(Press-News.org) With the offshore wind industry expanding in the United States and elsewhere, a new study raises questions about how the noise from impact pile driving to install turbine supports can affect feeding behaviors of longfin squid, a commercially and ecologically important cephalopod.
The research, conducted by scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and other institutions, is believed to be the first to demonstrate that anthropogenic noise prompts changes in cephalopod feeding behaviors.
"The whole reason we are doing this study is because we are concerned about how construction from offshore wind farms and the sounds associated with that are going to affect important fisheries species, one of them being this species of squid," said lead author Ian Jones about the paper published in this month's Marine Environmental Research. Jones is a student in the MIT-WHOI Joint Program in Oceanography/Applied Ocean Science and Engineering.
Longfin squid (Doryteuthis pealeii), whose habitat stretches among continental shelf waters from Newfoundland to the Gulf of Venezuela, are most abundant in waters off the Northeast U.S. coast, where offshore wind farms are planned for the 2020s and 2030s within 18 lease areas. Since 2010, longfin squid landings annually have amounted to about 11,000 metric tons and a value of $30 million, according to the U.S. National Marine Fisheries Service. Longfin squid also are important ecologically as a link between top predators and smaller fish and invertebrates.
The study found that when squid in an experimental tank were exposed to audio recordings of pile driving, they were less likely to capture prey during the noise playback and are more likely to abandon pursuing prey, if the noise started during their hunt. Because the squid have a high metabolic rate and need to feed frequently, "[I]f cessation of feeding during noise leads to longer-term reduced food intake, then the potential exists for population-level reductions in squid abundance," according to the researchers.
Pile driving involves repeated hammer strikes about every two seconds, to drive piles into the seabed and create support foundations for offshore development. The volume of underwater pile driving can exceed 200 decibels over a range of several hundred meters and the pitch of the noise can span frequencies from less than 100 Hz to over 10,000 Hz that can propagate for more than 10 kilometers.
The study addressed short-term impacts to squid feeding behavior and noted that future research should look at longer exposures to noise and field work with free-swimming squid. In particular, the study found that rates of anti-predator behaviors were similar when subjected to recordings of piledriving whether the squid was hunting at the start of the noise, suggesting that the noise diverted squid attention from a feeding task toward predator defense.
The study also found that the prey fish used in the experiment, killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus), could detect the sound of pile driving between 80 and 200 Hz.
Jones said that historically research about the impact of noise on ocean organisms mostly has focused on marine mammals and, to some extent, on fish.
"There is such a huge knowledge gap for marine invertebrates in general, including squid," he said. "This study could help make a difference in closing that knowledge gap and in helping developers and the fishing industry be more aware of potential impacts of anthropogenic noise on longfin squid."
INFORMATION:
About Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Massachusetts, dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate an understanding of the ocean's role in the changing global environment. WHOI's pioneering discoveries stem from an ideal combination of science and engineering--one that has made it one of the most trusted and technically advanced leaders in basic and applied ocean research and exploration anywhere. WHOI is known for its multidisciplinary approach, superior ship operations, and unparalleled deep-sea robotics capabilities. We play a leading role in ocean observation and operate the most extensive suite of data-gathering platforms in the world. Top scientists, engineers, and students collaborate on more than 800 concurrent projects worldwide--both above and below the waves--pushing the boundaries of knowledge and possibility. For more information, please visit http://www.whoi.edu
Additional authors and affiliations:
Ian T. Jones a,b,?, James F. Peyla b,1, Hadley Clark b,2, Zhongchang Song b,3, Jenni A. Stanley b,4,
T. Aran Mooney b
a. Massachusetts Institute of Technology-Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Joint Program in Oceanography/Applied Ocean Science and Engineering, 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, 02139, United States
b. Biology Department, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, 266 Woods Hole Road, Woods Hole, MA, 02543, United States
* corresponding author
1. Department of Ecology, Evolution, and Behavior, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, MN
2. California State University, Monterey Bay, Seaside, CA
3. State Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science, College of the Environment and Ecology, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
4. University of Waikato, New Zealand
A considerably higher dose of the anti-tuberculosis drug rifampicin is safe and can also lead to a shorter treatment for tuberculosis and less resistance. This is what researchers from Radboud university medical center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands, write in a recent publication. With this they complete a year-long search for the right dosing of an old drug against tuberculosis that appears to be the key drug.
Tuberculosis is a deadly, pertinacious bacterial infectious disease that affects nine million people worldwide each year, mainly in countries in low and middle income countries. For over a million, ...
Northwestern engineering researchers have demonstrated a new approach to chemical catalysis that results in high propylene yields using less energy. The findings could support more energy-efficient production processes for many plastics.
One of the highest volume chemical products, more than $100 billion worth of propylene is produced each year and used primarily to produce polypropylene for a variety of materials, from injection moldings in car parts to consumer products. Producing propylene is also energy intensive, requiring temperatures around 800 degrees Celsius to convert propane gas to propylene.
One technique, called oxidative dehydrogenation, ...
A researcher from Skoltech has filled in the gaps connecting quantum simulators with more traditional quantum computers, discovering a new computationally universal model of quantum computation, the variational model. The paper was published as a Letter in the journal Physical Review A. The work made the Editors' Suggestion list.
A quantum simulator is built to share properties with a target quantum system we wish to understand. Early quantum simulators were "dedicated" - that means they could not be programmed, tuned or adjusted and so could mimic one or very few target systems. Modern quantum simulators enable some control over their settings, offering more possibilities.
In contrast to quantum simulators, the long-promised quantum computer is a fully programmable quantum system. While ...
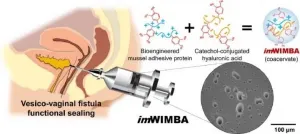
A Korean research team has recently developed an innovative vesico-vaginal fistula treatment method using the mussel adhesive protein (MAP) that can effectively seal fistulas in organs even when exposed to urine.
Professor Hyung Joon Cha, Dr. Hyo Jeong Kim (currently at Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology), and Dr. Tae Yoon Park of POSTECH's Department of Chemical Engineering with Professor Seok Ho Kang of the Department of Urology at Korea University School of Medicine and Professor Jong Hyun Pyun of the Department of Urology at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital have together improved the underwater adhesive using mussel protein and applied it to a pig model that simulated a vesico-vaginal fistula. ...
Osaka, Japan - Scientists from the Graduate School of Science at Osaka University created superabsorbent polymer (SAP) microparticles that self-assemble into structures that can be modified by adjusting the proportion of particle type. This research may lead to new tunable biomimetic "smart materials" that can sense and respond to specific chemicals.
Biological molecules in living organisms have a remarkable ability to form self-assembled structures when triggered by an external molecule. This has led scientists to try to create other "smart materials" that respond to their environment. Now, a team of researchers at Osaka University has come up with a tunable system involving poly(sodium acrylate) microparticles that can have one of two types of chemical ...
The white paper, published today (March 22) by REPHRAIN, the National Research Centre on Privacy, Harm Reduction and Adversarial Influence Online in collaboration with the Dutch National Police, offers a solution to big data problems that tend to hamper police probes into this type of law-breaking.
The practice of attribution - who did what - is becoming increasingly complex as organised crimes incorporate deception, deletion and encryption in today's Information Age. Even when law enforcement are able to retrieve evidence via digital forensics, the complexities of the collected data mean it cannot be easily processed into factual police reports. ...
One prospective source of renewable energy is hydrogen gas produced from water with the aid of sunlight. Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a material, nanoporous cubic silicon carbide, that exhibits promising properties to capture solar energy and split water for hydrogen gas production. The study has been published in the journal ACS Nano.
"New sustainable energy systems are needed to meet global energy and environmental challenges, such as increasing carbon dioxide emissions and climate change", says Jianwu Sun, senior lecturer in the ...
A lot of the attention around "pandemic pets" has focused on families with children getting a cat, dog or other pet in 2020, during a time when many people were learning or working from home.
But a new poll shows that older adults also got in on the trend.
According to the National Poll on Healthy Aging, 10% of all people between the ages of 50 and 80 got a new pet between March 2020 and January 2021.
The percentage was indeed higher - 16% -- among the people in this age range who have at least one child or teen living with them. But the vast majority of people between the ages of 50 and 80 don't live with someone under age 18 -- and nearly 9% of them also got a pet during the pandemic.
All told, 59% of people age 50 to 80 who completed the poll in January 2021 are pet owners. ...
The Covid-19 pandemic severely impacted the mental health of young people, with increased levels of clinical depression being identified, a new study published in the journal Psychiatry Research reports. A decrease in alcohol consumption was also identified amongst young people during the pandemic.
During this unique study researchers from the University of Surrey surveyed 259 young people pre- pandemic (autumn 2019) and in the midst of initial lockdown measures (May/June 2020) on their levels of depression, anxiety, wellbeing, alcohol use and sleep quality.
Researchers found evidence of a substantial impact on the mental health of these young adults due ...
Research has found that experiencing a traumatic event at close quarters changes people's political attitudes. However, in the case of the 2017 terrorist attack in Stockholm, proximity to the attack had no additional political significance. Research from the University of Gothenburg shows that Swedes' attitudes toward terrorism-related questions were affected equally, regardless of whether they happened to be close to the attack.
On 7 April 2017, Rakhmat Akilov stole a truck and ran down multiple people on Drottninggatan, a street in central Stockholm. Five people died, fifteen were injured and many people witnessed ...