Pregnant women show robust immune response to COVID vaccines, pass antibodies to newborns
The largest study of its kind to date also found benefit for lactating women
2021-03-25
(Press-News.org) BOSTON - In the largest study of its kind to date, researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital, Brigham and Women's Hospital and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard have found the new mRNA COVID-19 vaccines to be highly effective in producing antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 virus in pregnant and lactating women. They also demonstrated the vaccines confer protective immunity to newborns through breastmilk and the placenta.
The study, published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (AJOG), looked at 131 women of reproductive age (84 pregnant, 31 lactating and 16 non-pregnant), all of whom received one of the two new mRNA vaccines: Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna. The vaccine-induced titers - or antibody levels - were equivalent in all three groups. Reassuringly, side effects after vaccination were rare and comparable across the study participants.
"This news of excellent vaccine efficacy is very encouraging for pregnant and breastfeeding women, who were left out of the initial COVID-19 vaccine trials," says Andrea Edlow, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at MGH, director of the Edlow Lab in the Vincent Center for Reproductive Biology and co-senior author of the new study. "Filling in the information gaps with real data is key - especially for our pregnant patients who are at greater risk for complications from COVID-19. This study also highlights how eager pregnant and lactating individuals are to participate in research."
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, individuals who are pregnant are more likely to become severely ill with COVID-19, require hospitalization, intensive care or ventilation - and may be at increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes. The team also compared vaccination-induced antibody levels to those induced by natural infection with COVID-19 in pregnancy, and found significantly higher levels of antibodies from vaccination.
Vaccine-generated antibodies were also present in all umbilical cord blood and breastmilk samples taken from the study, showing the transfer of antibodies from mothers to newborns.
"We now have clear evidence the COVID vaccines can induce immunity that will protect infants," says Galit Alter, PhD, core member of the Ragon Institute and co-senior author of the study. "We hope this study will catalyze vaccine developers to recognize the importance of studying pregnant and lactating individuals, and include them in trials. The potential for rational vaccine design to drive improved outcomes for mothers and infants is limitless, but developers must realize that pregnancy is a distinct immunological state, where two lives can be saved simultaneously with a powerful vaccine. We look forward to studying all vaccine platforms in pregnancy as they become available."
The study was also able to provide insight into potential differences between the immune response elicited by the Pfizer vaccine compared to the Moderna vaccine, finding the levels of mucosal (IgA) antibodies were higher after the second dose of Moderna compared to the second dose of Pfizer.
"This finding is important for all individuals, since SARS-CoV-2 is acquired through mucosal surfaces like the nose, mouth and eyes," says Kathryn Gray, MD, PhD, an obstetrician at Brigham and Women's Hospital and a first author of the paper. "But it also holds special importance for pregnant and lactating women because IgA is a key antibody present in breastmilk."
INFORMATION:
Gray's co-first authors on the study are Evan Bordt, PhD, of MGH and Caroline Atyeo of the Ragon Institute.
Funding for the study included grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), the Gates Foundation, the Massachusetts Consortium on Pathogen Readiness (MassCPR) and the Musk Foundation.
About the Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital, founded in 1811, is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. The END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-25
Chronic side effects among melanoma survivors after treatment with anti-PD-1 immunotherapies are more common than previously recognized, according to a study published March 25 in JAMA Oncology.
The chronic complications, which occurred in 43% of patients, affected the joints and endocrine system most commonly, and less often involved salivary glands, eyes, peripheral nerves and other organs. These complications may be long lasting, with only 14% of cases having been resolved at last follow-up. This finding contrasted with previously reported immunotherapy-related acute complications that affected visceral organs -- including the liver, colon, lungs and kidneys -- which were effectively treated with steroids. However, the vast ...
2021-03-25
Pregnant women who consumed the caffeine equivalent of as little as half a cup of coffee a day on average had slightly smaller babies than pregnant women who did not consume caffeinated beverages, according to a study by researchers at the National Institutes of Health. The researchers found corresponding reductions in size and lean body mass for infants whose mothers consumed below the 200 milligrams of caffeine per day--about two cups of coffee--believed to increase risks to the fetus. Smaller birth size can place infants at higher risk of obesity, heart ...
2021-03-25
Scientists at the Proteomics Core Unit of the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), headed by Javier Muñoz, have described the mechanisms, unknown to date, involved in maintaining embryonic stem cells in the best possible state for their use in regenerative medicine. Their results, published in Nature Communications, will help to find novel stem-cell therapies for brain stroke, heart disease or neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's or Parkinson's disease.
Naïve pluripotent stem cells, ideal for doing research
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent cells that can grow ...
2021-03-25
Quantum holds the promise of increasing the power of sensing technologies. While the field of quantum sensing has shown a lot of potential for detecting very small signals, the ability to truly optimize these sensors has been thwarted by the complexity of control schemes.
In a paper published on March 25 in Nature Partner Journals - Quantum Information, a research team based at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, explained how they applied two theoretical tools of quantum information to these types of extremely sensitive signal detection tasks. Their research suggests that honing this sensitivity to detect signals while rejecting background noise will enable the use of quantum ...
2021-03-25
HOUSTON - (March 25, 2021) - One of nature's most prolific cannibals could be hiding in your pantry, and biologists have used it to show how social structure affects the evolution of selfish behavior.
Researchers revealed that less selfish behavior evolved under living conditions that forced individuals to interact more frequently with siblings. While the finding was verified with insect experiments, Rice University biologist Volker Rudolf said the evolutionary principal could be applied to study any species, including humans.
In a study published online this week in Ecology Letters, Rudolf, longtime collaborator Mike Boots of the University of California, Berkeley, and colleagues showed they could drive the evolution of cannibalism in ...
2021-03-25
An 'astonishing' deficit of data about how the global boom in educational technology could help pupils with disabilities in low and middle-income countries has been highlighted in a new report.
Despite widespread optimism that educational technology, or 'EdTech', can help to level the playing field for young people with disabilities, the study found a significant shortage of evidence about which innovations are best-positioned to help which children, and why; specifically in low-income contexts.
The review also found that many teachers lack training on how to use new technology, or are reluctant to do so.
The ...
2021-03-25
Fish oil supplements are a billion-dollar industry built on a foundation of purported, but not proven, health benefits. Now, new research from a team led by a University of Georgia scientist indicates that taking fish oil only provides health benefits if you have the right genetic makeup.
The study, led by Kaixiong Ye and published in PLOS Genetics, focused on fish oil (and the omega-3 fatty acids it contains) and its effect on triglycerides, a type of fat in the blood and a biomarker for cardiovascular disease.
"We've known for a few decades that a higher level of omega-3 fatty acids in the blood is associated with a lower risk of heart disease," said Ye, assistant professor ...
2021-03-25
Cholinesterase inhibitors are a group of drugs recommended for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but their effects on cognition have been debated and few studies have investigated their long-term effects. A new study involving researchers from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden and published in the journal Neurology shows persisting cognitive benefits and reduced mortality for up to five years after diagnosis.
Alzheimer's disease is a cognitive brain disease that affects millions of patients around the world. Some 100,000 people in Sweden live with the diagnosis, which has a profound impact on the lives of both them and their families. Most of those who receive a diagnosis are over 65, but there are some patients ...
2021-03-25
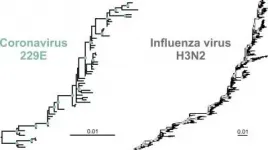
Influenza vaccines need to be evaluated every year to ensure they remain effective against new influenza viruses. Will the same apply to COVID-19 vaccines? In order to gauge whether and to what extent this may be necessary, a team of researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin compared the evolution of endemic 'common cold' coronaviruses with that of influenza viruses. The researchers predict that, while the pandemic is ongoing, vaccines will need to undergo regular updates. A few years into the post-pandemic period, however, vaccines ...
2021-03-25
Alzheimer's disease seems to progress faster in women than in men. The protein tau accumulates at a higher rate in women, according to research from Lund University in Sweden. The study was recently published in Brain.
Over 30 million people suffer from Alzheimer's disease worldwide, making it the most common form of dementia. Tau and beta-amyloid are two proteins known to aggregate and accumulate in the brain in patients with Alzheimer's.
The first protein to aggregate in Alzheimer's is beta-amyloid. Men and women are equally affected by the first disease stages, and the analysis did not show any differences in the accumulation of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Pregnant women show robust immune response to COVID vaccines, pass antibodies to newborns
The largest study of its kind to date also found benefit for lactating women