New study implicates disease-driving B cells in fatty liver disease development
University of Minnesota Medical School research suggests a Western diet and changes in gut microbes turn pathogen-fighting B-cells into 'disease-promoters'
2021-03-22
(Press-News.org) MINNEAPOLIS/ST.PAUL (03/22/2021) -- New research from the University of Minnesota Medical School suggests that disease-driving B cells, a white blood cell, play a role in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) - the most common chronic liver condition in the U.S. Their findings could lead to targeted therapies for NAFLD, which currently affects a quarter of the nation and has no FDA-approved treatments.
After noticing that patients with the disease showed a large number of inflammatory B cells in their livers, Xavier Revelo, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Integrative Biology and Physiology and senior author, began studying B cells in NAFLD.
"This disease is increasing in prevalence with no approved therapies in sight," Revelo said. "Despite considerable efforts to better understand this disease, the triggers of inflammation during NAFLD are unclear. Our laboratory investigates those inflammatory triggers to provide potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets for its prevention and treatment."
This study was led by Fanta Barrow, a U of M Medical School second-year graduate student from the Revelo laboratory, and was published in Hepatology. The major findings are:
Humans with NAFLD have higher numbers of B cells;
A Western diet -- defined as high in fat, cholesterol and carbohydrates, such as sucrose and fructose -- was responsible for programming these pathogen-fighting B cells into disease-promoters;
And, changes in the gut microbes were responsible for the activation of these disease-promoting B cells.
"These findings lay the foundation for the potential targeting of B cells, or pathways involved in their activation, for NAFLD treatment," Revelo said. "Further work is needed to study the efficacy, safety and potential side effects of such strategies."
INFORMATION:
This research was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (DK122056), "Mechanisms of B Cell Pathogenicity in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease."
About the University of Minnesota Medical School
The University of Minnesota Medical School is at the forefront of learning and discovery, transforming medical care and educating the next generation of physicians. Our graduates and faculty produce high-impact biomedical research and advance the practice of medicine. Visit med.umn.edu to learn how the University of Minnesota is innovating all aspects of medicine.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-22
Although Tuberculosis, or TB, killed nearly as many people as COVID-19 (approx. 1.8 million) in 2020, it did not receive as much media and public attention. The pandemic has proven that transmissible infection is indeed a global issue. TB remains a serious public health concern in Ireland, particularly with the presence of multi-drug resistant types and the numbers of complex cases here continuing to rise, with cases numbering over 300 annually.
Science tells us that iron is crucial for daily human function, but it is also an essential element for the survival of ...
2021-03-22
Batteries charge and recharge--apparently all thanks to a perfect interplay of electrode material and electrolyte. However, for ideal battery function, the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) plays a crucial role. Materials scientists have now studied nucleation and growth of this layer in atomic detail. According to the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie, the properties of anions and solvent molecules need to be well balanced.
In lithium-ion batteries, the SEI forms at the beginning of the first charging process, when a potential is applied. Elements from the electrolyte deposit on the graphite electrode and form a coating that soon ...
2021-03-22
Antibiotics have revolutionized the field of medicine by making it possible to treat most known microbial diseases today. However, their uncontrolled usage has led to the major global problem of antibiotic resistance. As we continue to exploit antibiotics, sometimes at doses much higher than needed, disease-causing bacteria are rapidly evolving defense strategies to evade them. These drug-resistant bacteria, also known as "superbugs," cause severe infections that are difficult to treat and can eventually be fatal.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a particularly vicious group of superbugs that have developed resistance to the antibiotic methicillin, is a major cause of hospital-acquired infections. Accurate and timely diagnosis ...
2021-03-22
Boulder, Colo., USA: Beneath the cold, dark depths of the Arctic ocean sit vast reserves of methane. These stores rest in a delicate balance, stable as a solid called methane hydrates, at very specific pressures and temperatures. If that balance gets tipped, the methane can get released into the water above and eventually make its way to the atmosphere. In its gaseous form, methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases, warming the Earth about 30 times more efficiently than carbon dioxide. Understanding possible sources of atmospheric methane is critical for accurately predicting future climate change.
In the Arctic Ocean today, ice sheets exert pressure on the ground below them. That pressure diffuses ...
2021-03-22
Screenings for breast cancer and colon cancer dropped dramatically during the early months of the coronavirus pandemic, but use of the procedures returned to near-normal levels by the end of July 2020, according to a new study.
Analyzing insurance claims from more than 6 million Americans with private health coverage, researchers found that mammography rates among women aged 45 to 64 declined by 96% during March and April 2020 as compared to January and February.
Similarly, the weekly rate of colorectal cancer screenings among adults aged 45 to 64 and older declined by 95% during the period.
By the end of July 2020, however, the rate of mammograms among women had rebounded and was slightly higher than it had been before the pandemic was declared. The rate of colonoscopies also rebounded, ...
2021-03-22
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin have been shedding light on the enigmatic "spiders from Mars", providing the first physical evidence that these unique features on the planet's surface can be formed by the sublimation of CO2 ice.
Spiders, more formally referred to as araneiforms, are strange-looking negative topography radial systems of dendritic troughs; patterns that resemble branches of a tree or fork lightning. These features, which are not found on Earth, are believed to be carved into the Martian surface by dry ice changing directly from solid to gas (sublimating) in the spring. Unlike Earth, Mars' atmosphere comprises mainly of CO2 and as temperatures decrease in winter, this deposits onto the surface as CO2 ...
2021-03-22
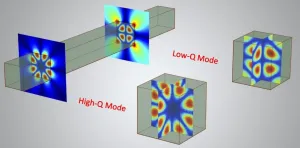
Optical resonators provide the foundation of modern photonics and optics. Thanks to its extreme energy confinement, the high-Q-factor optical resonator optimizes light-matter interaction and photonic device performance by enabling low-threshold laser and enhanced nonlinear harmonic generation.
Two typical structures, the photonic crystal cavity and the whispering gallery cavity, are frequently used to obtain extremely high-Q factors. However, these structures may require dimensions that are comparable to--or several times larger than--the operating wavelength. Whether there is a general way to find out all high-Q modes in a dielectric ...
2021-03-22
The tuberculosis (TB) burden in the WHO European Region as a whole is decreasing, and is down 19% overall for 2015-2019, according to the latest WHO/European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) report Tuberculosis surveillance and monitoring in Europe 2021 (2019 data).
Regional TB mortality has gone down, declining by 9.4% between 2018 and 2019. This is notably higher than the average global decline in TB mortality (3.7%) and enough to have reached the End TB Strategy milestone of a 35% reduction by 2020 compared to 2015.
However, TB is second only to COVID-19 as an infectious disease that kills, and drug resistance is a major concern. There are also worrying indications that the COVID-19 pandemic may stall progress or cause significant setbacks in the fight against TB.
The ...
2021-03-22
Developing a standardized drying protocol for goldenseal could lead to more predictable health applications and outcomes by preserving the alkaloids found in the plant, which is native to Appalachia, according to Penn State researchers, who conducted a new study of the medicinal forest herb.
The roots and rhizomes of goldenseal -- Hydrastis canadensis -- have been used for hundreds of years as a source of antimicrobials and compounds to treat intestinal ailments, noted study co-author Eric Burkhart, associate teaching professor, ecosystem science ...
2021-03-22
Antibody injections are a highly desirable treatment for people with chronic diseases such as cancer, psoriasis, Crohn's disease and arthritis. And recently, antibodies have been in the news as a promising treatment for severe cases of COVID-19.
But the costly, time-consuming manufacturing process to produce antibodies prevents these treatments from being accessible to most patients.
Andrew Zydney, Bayard D. Kunkle Chair and professor of chemical engineering at Penn State, has identified a new method to manufacture antibodies, which could drive down the production cost. His research results were recently published in Biotechnology Progress.
"If you look at the top 10 best-selling medications, by annual sales, eight ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study implicates disease-driving B cells in fatty liver disease development
University of Minnesota Medical School research suggests a Western diet and changes in gut microbes turn pathogen-fighting B-cells into 'disease-promoters'