INFORMATION:
Scientists from the Sri Venkateswara and Sri Padmavati Mahila Viswavidyalayam Universities (Tirupati, India), Ural Federal University and Ural Branch of the RAS (Ekaterinburg, Russia) worked on the creation of the films. The research was supported by the University Grants Commission (New Delhi, India, Rajiv Gandhi National Scholarship F1-17.1 / 2016-17 / RGNF-2015-17-SC -AND-18494 / SAIII) and the Central Institute of Plastics Engineering and Technology (Vijayawada, India).
Reference
Sodium alginate is a well-known edible biopolymer of natural origin used as a thickener and stabilizer (food additive E401), used as a thickener or stabilizer. Ferulic acid (a derivative of cinnamic acid) has a wide range of pharmacological properties, in particular, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antitoxic, hepato- and cardioprotective, antiviral and antibacterial ones, which is mainly due to the antioxidant properties of this acid.
Scientists created edible food films for food packaging
Films consist of natural ingredients, they are healthy-safe and water-solubility
2021-03-23
(Press-News.org) An international group of scientists from India and Russia has created edible food films for packaging fruits, vegetables, poultry, meat, and seafood. Films consist of natural ingredients, they are safe for health and the environment. In addition, films are water-soluble and dissolve by almost 90% in 24 hours. Description of the research and results of experiments are published in the Journal of Food Engineering.
"We have created three types of food films based on the well-known naturally occurring seaweed biopolymer sodium alginate," said Rammohan Aluru, senior researcher Organic synthesis laboratory at Ural Federal University and co-author of the paper. "Its molecules have film-forming properties. Sodium alginate is an auspicious carbohydrate macromolecule that has the potential film-forming properties upon hydrolysis and abundantly existed in cell walls as a mixture of various salts. The greatest advantage of sodium alginate is that it performs as liquid-gel in an aqueous medium."
Alginate molecules were cross-linked with a natural antioxidant ferulic acid. It makes the film not only strong, but also homogeneous, more rigid, and prolongs the life of the products.
"Food stays fresh longer due to the antioxidant components that slow down the oxidation processes," said Grigory Zyryanov, professor of the Department of Organic and Biomolecular Chemistry at Ural Federal University. "In addition, we can add to the films natural antiviral agents, that will also extend the shelf life of food. Garlic, turmeric, and ginger contain compounds that may prevent the spread of the viruses."
According to the authors, no special equipment for the production of films is required. On an industrial scale, it can be created by food products and films manufacturers.
"It can also be produced at a polymer production plant. The only condition is that it must meet the standards that apply to food production. And if an inexhaustible source of algae the ocean is nearby it will be quite simple to create such films," said Grigory Zyryanov.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
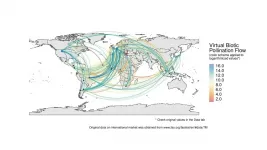
Virtual pollination trade uncovers global dependence on biodiversity for food consumption
2021-03-23
Recently, a published study in Science Advances assessed the contribution of pollinators to international market flows and showed that biodiversity conservation is essential to sustain global consumption patterns. This study results from the work of an interdisciplinary team that integrated researchers across the fields of economics, ecology, environmental sciences and social sciences.
Given the growing global demand for crops, sustainability in agriculture is one of the main challenges for human society. Together with the excessive use of chemical inputs, the loss of natural habitat associated with cropland expansion is one of the main drivers ...
CHOP researchers find supplement prevents strokes in patients with rare genetic disorder
2021-03-23
Philadelphia, March 23, 2021 - Researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have discovered that a widely used nutritional supplement may significantly reduce the risk of fatal strokes caused by a rare genetic disorder. Additionally, the findings suggest that the supplement could be used to both block precipitation of and break up the formation of amyloid plaque deposits, a common feature found in serious forms of dementia. The findings were published online today by the journal Nature Communications.
The findings centered around a genetic disorder known as hereditary cystatin C amyloid angiopathy (HCCAA). HCCAA is part ...
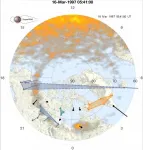
Algorithms inspired by social networks reveal lifecycle of substorms, a key element of space weather
2021-03-23
Evolution of auroral substorms revealed by physicists at University of Warwick using the same methods that link people through social media
'If you like this magnetometer, you might like this one too:' historical data from magnetometers used to match them with 'like-minded friends' during 41 substorms
Shows that a single coherent electrical current, that accompanies the Northern Lights during substorms, covers most of the Earth's night-side at high latitudes
Will help to validate models used to predict auroral substorms, which can disrupt electronics and power distribution systems
Space weather often manifests as substorms, where a beautiful auroral display such as the Northern Lights is accompanied ...
Parkinson's gene may impair how new neurons are made throughout our lifetime
2021-03-23
A pioneering study, published in Scientific Reports, found that the Parkinon's gene PINK1 is important for the generation of dopamine-producing neurons throughout life, and is not just responsible for the premature death of these neurons
The international research, led by University of Sheffield's Neuroscience Institute, used two model systems to examine how neurons are produced throughout our lifetime
Parkinson's disease is a relentlessly progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects around 145,000 people in the UK
A gene defect linked to Parkinson's disease may not only cause the early death of neurons, ...
New diagnostic tool for the management of patients with sepsis
2021-03-23
Hennigsdorf/Berlin, Germany, March 23, 2021 - Diagnostics company SphingoTec GmbH ("SphingoTec") announced today the first published data (1) on the biomarker DPP3 that can predict the evolution of organ function and survival in septic patients. Measured on top of routinely used standard parameters, such as Lactate and Procalcitonin, DPP3 is an early indicator of short-term outcomes and patient severity. Sepsis is a medical emergency caused by a dysregulated host response to an infection, with mortality rates increasing rapidly for each hour that appropriate treatment is delayed (2). The rapid evolution of sepsis into its severe form, septic shock, raises the need for more precise and faster testing to support better clinical decision-making.
DPP3 is an ...
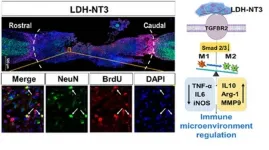
Nanobiomaterial boosts neuronal growth in mice with spinal cord injuries
2021-03-23
Researchers from the Department of Orthopedics of Tongji Hospital at Tongji University in Shanghai have successfully used a nanobiomaterial called layered double hydroxide (LDH) to inhibit the inflammatory environment surrounding spinal cord injuries in mice, accelerating regeneration of neurons and reconstruction of the neural circuit in the spine. The researchers were also able to identify the underlying genetic mechanism by which LDH works. This understanding should allow further modification of the therapy which, in combination with other elements, could finally produce a comprehensive, clinically applicable system for spinal cord injury relief in humans.
The ...
Food industry lobbying was intense on failed bill to limit marketing to Canadian children
2021-03-23
Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that food industry interactions with government heavily outnumbered non-industry interactions on Bill S-228, also known as the Child Health Protection Act, which died in the Senate of Canada in 2019.
The researchers looked at more than 3,800 interactions, which included meetings, correspondence and lobbying, in the three years before the bill failed. They found that over 80 per cent were by industry, compared to public health or not-for-profit organizations.
They also found that industry accounted for over 80 per cent of interactions with the highest-ranking government offices, including elected parliamentarians and their staff and unelected ...
A leader's gender plays a role in local government sustainability policymaking
2021-03-23
BINGHAMTON, NY -- When it comes to local government, does the gender of a mayor or county executive matter in sustainability policymaking? Yes, but only in certain ways, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Kristina Lambright, associate professor of public administration, and George Homsy, associate professor of public administration and director of the environmental studies program, explored the correlation between female leadership and local government adoption of sustainability policies in "Beyond community characteristics: a leader's gender and local government adoption of energy conservation practices and redistributive programmes," published recently ...
Novel thermometer can accelerate quantum computer development
2021-03-23
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, have developed a novel type of thermometer that can simply and quickly measure temperatures during quantum calculations with extremely high accuracy. The breakthrough provides a benchmarking tool for quantum computing of great value - and opens up for experiments in the exciting field of quantum thermodynamics.
A key component in quantum computers are coaxial cables and waveguides - structures which guide waveforms, and act as the vital connection between the quantum processor, and the classical electronics which control it. Microwave pulses travel along the waveguides to the quantum processor, and are cooled ...
Partnership with churches increases COVID-19 vaccine delivery among Black population
2021-03-23
Incorporating Black churches and clergy in COVID-19 vaccination education and distribution has been found to be an effective model in helping to increase vaccination delivery to historically at-risk populations in San Bernardino County, a study says.
Focused education efforts and an on-site mobile clinic in Black church parking lots resulted in the vaccinations of 417 people, 84% of whom were Black. The study also found an increase in Black attendance of mass vaccination clinics to 3.6% of total patients, up from 3%, in the week post-initiative.
Researchers at Loma Linda University School of Pharmacy published their findings on March 10 in The Lancet Global Health, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Scientists created edible food films for food packagingFilms consist of natural ingredients, they are healthy-safe and water-solubility