(Press-News.org) DETROIT (March 31, 2021) - In a study that looked at racial differences in outcomes of COVID-19 patients admitted to the intensive care unit, researchers at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit found that patients of color had a lower 28-day mortality than white patients.
Race, however, was not a factor in overall hospital mortality, length of stay in the ICU or in the rate of patients placed on mechanical ventilation, researchers said.
The findings, published in Critical Care Medicine, are believed to be one of the first in the United States to study racial differences and outcomes specific to patients hospitalized in the ICU with COVID-19.
Since the start of the pandemic, data have shown that Black and Hispanic populations have higher rates of COVID-19 infections, hospitalizations and mortality. The Henry Ford study found just the opposite.
"What we wanted to look at was once patients are in the ICU, does that same racial disproportion occur. And the answer is no," said Michael Lazar, M.D., a Henry Ford pulmonology and critical care medicine physician and the study's lead author. "The care we deliver is essentially the same and race makes no difference."
Researchers theorized that the 28-day mortality in patients of color could be easily explained: The deaths among patients of color were delayed. Seven of the nine patients who died in the hospital after 28 days were patients of color.
Still, they said their findings reflect more about the level of care provided in the ICU than racial differences.
"What we do in the intensive care is driven by protocol and everyone is approached similarly," said Jeffrey Jennings, M.D., a Henry Ford pulmonology and critical care medicine physician and the study's senior author.
Detroit was one of the cities hardest hit in the first surge of the pandemic. Henry Ford Hospital is the largest of the five acute-care hospitals in the Henry Ford Health System. To date, the health system has treated more than 44,000 patients with COVID-19 and more than 11,000 patients with COVID-19 have been hospitalized.
For the retrospective study, researchers evaluated the electronic medical records of 365 COVID-19 patients 18 and older who were admitted to the ICU between March 13, 2020 and July 31, 2020. The patients were divided into two groups: White and people of color, which included Black, Asian, Hispanic/Latino and Arab populations. Of the 365 patients, 219 were Black, 129 were White, eight were Hispanic/Latino, seven were Arab and two were Asian.
In other demographics, 205 patients were men and 160 women. The people of color group were slightly younger, 62.8 years, compared to the White group, 67.1 years. Co-morbidities ranged from COPD and asthma to hypertension, diabetes and coronary artery disease.
Other key highlights in the study:
Overall mortality in the two groups was 50%
Nearly 75% required mechanical ventilation
While most patients were treated with steroids early in their hospitalization, it was not a significant predictor of mortality
INFORMATION:
About Henry Ford Health System
Founded in 1915 by Henry Ford himself, Henry Ford Health System is a non-profit, integrated health system committed to improving people's lives through excellence in the science and art of healthcare and healing. Henry Ford Health System includes Henry Ford Medical Group, with more than 1,900 physicians and researchers practicing in more than 50 specialties at locations throughout Southeast and Central Michigan. Acute care hospitals include Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, MI and Henry Ford Allegiance Health in Jackson, MI - both Magnet® hospitals; Henry Ford Macomb Hospital; Henry Ford West Bloomfield Hospital; and Henry Ford Wyandotte Hospital.
The largest of these is Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit, a quaternary care research and teaching hospital and Level 1 Trauma Center recognized for clinical excellence in cardiology, cardiovascular surgery, neurology, neurosurgery, and multi-organ transplants. The health system also provides comprehensive, best-in-class care for cancer at the Brigitte Harris Cancer Pavilion, and orthopedics and sports medicine at the William Clay Ford Center for Athletic Medicine - both in Detroit.
As one of the nation's leading academic medical centers, Henry Ford Health System annually trains more than 3,000 medical students, residents, and fellows in more than 50 accredited programs, and has trained nearly 40% of the state's physicians. Our dedication to education and research is supported by nearly $100 million in annual grants from the National Institutes of Health and other public and private foundations.
Henry Ford's not-for-profit health plan, Health Alliance Plan (HAP), provides health coverage for more than 540,000 people.
Henry Ford Health System employs more than 33,000 people, including more than 1,600 physicians, more than 6,600 nurses and 5,000 allied health professionals.
MEDIA CONTACT: David Olejarz / David.Olejarz@hfhs.org / 313-303-0606
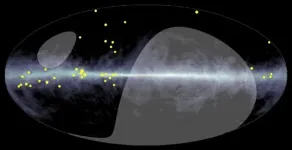
An enormous telescope complex in Tibet has captured the first evidence of ultrahigh-energy gamma rays spread across the Milky Way. The findings offer proof that undetected starry accelerators churn out cosmic rays, which have floated around our galaxy for millions of years. The research is to be published in the journal Physical Review Letters on Monday, April 5.
"We found 23 ultrahigh-energy cosmic gamma rays along the Milky Way," said Kazumasa Kawata, a coauthor from the University of Tokyo. "The highest energy among them amounts to a world record: nearly one petaelectron volt."
That's three ...
DURHAM, N.H.-- As the Biden administration announces a plan to expand the development of offshore wind energy development (OWD) along the East Coast, research from the University of New Hampshire shows significant support from an unlikely group, coastal recreation visitors. From boat enthusiasts to anglers, researchers found surprisingly widespread support with close to 77% of coastal recreation visitors supporting potential OWD along the N.H. Seacoast.
"This study takes a closer look at the lingering assumption that offshore wind in the United States might hurt coastal recreation ...
The first imaging of substantial freshwater plumes west of Hawai'i Island may help water planners to optimize sustainable yields and aquifer storage calculations. University of Hawai'i at Mānoa researchers demonstrated a new method to detect freshwater plumes between the seafloor and ocean surface in a study recently published in Geophysical Research Letters.
The research, supported by the Hawai'i EPSCoR 'Ike Wai project, is the first to demonstrate that surface-towed marine controlled-source electromagnetic (CSEM) imaging can be used to map oceanic freshwater plumes in high-resolution. It is an extension of the groundbreaking discovery of freshwater beneath the seafloor in 2020. Both are important findings in a world facing climate change, where ...
LOWELL, Mass. - Researchers studying mercury gas in the atmosphere with the aim of reducing the pollutant worldwide have determined a vast amount of the toxic element is absorbed by plants, leading it to deposit into soils.
Hundreds of tons of mercury each year are emitted into the atmosphere as a gas by burning coal, mining and other industrial and natural processes. These emissions are absorbed by plants in a process similar to how they take up carbon dioxide. When the plants shed leaves or die, the mercury is transferred to soils where large amounts also make their way into watersheds, threatening wildlife and people who eat contaminated fish.
Exposure to high levels of mercury over long ...
BRAZZAVILLE, Republic of Congo (March 31, 2021) - Researchers with the Wildlife Conservation Society's (WCS) Congo Program and the Nouabalé-Ndoki Foundation found that female putty-nosed monkeys (Cercopithecus nictitans) use males as "hired guns" to defend from predators such as leopards.
Publishing their results in the journal Royal Society Open Science, the team discovered that female monkeys use alarm calls to recruit males to defend them from predators. The researchers conducted the study among 19 different groups of wild putty-nosed monkeys, a type of forest guenon, in Mbeli Bai, a study area within the forests in Nouabalé-Ndoki National Park, Northern Republic of Congo.
The results promote the idea that females' general alarm requires males to assess the nature ...
(Denver, Colo., -- March 31, 2021)- A new Molecular Database Project initiated by the International Association for the Study of Lung (IASLC) will accelerate the understanding of lung cancer biology, clinical care and care delivery on a global scale and will improve the prognosis and optimal treatment of lung cancer across time and space, according to an editorial in the Journal of Thoracic Oncology, an official journal of the IASLC. The editorial can be viewed here: https://www.jto.org/article/S1556-0864(21)01781-0/fulltext.
In the editorial, the IASLC Staging and Prognostic Factors Committee's Molecular Sub-Committee, and committee members, emphasized that there is great opportunity, with the emergence of molecular biomarkers of disease behavior, to improve ...
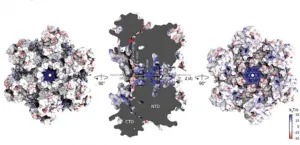
Viruses lurk in the grey area between the living and the nonliving, according to scientists. Like living things, they replicate but they don't do it on their own. The HIV-1 virus, like all viruses, needs to hijack a host cell through infection in order to make copies of itself.
Supercomputer simulations supported by the National Science Foundation-funded Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment (XSEDE) have helped uncover the mechanism for how the HIV-1 virus imports into its core the nucleotides it needs to fuel DNA synthesis, a key step in its replication. It's the first example ...
The qubit is the building block of quantum computing, analogous to the bit in classical computers. To perform error-free calculations, quantum computers of the future are likely to need at least millions of qubits. The latest study, published in the journal PRX Quantum, suggests that these computers could be made with industrial-grade silicon chips using existing manufacturing processes, instead of adopting new manufacturing processes or even newly discovered particles.
For the study, researchers were able to isolate and measure the quantum state of a single electron (the qubit) in a silicon transistor manufactured using a 'CMOS' technology similar to that used to make chips in computer processors.
Furthermore, the spin of the electron was found to remain stable for a period of up ...
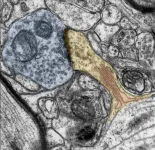
Neuroscientists agree that a person's brain is constantly changing, rewiring itself and adapting to environmental stimuli. This is how humans learn new things and create memories. This adaptability and malleability is called plasticity. "Physicians have long suspected that remodeling processes also take place in humans at the contact points between nerve cells, i.e. directly at the synapses. Until now, however, such a coordinated adaptation of structure and function could only be demonstrated in animal experiments," says Prof. Dr. Andreas Vlachos from the Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology at the University of Freiburg. But now Vlachos, together with Prof. Dr. Jürgen Beck, head of the Department of Neurosurgery at the University Medical Center Freiburg, has provided experimental evidence ...
Astronomers have detected X-rays from Uranus for the first time, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. This result may help scientists learn more about this enigmatic ice giant planet in our solar system.
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun and has two sets of rings around its equator. The planet, which has four times the diameter of Earth, rotates on its side, making it different from all other planets in the solar system. Since Voyager 2 was the only spacecraft to ever fly by Uranus, astronomers currently rely on telescopes much closer to Earth, like Chandra and the Hubble Space Telescope, to learn about this distant and cold planet that is made up almost entirely of hydrogen and helium.
In the new study, researchers used Chandra observations ...