Aging cells in abdominal fluid cause increased peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer
Closing in on complete control over peritoneal dissemination of cancer.
2021-03-23
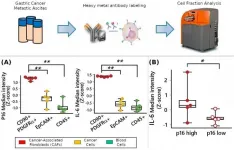
(Press-News.org) Through an analysis of cellular components (cell fractions) from malignant ascites (fluid buildup in the abdomen caused by gastric cancer), a research collaboration based in Kumamoto University (Japan) has demonstrated that cellular senescence of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play an important role in the peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer foci (cells different from surrounding cells). This understanding should enable the development of new treatments for cancer dissemination in the peritoneum by targeting cancer cells at focal sites and CAFs in patients with gastric cancer.
Peritoneal dissemination is one type of cancer metastasis in which cancer cells break through the walls of internal organs, scatter throughout the abdomen, and grow into the peritoneum. Highly malignant gastric cancers, such as scirrhous gastric cancer, are prone to peritoneal dissemination which make them very difficult to treat. Furthermore, the development of disseminated foci is known to be closely related to the prognosis. Thus, controlling peritoneal dissemination is an important issue for improved gastric cancer treatment.
CAFs are fibroblasts that make up the cancer microenvironment, the fluids and tissues surrounding cancer cells, and are known to secrete a variety of factors involved in malignant transformations. In this study, researchers used CAFs derived from post-operative specimens of scirrhous gastric cancer patients to mimic the inflammatory environment and found that CAFs cause cellular senescence due to the release of inflammatory substances (cytokines) from cancer and surrounding cells.
Senescent cells continue to secrete senescence-associated proteins that aid in cancer cell progression and are known to cause chronic inflammation. Thus, researchers focused on changes in the epigenome of CAFs as a mechanism for the chronic secretion of these proteins. A detailed genetic analysis revealed that CAFs that underwent cellular senescence showed characteristic changes in histone modifications resulting in the activation of genes that form cellular senescence-related substances. Senescent CAFs were found to continuously secrete senescence-related proteins that promote cancer progression. Furthermore, analysis of various cell fractions from malignant ascites from patients with scirrhous gastric cancer also revealed the presence of aging CAFs.
"Our study has revealed the significance of CAFs in ascites due to peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer," said study leader, Dr. Takatsugu Ishimoto. "Based on our findings, a new therapeutic strategy for gastric cancer that targets cancer cells at peritoneal dissemination sites and senescent CAFs could be possible for preventing peritoneal dissemination."
INFORMATION:
This research was posted in Cell Reports on 23 February 2021.
Source:
Yasuda, T., Koiwa, M., Yonemura, A., Miyake, K., Kariya, R., Kubota, S., ... Ishimoto, T. (2021). Inflammation-driven senescence-associated secretory phenotype in cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances peritoneal dissemination.
Cell Reports, 34(8), 108779.
doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108779
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-23
Plant species with short generation times are more sensitive to climate change than those with long generation times. This is one of the findings of a synthesis study by researchers from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the Helmholtz-Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ). The international team comprehensively compiled worldwide available data, mostly from Europe and North America, to address the question of how plant populations react to climate change. The study, published in Nature Communications, shows that plant characteristics such as generation ...
2021-03-23
Consumption of ultra-processed foods and drink could increase the risk of developing colorectal cancer. This was the conclusion of a large study undertaken by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, based on questionnaires about food behaviours completed by around 8,000 people in Spain. The study, the first of its kind in the country, also analysed the relationship between ultra-processed food and drink products and two other cancers; while no association was observed with prostate cancer, in the case of breast cancer a higher risk was observed in the sub-group of former and current smokers who reported a ...
2021-03-23
More extroverted people suffered mood declines while more introverted people saw mood improvements during the early COVID-19 pandemic, in survey of students at a U.S. university.
INFORMATION:
Publicly available article: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0248895
Article Title: "Personality trait predictors of adjustment during the COVID pandemic among college students"
Funding: This work was supported by a grant to Dr. Jim Hudziak from the Conrad Hilton Foundation (https://www.hiltonfoundation.org/). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
2021-03-23
The question of the origin of the language is one of the most important and at the same time one of the most difficult to solve. It was formulated in antiquity and has inspired religion and philosophy ever since, in some periods, above all the Enlightenment, becoming the axis of reflection on other fundamental issues, such as human nature. In the last few decades, research in this field has intensified, drawing on evolutionism and having an interdisciplinary character, involving linguists, psychologists, primatologists and neuroscientists. The study of language evolution is currently considered one of the most ...
2021-03-23
The Covid-19 Crisis is deepening the divide between energy transition frontrunners and laggards. In a new publication, researchers from the Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS) in Potsdam present an overview of the global impact of the coronavirus pandemic on the energy sector. Their findings show that low- and middle-income countries need more support in their efforts to ditch fossil fuels.
The crisis will heighten existing imbalances in an uneven energy transition landscape. Despite the crisis, frontrunners in the global energy transition will continue to expand their renewable energy capacities, while laggards will fall further behind. In Europe, the Green Deal ...
2021-03-23
A new study of mortality among young adults born prematurely includes 6.3 million adults under the age of 50 in Norway, Sweden, Finland and Denmark. Among this group, 5.4 per cent were born before term, according to Professor Kari Risnes at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Clinical and Molecular Medicine and St. Olavs Hospital.
Researchers used national birth registers and compared them with the cause of death registers that all Scandinavian countries have.
"We already know that preemies have increased mortality in childhood and early adulthood. Now we've confirmed the risk of death from chronic diseases such as heart disease, ...
2021-03-23
An international group of researchers led by the University of Adelaide has conducted a comprehensive genetic analysis and found no evidence of interbreeding between modern humans and the ancient humans known from fossil records in Island Southeast Asia. They did find further DNA evidence of our mysterious ancient cousins, the Denisovans, which could mean there are major discoveries to come in the region.
In the study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution, the researchers examined the genomes of more than 400 modern humans to investigate the interbreeding events between ancient humans and modern ...
2021-03-23
TALLAHASSEE, Fla. -- Scientists peering into the beating heart have solved a decades-old, fundamental mystery about how the heart works. The revelation could herald the development of new treatments for heart diseases -- the leading cause of death worldwide.
Researchers from Eastern Virginia Medical School, Florida State University and the University of Virginia have observed a tiny muscle filament during a crucial stage in a beating heart for the first time. The research was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The heart is a unique muscle which contracts and relaxes about once every second ...
2021-03-23
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- The COVID-19 pandemic has had devastating effects in U.S. nursing homes and long-term care facilities, resulting in an estimated 1.2 million infections and 147,000 deaths as of early 2021. Yet even as mortality rates in the general population have decreased over time, little evidence has been uncovered to determine whether nursing home residences have experienced similar reductions.
Now, new data collected and analyzed by researchers at Brown University shows that mortality rates among nursing home residents with COVID-19 declined from March to November 2020, and that the deadliest ...
2021-03-23
An international group of scientists from India and Russia has created edible food films for packaging fruits, vegetables, poultry, meat, and seafood. Films consist of natural ingredients, they are safe for health and the environment. In addition, films are water-soluble and dissolve by almost 90% in 24 hours. Description of the research and results of experiments are published in the Journal of Food Engineering.
"We have created three types of food films based on the well-known naturally occurring seaweed biopolymer sodium alginate," said Rammohan Aluru, senior researcher Organic synthesis laboratory at Ural Federal University and co-author of the paper. "Its molecules have film-forming ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Aging cells in abdominal fluid cause increased peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer
Closing in on complete control over peritoneal dissemination of cancer.




