INFORMATION:
A paper describing these results appears in the most recent issue of the Journal of Geophysical Research. The authors are William Dunn (University College London, United Kingdom), Jan-Uwe Ness (University of Marseille, France), Laurent Lamy (Paris Observatory, France), Grant Tremblay (Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian), Graziella Branduardi-Raymont (University College London), Bradford Snios (CfA), Ralph Kraft (CfA), Z. Yao (Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing), Affelia Wibisono (University College London).
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science from Cambridge Massachusetts and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
First X-rays from Uranus discovered
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) Astronomers have detected X-rays from Uranus for the first time, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. This result may help scientists learn more about this enigmatic ice giant planet in our solar system.
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun and has two sets of rings around its equator. The planet, which has four times the diameter of Earth, rotates on its side, making it different from all other planets in the solar system. Since Voyager 2 was the only spacecraft to ever fly by Uranus, astronomers currently rely on telescopes much closer to Earth, like Chandra and the Hubble Space Telescope, to learn about this distant and cold planet that is made up almost entirely of hydrogen and helium.
In the new study, researchers used Chandra observations taken in Uranus in 2002 and then again in 2017. They saw a clear detection of X-rays from the first observation, just analyzed recently, and a possible flare of X-rays in those obtained fifteen years later. The main graphic shows a Chandra X-ray image of Uranus from 2002 (in pink) superimposed on an optical image from the Keck-I Telescope obtained in a separate study in 2004. The latter shows the planet at approximately the same orientation as it was during the 2002 Chandra observations.
What could cause Uranus to emit X-rays? The answer: mainly the Sun. Astronomers have observed that both Jupiter and Saturn scatter X-ray light given off by the Sun, similar to how Earth's atmosphere scatters the Sun's light. While the authors of the new Uranus study initially expected that most of the X-rays detected would also be from scattering, there are tantalizing hints that at least one other source of X-rays is present. If further observations confirm this, it could have intriguing implications for understanding Uranus.
One possibility is that the rings of Uranus are producing X-rays themselves, which is the case for Saturn's rings. Uranus is surrounded by charged particles such as electrons and protons in its nearby space environment. If these energetic particles collide with the rings, they could cause the rings to glow in X-rays. Another possibility is that at least some of the X-rays come from auroras on Uranus, a phenomenon that has previously been observed on this planet at other wavelengths.
On Earth, we can see colorful light shows in the sky called auroras, which happen when high-energy particles interact with the atmosphere. X-rays are emitted in Earth's auroras, produced by energetic electrons after they travel down the planet's magnetic field lines to its poles and are slowed down by the atmosphere. Jupiter has auroras, too. The X-rays from auroras on Jupiter come from two sources: electrons traveling down magnetic field lines, as on Earth, and positively charged atoms and molecules raining down at Jupiter's polar regions. However, scientists are less certain about what causes auroras on Uranus. Chandra's observations may help figure out this mystery.
Uranus is an especially interesting target for X-ray observations because of the unusual orientations of its spin axis and its magnetic field. While the rotation and magnetic field axes of the other planets of the solar system are almost perpendicular to the plane of their orbit, the rotation axis of Uranus is nearly parallel to its path around the Sun. Furthermore, while Uranus is tilted on its side, its magnetic field is tilted by a different amount, and offset from the planet's center. This may cause its auroras to be unusually complex and variable. Determining the sources of the X-rays from Uranus could help astronomers better understand how more exotic objects in space, such as growing black holes and neutron stars, emit X-rays.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
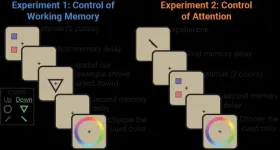
Attention and working memory: Two sides of the same neural coin?
2021-03-31
In 1890, psychologist William James described attention as the spotlight we shine not only on the world around us, but also on the contents of our minds. Most cognitive scientists since then have drawn a sharp distinction between what James termed "sensorial attention" and "intellectual attention," now usually called "attention" and "working memory," but James saw them as two varieties of the same mental process.
New research by Princeton neuroscientists suggests that James was on to something, finding that attention to the outside world and attention to our own thoughts are actually two sides of the same neural coin. What's more, they have observed the coin as it flips inside the brain.
A paper published in Nature on March 31 by END ...
Quantum material's subtle spin behavior proves theoretical predictions
2021-03-31
Using complementary computing calculations and neutron scattering techniques, researchers from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratories and the University of California, Berkeley, discovered the existence of an elusive type of spin dynamics in a quantum mechanical system.
The team successfully simulated and measured how magnetic particles called spins can exhibit a type of motion known as Kardar-Parisi-Zhang, or KPZ, in solid materials at various temperatures. Until now, scientists had not found evidence of this particular phenomenon outside of soft matter ...
Blacks, Latinos and Native Americans severely underrepresented in health workforce
2021-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2021) -- In 2019, Blacks, Latinos and Native Americans were severely underrepresented in the health care workforce, a trend that shows limited signs of improvement, according to a study published today by George Washington University researchers.
"Our findings suggest that Blacks, Latinos and other people of color have been left behind when it comes to the health professions," Edward Salsberg, senior research scientist and co-director of the Health Workforce Diversity Tracker project at the GW Fitzhugh Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity, said. The Fitzhugh Mullan Institute ...
How much are invasive species costing us?
2021-03-31
An invasive exotic species is one deliberately or unwittingly introduced by humans into a new habitat, where it becomes an environmental menace. In addition to the loss of biodiversity and other ecological impacts resulting from its presence, an invasive species can lead to economic losses in certain sectors, including agriculture, tourism, and public health. Though biological invasion is the second leading cause of species extinction, decision makers and the general public are still largely unaware of the issue.
After five years of study, the international research team* directed by scientists from the Écologie, Systématique et Évolution (CNRS ...
How comorbidities increase risks for COVID patients
2021-03-31
Comorbidities such as heart disease, respiratory disease, renal disease and cancer lead to an increased risk of death from Covid-19 according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) and the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital (NNUH).
At the start of the pandemic, there was concern that specific medications for high blood pressure could be linked with worse outcomes for Covid-19 patients.
Previous research from the UEA team showed this wasn't the case and that medications for high blood pressure could, in fact, improve Covid-19 survival rates and reduce the severity of infection.
New findings, published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Network Open, additionally show that it is comorbidities such as heart disease, respiratory ...
Mount Sinai study reveals genetic and cellular mechanisms of Crohn's disease
2021-03-31
Mount Sinai researchers have identified genetic and cellular mechanisms of Crohn's disease, providing new insights for future treatments that could offer a tailored approach to patients with the chronic inflammatory disease, according to a study published in END ...
Mice naturally engage in physical distancing, study finds
2021-03-31
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When someone is sick, it's natural to want to stay as far from them as possible. It turns out this is also true for mice, according to an MIT study that also identified the brain circuit responsible for this distancing behavior.
In a study that explores how otherwise powerful instincts can be overridden in some situations, researchers from MIT's Picower Institute for Learning and Memory found that when male mice encountered a female mouse showing signs of illness, the males interacted very little with the females and made no attempts to mate with them as they normally would. The researchers also showed that this behavior is controlled by a circuit in the amygdala, which detects distinctive odors from sick animals and triggers a warning signal ...
Changing hypertension definition may identify more high-risk pregnancies
2021-03-31
NEW YORK, NY (March 31, 2021)--A shift in the definition of high blood pressure may help identify more women who are at risk of developing life-threatening complications during pregnancy and delivery, suggests a new study from Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Under the stricter definition, more than 50,000 additional women each year in the United States could become eligible for treatment with aspirin in pregnancy, which lowers the risk of developing preeclampsia, a sudden increase in blood pressure that can lead to stroke, seizures, hemorrhage, and death.
The ...
Dermatologist perceptions of teledermatology implementation, future use after COVID-19
2021-03-31
What The Study Did: This study sought to assess dermatologists' perceptions of and experiences with teledermatology in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and new regulatory changes including parity in reimbursements between video and in-person visits.
Authors: Jules B. Lipoff, M.D., of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0195)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Association between renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19
2021-03-31
What The Study Did: Researchers compared mortality and severe adverse events in this systematic review and meta-analysis of 52 studies that evaluated clinical outcomes among nearly 102,000 patients with COVID-19 who did and didn't receive angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Authors: Vassilios S. Vassiliou, M.B.B.S., Ph.D., of the University of East Anglia in Norwich, United Kingdom is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3694)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...