(Press-News.org) Working with fruit flies, scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have identified a new molecular pathway that helps steer moving cells in specific directions. The set of interconnected proteins and enzymes in the pathway act as steering and rudder components that drive cells toward an "intended" rather than random destination, they say.
In a report on the work, published March 2 in Cell Reports, these same molecular pathways, say the scientists, may drive cancer cells to metastasize or travel to distant areas of the body and may also be important for understanding how cells assemble and migrate in an embryo to form organs and other structures.
The team of scientists was led by Deborah Andrew, Ph.D., professor of cell biology and associate director for faculty development for the Institute for Basic Biomedical Sciences at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Andrew and her colleagues began this research while studying a gene called Tre1 and its role in the development of salivary glands in fruit flies. The tools to study the effects of turning the gene on and off weren't ideal, she says. So, two of the team members, Caitlin Hanlon, Ph.D., of Quinnipiac University and JiHoon Kim, Ph.D., of Johns Hopkins, generated fruit flies that lack the protein-coding portion of the Tre1 gene. The pair also put a fluorescent tag on the Tre1 protein to learn where it localized during key steps in development.
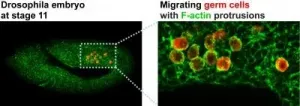
In experiments with fruit fly embryos carrying an intact Tre1 gene, cells that produce future generations of the organism, called germ cells, migrate correctly to the sex organ, known as the gonad.
"Without the Tre1 gene, however, most of the germ cells failed to meet up with other nongerm cells, or somatic cells, of the gonad," says Andrew. "Correct navigation of germ cells is important to ensure that future generations of the organism will happen."
This is not the first time that scientists noted Tre1's importance in germ cell navigation. Two research teams from Indiana University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology had previously made the link. However, says Andrew, questions remained about what happens inside germ cells to get cells to the right place once Tre1 activates.
It was already known that the Tre1 gene encodes a protein that spans the cell membrane multiple times and pokes out onto the cell's surface. It's a member of a large family of proteins called G protein-coupled receptors, which enable cells to communicate and respond to signals from other cells and light and odor cues. Nearly 35% of FDA approved medicines target G protein-coupled receptors, says Andrew.
To more precisely track the molecular events downstream of Tre1, Kim, a research associate and postdoctoral fellow at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, used tissue cultures of fruit fly cells to find the location of fluorescently tagged molecules that are potentially triggered by the activated Tre1 protein. In the tissue cultures and germ cells of living flies, Kim uncovered the downstream genetic pathway.
He found that Tre1 functions as the cell's helmsman, controlling steering of the cell. Tre1 activates the cell's steering and rudder components by spurring on a cascade of proteins and enzymes, including a phospho-inositol kinase, PI(4,5)P2, dPIP5K, dWIP and WASp.
At the end of the molecular cascade, a chain of actin proteins forms in a protrusion at the cell's leading edge to exert mechanical forces for movement.
The scientists also searched for the upstream signal that activates Tre1. They used a genetically engineered protein made by researchers at the University of California, San Francisco to track the location of a signaling protein called Hedgehog, which has previously been linked to germ cell migration, although its role in this process has been disputed.
In germ cells, Hedgehog signaling increases the membrane levels of a protein called Smoothened, which is found in the cells' leading edge protrusion where Tre1 is also found.
The scientists plan to continue studying the pathways surrounding Tre1 and connections between the proteins and enzymes involved in the pathway.
"A deeper understanding of how moving cells navigate and spread has the potential to provide more targets for interrupting the spread of cancer cells," says Andrew.
INFORMATION:
Funding for the research was provided by the National Institutes of Health (RO1DE013899, R35GM118177 and F31DE022233).
In addition to Andrew, Hanlon and Kim, other scientists who contributed to the research include Sunaina Vohra and Peter Devreotes of Johns Hopkins.
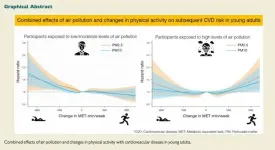
Physical activity is important in preventing heart and blood vessel disease in young people so long as they don't undertake very strenuous activity on days when air pollution levels are high, according to a nationwide study of nearly 1.5 million people published today (Tuesday) in the European Heart Journal [1].
Until now, little has been known about the trade-offs between the health benefits of physical activity taking place outdoors and the potentially harmful effects of air pollution. Previous research by the authors of the current study had investigated the question in middle-aged people at a single point in time, but this is the first time that it has been investigated in people aged between 20-39 years over a period of several years. In addition, the researchers wanted to ...
Scientists have identified three genes associated with an increased risk of developing cervical cancer.
The study, led by scientists from Imperial College London and published in the journal The Lancet Oncology, studied data from over 150,000 European women.
The research is one of the first studies to pinpoint genetic variants associated with an increased risk of cervical precancer and cancer.
The study team say the findings open avenues for identifying women at higher risk and monitoring their health more closely - particularly if genetic information is ...
Markers of the pandemic's impact - testing rates, positivity ratio (cases among total tests), case rates by overall population and deaths - are clustered in neighborhoods, with low-income and predominantly minority communities experiencing worse outcomes than wealthier and predominantly white neighborhoods. The findings, part of the first research to look at comprehensive neighborhood-level data from March through September 2020 from three large U.S. cities - Chicago, New York and Philadelphia - were published today in Annals of Internal Medicine by researchers from Drexel University's Dornsife School of Public Health.
The ...
March 29, 2021 - Acute kidney injury (AKI) occurred in nearly 20 percent of patients who underwent surgery with implantation of antibiotic-loaded "spacers" and intravenous (IV) antibiotics for the treatment of deep infections after total knee arthroplasty, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Patients with preexisting chronic kidney disease (CKD) are at particularly high risk of AKI, according to the new research by Matthew P. Abdel, MD, and colleagues of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
High doses of antibiotics in bone cement linked to higher ...
Paris, Nairobi, London, 29 March 2021 - Five major cooling suppliers are racing to net zero but they represent fewer than ten per cent of the 54 suppliers assessed in a new report, meaning the industry has a lot of work to do to catch up on climate action and reduce pollution from the sector, currently estimated at 7% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
With the world still falling short of meeting the Paris Agreement goals of holding global temperature rise this century to under 2 degrees C, and pursue 1.5 degrees C, action to reduce the climate impact of cooling will be essential.
According to the International Energy Agency, emissions from cooling are expected to double by 2030 and triple by 2100, driven by heat waves, population growth, urbanization, and a growing middle ...
A new study by Simon Fraser University's Faculty of Health Sciences researchers - published today in the American Journal of Epidemiology - found correlations between increased expressions of autistic-like behaviours in pre-school aged children to gestational exposure to select environmental toxicants, including metals, pesticides, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), phthalates, and bisphenol-A (BPA).
This population study measured the levels of 25 chemicals in blood and urine samples collected from 1,861 Canadian women during the first trimester of pregnancy. A follow up survey was conducted with 478 participants, using the Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS) ...
Heavy caseloads, job stress and biases can strain relations between parole and probation officers and their clients, upping offenders' likelihood of landing back behind bars.
On a more hopeful note, a new University of California, Berkeley, study suggests that nonjudgmental empathy training helps court-appointed supervision officers feel more emotionally connected to their clients and, arguably, better able to deter them from criminal backsliding.
The findings, published March 29 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, show, on average, a 13% decrease in recidivism among the clients of parole and probation officers who participated in the UC Berkeley empathy training experiment.
"If an officer received this empathic ...
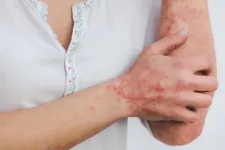
Psoriasis is a chronic disease that causes patients to develop patches of dry, scaly, and itchy skin. It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that it arises from a person's immune system inappropriately targeting that person's own healthy body parts. It is a deeply unpleasant condition, and patients commonly take various medications so that they can live their lives more comfortably.
Professor Min Chen of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and the Peking Union Medical College has conducted extensive research on psoriasis. "There are many patients with psoriasis who also have cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and coronary heart disease," she notes. The presence of such cardiovascular diseases is an important consideration ...
One of the biggest longitudinal research studies of its kind in the world led by The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) and the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) suggests that positive outcomes for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) are more common than previously thought.
ASD refers to a group of neurodevelopmental conditions resulting in challenges related to communication, social understanding and behaviour. One in 100 people may have ASD and although a person can be diagnosed at any time, ASD symptoms generally appear and are diagnosed in the first few years ...
PRINCETON--Slanted media outlets are often blamed for growing polarization, but new research points to another consequence of consuming partisan news: an erosion of trust in the media.
A team of researchers combined computational social science techniques and experimentation to study the long-term effects of online partisan media on political opinions and trust.
Internet users were asked to change their default browser homepages to either the Huffington Post, a left-leaning news site, or Fox News, a more conservative outlet, during the 2018 U.S. midterm elections. As participants went about their daily activities, they allowed the researchers to survey them multiple times ...