, additional lessons learned will be integrated into future versions. This will ensure CSAE is meeting the needs of law enforcement in the dynamic and challenging environment of crime and investigations.
Erik van de Sandt of the National Police, The Netherlands; University of Bristol, National Research Centre on Privacy, Harm Reduction and Adversarial Influence Online (REPHRAIN), said: "The Dutch National Police is known for executing technically complex operations. Over the years, our experts have developed, implemented and refined a new type of law enforcement operations that we call data scientific investigations. "
"We have experienced how our comprehensive data science framework promotes harmonization between law enforcement agencies as well as critical thinking by academics. It is because of this public interest philosophy that we share our framework with a broader audience. After all, both the effectiveness and legitimacy of criminal investigations are cornerstones of liberal democracies."
INFORMATION:
REPHRAIN consolidates the UK's considerable academic, industry, policy and third sector capabilities, and led by Bristol, provides a single body to engage with government, industry and citizens. The interdisciplinary team includes experts from the Universities of Bristol, Bath, Edinburgh, King's College London and UCL, across a wide range of fields including - but not limited to - Computer Science, Law, Psychology and Criminology.
Paper:
"Towards Data Scientific Investigations: A Comprehensive Data Science Framework and Case Study for Investigating Organized Crime and Serving the Public Interest" and has been prepared by Erik van de Sandt, Arthur van Bunningen, Jarmo van Lenthe and John Fokker.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
One prospective source of renewable energy is hydrogen gas produced from water with the aid of sunlight. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a material, nanoporous cubic silicon carbide, that exhibits promising properties to capture solar energy and split water for hydrogen gas production. The study has been published in the journal ACS Nano.
"New sustainable energy systems are needed to meet global energy and environmental challenges, such as increasing carbon dioxide emissions and climate change", says Jianwu Sun, senior lecturer in the ...
2021-03-22
A lot of the attention around "pandemic pets" has focused on families with children getting a cat, dog or other pet in 2020, during a time when many people were learning or working from home.
But a new poll shows that older adults also got in on the trend.
According to the National Poll on Healthy Aging, 10% of all people between the ages of 50 and 80 got a new pet between March 2020 and January 2021.
The percentage was indeed higher - 16% -- among the people in this age range who have at least one child or teen living with them. But the vast majority of people between the ages of 50 and 80 don't live with someone under age 18 -- and nearly 9% of them also got a pet during the pandemic.
All told, 59% of people age 50 to 80 who completed the poll in January 2021 are pet owners. ...
2021-03-22
The Covid-19 pandemic severely impacted the mental health of young people, with increased levels of clinical depression being identified, a new study published in the journal Psychiatry Research reports. A decrease in alcohol consumption was also identified amongst young people during the pandemic.
During this unique study researchers from the University of Surrey surveyed 259 young people pre- pandemic (autumn 2019) and in the midst of initial lockdown measures (May/June 2020) on their levels of depression, anxiety, wellbeing, alcohol use and sleep quality.
Researchers found evidence of a substantial impact on the mental health of these young adults due ...
2021-03-22
Research has found that experiencing a traumatic event at close quarters changes people's political attitudes. However, in the case of the 2017 terrorist attack in Stockholm, proximity to the attack had no additional political significance. Research from the University of Gothenburg shows that Swedes' attitudes toward terrorism-related questions were affected equally, regardless of whether they happened to be close to the attack.
On 7 April 2017, Rakhmat Akilov stole a truck and ran down multiple people on Drottninggatan, a street in central Stockholm. Five people died, fifteen were injured and many people witnessed ...
2021-03-22
A study which looked at activity levels before and during the COVID-19 pandemic has found lockdown restrictions significantly reduced light activity associated with socialising and work.
The study, published recently in BMJ Neurology and led by King's College London, examined how activity levels changed in study participants with muscular dystrophy and other inheritable myopathies. The sample included people with a range of physical abilities, from highly independent to assisted mobility, including 41 wheelchair users, who are often underrepresented in research. However, the authors say the findings are likely to be relevant to adults of various ...
2021-03-22
The excavation of shell middens off two sites in the Gulf of Mexico and Northern Europe dating back to when the seabed was dry land thousands of years ago, reveal how they can offer new ground-breaking insights into the hidden history of submerged landscapes.
An international team of archaeologists from Moesgaard Museum (Denmark), the University Of Georgia (USA), the University of York (UK) Flinders University and James Cook University partnered to excavate two sites containing shell middens in the Gulf of Mexico and Eastern Jutland in Denmark in 2018, showing that middens can be ...
2021-03-22
Crystals inherently possess imperfections. Vacancies, as the simplest form of point defects, significantly alter the optical, thermal, and electrical properties of materials. Well-known examples include colour centres in many gemstones, the nitrogen-vacancy centre in diamond, vacancy migration in solid-state batteries, and the metal-insulator transition in phase-change materials. The vacancies in these cases are in frame-works with no or weak interactions. However, the role of vacancies in strongly correlated materials is thus far unclear due to the lack of an ideal prototype.
Strongly ...
2021-03-22
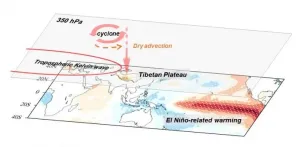
El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a recurring climate phenomenon involving changes in the temperature of waters in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean. It is one of the most important climate perturbations on Earth because it can change the global atmospheric circulation, which in turn, influences temperature and precipitation across the globe. Scientists have found ENSO has an impact on hydroclimate over the Tibetan Plateau but how it works, or its physical mechanism, remains unclear.
In a recently published research article in Journal of Climate, Shuai Hu, Tianjun Zhou and Bo Wu from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, explored the dynamical processes that ...
2021-03-22
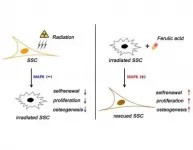
Durham, NC - The standard of treatment for bone tumors is often two-fold: surgery to remove the cancerous section followed by radiation therapy to ensure all the cancerous cells have been killed off. This is an effective way to defeat bone tumors; however, it often results in large bone defects and hampers wound healing because of extensive tissue cutoff and irradiation-induced tissue damage. A new study published in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine demonstrates how stem cells primed with ferulic acid can repair such bone damage and how this occurs. The information this study provides could aid in the development of new treatments for irradiated bone injuries.
Heng Zhu, M.D., Ph.D., of the Beijing Institute of ...
2021-03-22
As World Water Day is observed around the globe, new research from UBC Okanagan suggests a systematic approach to forest and water supply research may yield an improved assessment and understanding of connections between the two.
Healthy forests play a vital role in providing a clean, stable water supply, says eco-hydrologist Dr. Adam Wei.
Acting as natural reservoirs, forests in watersheds release and purify water by slowing erosion and delaying its release into streams. But forests are changing--in part because of human activity--and that's having an impact on forests' interaction with hydrological ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cyber security experts launch guidelines to help police crackdown on organised crime