(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers has found that three commonly used antiviral and antimalarial drugs are effective in vitro at preventing replication of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The work also underscores the necessity of testing compounds against multiple cell lines to rule out false negative results.
The team, which included researchers from North Carolina State University and Collaborations Pharmaceuticals, looked at three antiviral drugs that have proven effective against Ebola and the Marburg virus: tilorone, quinacrine and pyronaridine.
"We were looking for compounds that could block the entry of the virus into the cell," says Ana Puhl, senior scientist at Collaborations Pharmaceuticals and co-corresponding author of the research. "We chose these compounds because we know that other antivirals which successfully act against Ebola are also effective inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2."
The compounds were tested in vitro against SARS-CoV-2, as well as against a common cold virus (HCoV 229E) and murine hepatitis virus (MHV). Researchers utilized a variety of cell lines that represented potential targets for SARS-CoV-2 infection in the human body. They infected the cell lines with the different viruses and then looked at how well the compounds prevented viral replication in the cells.
The results were mixed, with the compounds' effectiveness depending upon whether they were used in human-derived cell lines versus monkey-derived cell lines, known as Vero cell lines.
"In the human-derived cell lines, we found that all three compounds worked similarly to remdesivir, which is currently being used to treat COVID-19," says Frank Scholle, associate professor of biology at NC State and co-author of the research. "However, they were not at all effective in the Vero cells."
"Researchers saw similar results when these compounds were initially tested against Ebola," says Sean Ekins, CEO of Collaborations Pharmaceuticals and co-corresponding author of the research. "They were effective in human-derived cell lines, but not in Vero cells. This is important because Vero cells are one of the standard models used in this type of testing. In other words, different cells lines may have differing responses to a compound. It points to the necessity of testing compounds in many different cell lines to rule out false negatives."
Next steps for the research include testing the compounds' effectiveness in a mouse model and further work on understanding how they inhibit viral replication.
"One of the more interesting findings here is that these compounds don't just prevent the virus from potentially binding to the cells, but that they may also inhibit viral activity because these compounds are acting on the lysosomes," Puhl says. "Lysosomes, which are important for normal cell function, are hijacked by the virus for entry and exit out of the cell. So, if that mechanism is disrupted, it cannot infect other cells."
"It's also interesting that these compounds are effective not just against SARS-CoV-2, but against related coronaviruses," Scholle says. "It could give us a head start on therapies as new coronaviruses emerge."
INFORMATION:
The work appears in ACS Omega and was supported in part by NC State's Comparative Medicine Institute and the National Institutes of Health. NC State undergraduates James Levi and Nicole Johnson, as well as Ralph Baric, from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, contributed to the work. Other collaborating institutions included: Instituto Oswaldo Cruz and University of Campinas, both in Brazil; Utah State University; the University of Maryland; and SRI International.
-peake-
Note to editors: An abstract follows.
"Repurposing the Ebola and Marburg Virus Inhibitors Tilorone, Quinacrine, and Pyronaridine: In Vitro Activity against SARS-CoV?2 and Potential Mechanisms"
DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c05996
Authors: Ana Puhl, Sean Ekins, Collaborations Pharmaceuticals; Frank Scholle, James Levi, Nicole Johnson, NC State University; et al
Published: March 12, 2021 in ACS Omega
Abstract:
Severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a newly identified virus that has resulted in over 2.5 million deaths globally and over 116 million cases globally in March, 2021. Small-molecule inhibitors that reverse disease severity have proven difficult to discover. One of the key approaches that has been widely applied in an effort to speed up the translation of drugs is drug repurposing. A few drugs have shown in vitro activity against Ebola viruses and demonstrated activity against SARS-CoV-2 in vivo. Most notably, the RNA polymerase targeting remdesivir demonstrated activity in vitro and efficacy in the early stage of the disease in humans. Testing other small-molecule drugs that are active against Ebola viruses (EBOVs) would appear a reasonable strategy to evaluate their potential for SARS-CoV-2. We have previously repurposed pyronaridine, tilorone, and quinacrine (from malaria, influenza, and antiprotozoal uses, respectively) as inhibitors of Ebola and Marburg viruses in vitro in HeLa cells and mouse-adapted EBOV in mice in vivo. We have now tested these three drugs in various cell lines (VeroE6, Vero76, Caco-2, Calu-3, A549-ACE2, HUH-7, and monocytes) infected with SARS-CoV-2 as well as other viruses (including MHV and HCoV 229E). The compilation of these results indicated considerable variability in antiviral activity observed across cell lines. We found that tilorone and pyronaridine inhibited the virus replication in A549-ACE2 cells with IC50 values of 180 nM and IC50 198 nM, respectively. We used microscale thermophoresis to test the binding of these molecules to the spike protein, and tilorone and pyronaridine bind to the spike receptor binding domain protein with Kd values of 339 and 647 nM, respectively. Human Cmax for pyronaridine and quinacrine is greater than the IC50 observed in A549-ACE2 cells. We also provide novel insights into the mechanism of these compounds which is likely lysosomotropic.
Scientists investigating the genetics of chilli pepper species have discovered a whole host of new chilli hybrids that can be grown by crossing domesticated peppers with their wild cousins. This will allow plant breeders to create new varieties that have better disease resistance and could increase productivity.
Despite their huge world-wide culinary appeal, chillies are relatively difficult to cultivate, being prone to disease and sensitive to growing conditions.
There are 35 species of pepper in the Capsicum family, including five domesticated species. The most well-known ...
The process of fabricating materials is complicated, time-consuming and costly. Too much of one material, or too little, can create problems with the product, forcing the design process to begin again. Advancements in the design process are needed to reduce the cost and time it takes to produce materials with targeted properties.
Funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF), researchers at Texas A&M University are using advanced computational and machine-learning techniques to create a framework capable of optimizing the process of developing materials, cutting time and costs.
"Our general focus ...
Curtin University research has uncovered the first solid clues about the very beginning of the supercontinent cycle of Earth, finding it was kick-started two billion years ago.
Detailed in a paper published in Geology, a team of researchers from Curtin's Earth Dynamics Research Group found that plate tectonics operated differently before two billion years ago, and the 600 million years supercontinent cycle likely only started during the second half of Earth's life.
Lead researcher Dr Yebo Liu from Curtin's School of Earth and Planetary Sciences said that the shift in plate tectonics marked a regime change in the Earth System.
"This regime change impacted on the eventual emergence of complex life and even ...
The talented athletes are there. The cheering fans are there. But the media? It's nowhere to be found.
This is the reality of women's sports, which continue to be almost entirely excluded from television news and sports highlights shows, according to a USC/Purdue University study published on March 24th in Communication & Sport.
The survey of men's and women's sports news coverage has been conducted every five years since 1989. In the latest study, researchers found that 95% of total television coverage as well as the ESPN sports highlights show SportsCenter focused on men's sports in 2019. They saw a similar lopsidedness ...
A research group at the RIKEN Center for Computational Science (R-CCS) has found that glycans--sugar molecules--play an important role in the structural changes that take place when the virus which causes COVID-19 invades human cells. Their discovery, which was based on supercomputer-based simulations, could contribute to the molecular design of drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. The research was published in the Biophysical Journal.
When SARS-CoV-2--the coronavirus that causes COVID-19--invades a human cell, a spike protein on its surface binds to an enzyme called ACE2 on the surface of the cell. The ...
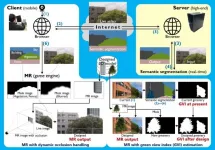
Osaka, Japan - Scientists from the Division of Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering at Osaka University employed deep learning artificial intelligence to improve mobile mixed reality generation. They found that occluding objects recognized by the algorithm could be dynamically removed using a video game engine. This work may lead to a revolution in green architecture and city revitalization.
Mixed reality (MR) is a type of visual augmentation in which real-time images of existing objects or landscapes can be digitally altered. As anyone who has played Pokémon Go! or similar games knows, looking at a smartphone ...
Osaka, Japan - Most of the devices used in our daily lives are operated and controlled by electricity. From the standpoint of safety and the tight supply and demand of electricity, circuit design that satisfies low electromagnetic noise and power saving is becoming increasingly important.
In an electric circuit, electric signals transmit inside the conductor, and electromagnetic fields radiate outside the conductor. Furthermore, the electromagnetic field propagates through the air and is converted into signals for itself and other circuits, which leads to electromagnetic noise. Now, a research team at Osaka University has formulated a numerical method ...
At the bottom of the world, there's a small island about four kilometers off the coast of Antarctica. In summer, temperatures climb to freezing with uninterrupted daylight for two months. In winter, they fall to minus 40 degrees Celsius without a single sunrise for two months. It is isolated and desolate, uninhabitable to all humans -- except for the Japanese Antarctic Research Expedition (JARE). Almost every year since 1956, a JARE team winters over on the island, staying in Syowa Station, from February to January to conduct various research projects. From 2004 to 2014, however, they were also research subjects themselves.
As part of a joint project between the National Institute of Polar Research at the Research Organization of Information and Systems ...
Materials science likes to take nature and the special properties of living beings that could potentially be transferred to materials as a model. A research team led by chemist Professor Andreas Walther of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has succeeded in endowing materials with a bioinspired property: Wafer-thin stiff nanopaper instantly becomes soft and elastic at the push of a button. "We have equipped the material with a mechanism so that the strength and stiffness can be modulated via an electrical switch," explained Walther. As soon as an electric current is applied, the nanopaper becomes soft; when the current flow stops, it regains its strength. From an application perspective, this switchability could be interesting for damping ...
Tokyo, Japan - Scientists from the Graduate School of Information Science and Technology at The University of Tokyo calculated the efficiency of the sensory network that bacteria use to move towards food and found it to be optimal from an information theory standpoint. This work may lead to a better understanding of bacterial behavior and their sensory networks.
Despite being single-celled organisms, bacteria such as E. Coli can perform some impressive feats of sensing and adaptation in constantly changing environmental conditions. For example, these bacteria can sense the presence of a chemical ...