INFORMATION:
Publicly available article: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0248895
Article Title: "Personality trait predictors of adjustment during the COVID pandemic among college students"
Funding: This work was supported by a grant to Dr. Jim Hudziak from the Conrad Hilton Foundation (https://www.hiltonfoundation.org/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: Dr. Rettew receives royalties from Oxford University Press and Psychology Today and is a consultant to Happy Health, Inc. Dr. Hudziak is a consultant to Happy Health Inc.. The other authors report that no competing interests exist. These interests do not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials. There are no patents, products in development or marketed products associated with this research to declare.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0248895
Extroverts and introverts showed differences in mood during early COVID 19 pandemic
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) More extroverted people suffered mood declines while more introverted people saw mood improvements during the early COVID-19 pandemic, in survey of students at a U.S. university.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Words conveyed with gesture
2021-03-23
The question of the origin of the language is one of the most important and at the same time one of the most difficult to solve. It was formulated in antiquity and has inspired religion and philosophy ever since, in some periods, above all the Enlightenment, becoming the axis of reflection on other fundamental issues, such as human nature. In the last few decades, research in this field has intensified, drawing on evolutionism and having an interdisciplinary character, involving linguists, psychologists, primatologists and neuroscientists. The study of language evolution is currently considered one of the most ...
Pandemic exacerbates challenges for international energy transition
2021-03-23
The Covid-19 Crisis is deepening the divide between energy transition frontrunners and laggards. In a new publication, researchers from the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) in Potsdam present an overview of the global impact of the coronavirus pandemic on the energy sector. Their findings show that low- and middle-income countries need more support in their efforts to ditch fossil fuels.
The crisis will heighten existing imbalances in an uneven energy transition landscape. Despite the crisis, frontrunners in the global energy transition will continue to expand their renewable energy capacities, while laggards will fall further behind. In Europe, the Green Deal ...
Preemies at greater risk for mortality in adulthood
2021-03-23
A new study of mortality among young adults born prematurely includes 6.3 million adults under the age of 50 in Norway, Sweden, Finland and Denmark. Among this group, 5.4 per cent were born before term, according to Professor Kari Risnes at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine and St. Olavs Hospital.
Researchers used national birth registers and compared them with the cause of death registers that all Scandinavian countries have.
"We already know that preemies have increased mortality in childhood and early adulthood. Now we've confirmed the risk of death from chronic diseases such as heart disease, ...
New evidence in search for the mysterious Denisovans
2021-03-23
An international group of researchers led by the University of Adelaide has conducted a comprehensive genetic analysis and found no evidence of interbreeding between modern humans and the ancient humans known from fossil records in Island Southeast Asia. They did find further DNA evidence of our mysterious ancient cousins, the Denisovans, which could mean there are major discoveries to come in the region.
In the study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, the researchers examined the genomes of more than 400 modern humans to investigate the interbreeding events between ancient humans and modern ...
Key research advance could spawn new treatments for heart diseases
2021-03-23
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. -- Scientists peering into the beating heart have solved a decades-old, fundamental mystery about how the heart works. The revelation could herald the development of new treatments for heart diseases -- the leading cause of death worldwide.
Researchers from Eastern Virginia Medical School, Florida State University and the University of Virginia have observed a tiny muscle filament during a crucial stage in a beating heart for the first time. The research was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The heart is a unique muscle which contracts and relaxes about once every second ...
Deaths from COVID-19 have progressively declined at nursing homes, researchers find
2021-03-23
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- The COVID-19 pandemic has had devastating effects in U.S. nursing homes and long-term care facilities, resulting in an estimated 1.2 million infections and 147,000 deaths as of early 2021. Yet even as mortality rates in the general population have decreased over time, little evidence has been uncovered to determine whether nursing home residences have experienced similar reductions.
Now, new data collected and analyzed by researchers at Brown University shows that mortality rates among nursing home residents with COVID-19 declined from March to November 2020, and that the deadliest ...
Scientists created edible food films for food packaging
2021-03-23
An international group of scientists from India and Russia has created edible food films for packaging fruits, vegetables, poultry, meat, and seafood. Films consist of natural ingredients, they are safe for health and the environment. In addition, films are water-soluble and dissolve by almost 90% in 24 hours. Description of the research and results of experiments are published in the Journal of Food Engineering.
"We have created three types of food films based on the well-known naturally occurring seaweed biopolymer sodium alginate," said Rammohan Aluru, senior researcher Organic synthesis laboratory at Ural Federal University and co-author of the paper. "Its molecules have film-forming ...
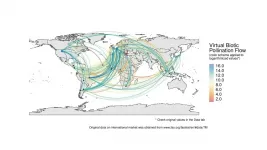
Virtual pollination trade uncovers global dependence on biodiversity for food consumption
2021-03-23
Recently, a published study in Science Advances assessed the contribution of pollinators to international market flows and showed that biodiversity conservation is essential to sustain global consumption patterns. This study results from the work of an interdisciplinary team that integrated researchers across the fields of economics, ecology, environmental sciences and social sciences.
Given the growing global demand for crops, sustainability in agriculture is one of the main challenges for human society. Together with the excessive use of chemical inputs, the loss of natural habitat associated with cropland expansion is one of the main drivers ...
CHOP researchers find supplement prevents strokes in patients with rare genetic disorder
2021-03-23
Philadelphia, March 23, 2021 - Researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have discovered that a widely used nutritional supplement may significantly reduce the risk of fatal strokes caused by a rare genetic disorder. Additionally, the findings suggest that the supplement could be used to both block precipitation of and break up the formation of amyloid plaque deposits, a common feature found in serious forms of dementia. The findings were published online today by the journal Nature Communications.
The findings centered around a genetic disorder known as hereditary cystatin C amyloid angiopathy (HCCAA). HCCAA is part ...
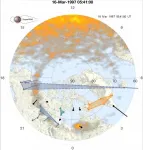
Algorithms inspired by social networks reveal lifecycle of substorms, a key element of space weather
2021-03-23
Evolution of auroral substorms revealed by physicists at University of Warwick using the same methods that link people through social media
'If you like this magnetometer, you might like this one too:' historical data from magnetometers used to match them with 'like-minded friends' during 41 substorms
Shows that a single coherent electrical current, that accompanies the Northern Lights during substorms, covers most of the Earth's night-side at high latitudes
Will help to validate models used to predict auroral substorms, which can disrupt electronics and power distribution systems
Space weather often manifests as substorms, where a beautiful auroral display such as the Northern Lights is accompanied ...