Vitamin A for nerve cells
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) Neuroscientists agree that a person's brain is constantly changing, rewiring itself and adapting to environmental stimuli. This is how humans learn new things and create memories. This adaptability and malleability is called plasticity. "Physicians have long suspected that remodeling processes also take place in humans at the contact points between nerve cells, i.e. directly at the synapses. Until now, however, such a coordinated adaptation of structure and function could only be demonstrated in animal experiments," says Prof. Dr. Andreas Vlachos from the Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology at the University of Freiburg. But now Vlachos, together with Prof. Dr. Jürgen Beck, head of the Department of Neurosurgery at the University Medical Center Freiburg, has provided experimental evidence for synaptic plasticity in humans. In addition to Vlachos and Beck, the research team consists of Dr. Maximilian Lenz, Pia Kruse and Amelie Eichler from the University of Freiburg, Dr. Jakob Strähle from the University Medical Center Freiburg and colleagues from Goethe University Frankfurt. The results were presented in the scientific journal eLife.
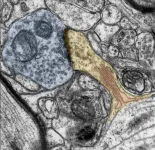
In the experiments, the team investigated whether so-called dendritic spines change when exposed to a vitamin A derivative called retionic acid. Dendritic spines are the parts of the synapse that receive, process and transmit signals during communication between neurons. As such, they play a crucial role in brain plasticity and are constantly adapting to everyday experience. For example, learning can change the number and shape of dendritic spines. However, a transformation in the number or shape of the spines is also found in diseases such as depression or dementia.
The research shows that retinoic acid not only increases the size of dendritic spines, but also strengthens their ability to transmit signals between neurons. "We have concluded from our results that retinoic acids are important messengers for synaptic plasticity in the human brain. Thus, this finding contributes to the identification of key mechanisms of synaptic plasticity in the human brain and could support the development of new therapeutic strategies for brain diseases, such as depression," says Vlachos.
To experimentally demonstrate that synaptic plasticity also exists in humans, the researchers use tiny samples of human cerebral cortex, which must be compulsorily removed during neurosurgical procedures for therapeutic reasons. The removed brain tissue was then treated with retinoic acid before functional and structural properties of neurons were analyzed using electrophysiological and microscopic techniques.
INFORMATION:
A popular scientific summary of the results is also published on the eLife Journal website.
Popular scientific summary:
https://elifesciences.org/digests/63026/vitamins-for-your-neurons
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
Astronomers have detected X-rays from Uranus for the first time, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. This result may help scientists learn more about this enigmatic ice giant planet in our solar system.
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun and has two sets of rings around its equator. The planet, which has four times the diameter of Earth, rotates on its side, making it different from all other planets in the solar system. Since Voyager 2 was the only spacecraft to ever fly by Uranus, astronomers currently rely on telescopes much closer to Earth, like Chandra and the Hubble Space Telescope, to learn about this distant and cold planet that is made up almost entirely of hydrogen and helium.
In the new study, researchers used Chandra observations ...
2021-03-31
In 1890, psychologist William James described attention as the spotlight we shine not only on the world around us, but also on the contents of our minds. Most cognitive scientists since then have drawn a sharp distinction between what James termed "sensorial attention" and "intellectual attention," now usually called "attention" and "working memory," but James saw them as two varieties of the same mental process.
New research by Princeton neuroscientists suggests that James was on to something, finding that attention to the outside world and attention to our own thoughts are actually two sides of the same neural coin. What's more, they have observed the coin as it flips inside the brain.
A paper published in Nature on March 31 by END ...
2021-03-31
Using complementary computing calculations and neutron scattering techniques, researchers from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge and Lawrence Berkeley national laboratories and the University of California, Berkeley, discovered the existence of an elusive type of spin dynamics in a quantum mechanical system.
The team successfully simulated and measured how magnetic particles called spins can exhibit a type of motion known as Kardar-Parisi-Zhang, or KPZ, in solid materials at various temperatures. Until now, scientists had not found evidence of this particular phenomenon outside of soft matter ...
2021-03-31
WASHINGTON (March 31, 2021) -- In 2019, Blacks, Latinos and Native Americans were severely underrepresented in the health care workforce, a trend that shows limited signs of improvement, according to a study published today by George Washington University researchers.
"Our findings suggest that Blacks, Latinos and other people of color have been left behind when it comes to the health professions," Edward Salsberg, senior research scientist and co-director of the Health Workforce Diversity Tracker project at the GW Fitzhugh Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity, said. The Fitzhugh Mullan Institute ...
2021-03-31
An invasive exotic species is one deliberately or unwittingly introduced by humans into a new habitat, where it becomes an environmental menace. In addition to the loss of biodiversity and other ecological impacts resulting from its presence, an invasive species can lead to economic losses in certain sectors, including agriculture, tourism, and public health. Though biological invasion is the second leading cause of species extinction, decision makers and the general public are still largely unaware of the issue.
After five years of study, the international research team* directed by scientists from the Écologie, Systématique et Évolution (CNRS ...
2021-03-31
Comorbidities such as heart disease, respiratory disease, renal disease and cancer lead to an increased risk of death from Covid-19 according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA) and the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital (NNUH).
At the start of the pandemic, there was concern that specific medications for high blood pressure could be linked with worse outcomes for Covid-19 patients.
Previous research from the UEA team showed this wasn't the case and that medications for high blood pressure could, in fact, improve Covid-19 survival rates and reduce the severity of infection.
New findings, published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Network Open, additionally show that it is comorbidities such as heart disease, respiratory ...
2021-03-31
Mount Sinai researchers have identified genetic and cellular mechanisms of Crohn's disease, providing new insights for future treatments that could offer a tailored approach to patients with the chronic inflammatory disease, according to a study published in END ...
2021-03-31
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When someone is sick, it's natural to want to stay as far from them as possible. It turns out this is also true for mice, according to an MIT study that also identified the brain circuit responsible for this distancing behavior.
In a study that explores how otherwise powerful instincts can be overridden in some situations, researchers from MIT's Picower Institute for Learning and Memory found that when male mice encountered a female mouse showing signs of illness, the males interacted very little with the females and made no attempts to mate with them as they normally would. The researchers also showed that this behavior is controlled by a circuit in the amygdala, which detects distinctive odors from sick animals and triggers a warning signal ...
2021-03-31
NEW YORK, NY (March 31, 2021)--A shift in the definition of high blood pressure may help identify more women who are at risk of developing life-threatening complications during pregnancy and delivery, suggests a new study from Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons.
Under the stricter definition, more than 50,000 additional women each year in the United States could become eligible for treatment with aspirin in pregnancy, which lowers the risk of developing preeclampsia, a sudden increase in blood pressure that can lead to stroke, seizures, hemorrhage, and death.
The ...
2021-03-31
What The Study Did: This study sought to assess dermatologists' perceptions of and experiences with teledermatology in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic and new regulatory changes including parity in reimbursements between video and in-person visits.
Authors: Jules B. Lipoff, M.D., of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.0195)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Vitamin A for nerve cells