Key research advance could spawn new treatments for heart diseases
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) TALLAHASSEE, Fla. -- Scientists peering into the beating heart have solved a decades-old, fundamental mystery about how the heart works. The revelation could herald the development of new treatments for heart diseases -- the leading cause of death worldwide.
Researchers from Eastern Virginia Medical School, Florida State University and the University of Virginia have observed a tiny muscle filament during a crucial stage in a beating heart for the first time. The research was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The heart is a unique muscle which contracts and relaxes about once every second in most people. Each heartbeat relies on cyclical interactions between thick and thin filaments in the heart muscle -- a process orchestrated by rising and falling levels of calcium, said Vitold Galkin, associate professor of physiological sciences at Eastern Virginia Medical School and an author of the study.
During the "systolic" phase, calcium binds to thin filaments and allows interactions with thick filaments to produce the force required for heart muscle to contract.
"For decades the structure of the thin filament at this important point was unknown," Galkin said. "This dramatically limited our understanding of the thin filament regulation by calcium."
Researchers worked for two years to tackle the technical challenges presented by the complex structure of the thin filament and the difficulty in preparing the specimen for examination.
With those challenges overcome, the team used cryo-electron microscopy to directly observe the thin filament structure as the heart contracts and beats, findings that open up a new avenue for heart disease research.
"We can now fully understand how inherited diseases of the heart affect its capability to work," said Jose R. Pinto, associate professor of biomedical sciences at Florida State University. "Basically, we created a new structural model for the cardiac thin filament, and based on that, we can now address several existing questions about the functioning of the heart in health and disease."
The research team's data reveal how parts of the thin filament cooperate to transition from the diastole phase of the heartbeat -- when the heart muscle is relaxed -- to systole, when the heart muscle contracts and pumps blood.
"The advance in our fundamental knowledge of cardiac muscle regulation paves the way to the rational design of tailored therapeutic interventions that could potentially improve cardiac muscle function in diseased hearts," Galkin said.
The research was groundbreaking for several reasons, said co-investigator P. Bryant Chase, a professor of biological science at Florida State University. That includes the identification of individual structures along thin filaments at three concentrations of calcium -- including a previously unknown structure at systolic calcium -- and the use of thin filaments from a pig heart, which is very similar in size and heart rate to a human heart.
"Our results provide a new, fundamental basis for understanding and modeling the thin filament in health and disease because a number of genetic heart diseases affect proteins of the thin filament," he said.
INFORMATION:
This research was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
The EVMS research team included Galkin; Cristina Risi, research scholar in physiological sciences; Ian Pepper, graduate student; Betty Belknap, research associate in physiological sciences; and Howard White, professor of Physiological Sciences. The FSU research team included Pinto, Chase and graduate student Maicon Landim-Vieira. The University of Virginia researcher was Kelly A. Dryden, associate professor of research, molecular physiology and biological physics.
ADDITIONAL CONTACT:
Doug Gardner,
Eastern Virginia Medical School
(757) 446-6073;
gardneda@evms.edu
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- The COVID-19 pandemic has had devastating effects in U.S. nursing homes and long-term care facilities, resulting in an estimated 1.2 million infections and 147,000 deaths as of early 2021. Yet even as mortality rates in the general population have decreased over time, little evidence has been uncovered to determine whether nursing home residences have experienced similar reductions.
Now, new data collected and analyzed by researchers at Brown University shows that mortality rates among nursing home residents with COVID-19 declined from March to November 2020, and that the deadliest ...
2021-03-23
An international group of scientists from India and Russia has created edible food films for packaging fruits, vegetables, poultry, meat, and seafood. Films consist of natural ingredients, they are safe for health and the environment. In addition, films are water-soluble and dissolve by almost 90% in 24 hours. Description of the research and results of experiments are published in the Journal of Food Engineering.
"We have created three types of food films based on the well-known naturally occurring seaweed biopolymer sodium alginate," said Rammohan Aluru, senior researcher Organic synthesis laboratory at Ural Federal University and co-author of the paper. "Its molecules have film-forming ...
2021-03-23
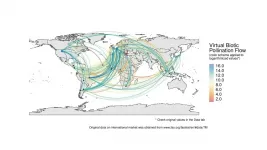
Recently, a published study in Science Advances assessed the contribution of pollinators to international market flows and showed that biodiversity conservation is essential to sustain global consumption patterns. This study results from the work of an interdisciplinary team that integrated researchers across the fields of economics, ecology, environmental sciences and social sciences.
Given the growing global demand for crops, sustainability in agriculture is one of the main challenges for human society. Together with the excessive use of chemical inputs, the loss of natural habitat associated with cropland expansion is one of the main drivers ...
2021-03-23
Philadelphia, March 23, 2021 - Researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have discovered that a widely used nutritional supplement may significantly reduce the risk of fatal strokes caused by a rare genetic disorder. Additionally, the findings suggest that the supplement could be used to both block precipitation of and break up the formation of amyloid plaque deposits, a common feature found in serious forms of dementia. The findings were published online today by the journal Nature Communications.
The findings centered around a genetic disorder known as hereditary cystatin C amyloid angiopathy (HCCAA). HCCAA is part ...
2021-03-23
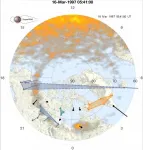
Evolution of auroral substorms revealed by physicists at University of Warwick using the same methods that link people through social media
'If you like this magnetometer, you might like this one too:' historical data from magnetometers used to match them with 'like-minded friends' during 41 substorms
Shows that a single coherent electrical current, that accompanies the Northern Lights during substorms, covers most of the Earth's night-side at high latitudes
Will help to validate models used to predict auroral substorms, which can disrupt electronics and power distribution systems
Space weather often manifests as substorms, where a beautiful auroral display such as the Northern Lights is accompanied ...
2021-03-23
A pioneering study, published in Scientific Reports, found that the Parkinon's gene PINK1 is important for the generation of dopamine-producing neurons throughout life, and is not just responsible for the premature death of these neurons
The international research, led by University of Sheffield's Neuroscience Institute, used two model systems to examine how neurons are produced throughout our lifetime
Parkinson's disease is a relentlessly progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects around 145,000 people in the UK
A gene defect linked to Parkinson's disease may not only cause the early death of neurons, ...
2021-03-23
Hennigsdorf/Berlin, Germany, March 23, 2021 - Diagnostics company SphingoTec GmbH ("SphingoTec") announced today the first published data (1) on the biomarker DPP3 that can predict the evolution of organ function and survival in septic patients. Measured on top of routinely used standard parameters, such as Lactate and Procalcitonin, DPP3 is an early indicator of short-term outcomes and patient severity. Sepsis is a medical emergency caused by a dysregulated host response to an infection, with mortality rates increasing rapidly for each hour that appropriate treatment is delayed (2). The rapid evolution of sepsis into its severe form, septic shock, raises the need for more precise and faster testing to support better clinical decision-making.
DPP3 is an ...
2021-03-23
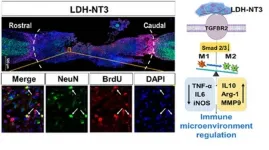
Researchers from the Department of Orthopedics of Tongji Hospital at Tongji University in Shanghai have successfully used a nanobiomaterial called layered double hydroxide (LDH) to inhibit the inflammatory environment surrounding spinal cord injuries in mice, accelerating regeneration of neurons and reconstruction of the neural circuit in the spine. The researchers were also able to identify the underlying genetic mechanism by which LDH works. This understanding should allow further modification of the therapy which, in combination with other elements, could finally produce a comprehensive, clinically applicable system for spinal cord injury relief in humans.
The ...
2021-03-23
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that food industry interactions with government heavily outnumbered non-industry interactions on Bill S-228, also known as the Child Health Protection Act, which died in the Senate of Canada in 2019.
The researchers looked at more than 3,800 interactions, which included meetings, correspondence and lobbying, in the three years before the bill failed. They found that over 80 per cent were by industry, compared to public health or not-for-profit organizations.
They also found that industry accounted for over 80 per cent of interactions with the highest-ranking government offices, including elected parliamentarians and their staff and unelected ...
2021-03-23
BINGHAMTON, NY -- When it comes to local government, does the gender of a mayor or county executive matter in sustainability policymaking? Yes, but only in certain ways, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Kristina Lambright, associate professor of public administration, and George Homsy, associate professor of public administration and director of the environmental studies program, explored the correlation between female leadership and local government adoption of sustainability policies in "Beyond community characteristics: a leader's gender and local government adoption of energy conservation practices and redistributive programmes," published recently ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Key research advance could spawn new treatments for heart diseases