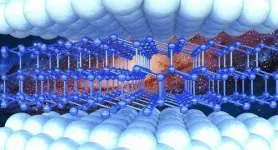
A Skoltech method helps model the behavior of 2D materials under pressure
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) Scientists from the Skoltech Center for Energy Science and Technology (CEST) have developed a method for modeling the behavior of 2D materials under pressure. The research will help create pressure sensors based on silicene or other 2D materials. The paper was published in the ACS Nano journal.
Silicene, which is regarded as the silicon analog of graphene, is a two-dimensional allotrope of silicon. In its normal state, bulk silicon is a semiconductor with a diamond crystal type structure. As it thins down to one or several layers, its properties change dramatically. However, it has not yet been possible to study the change in the electronic properties of 2D materials at high pressure.
Scientists from Russia, Italy, the United States, and Belgium have developed a theoretical research method relying on quantum chemistry to study the electronic properties of 2D materials under pressure using silicene as an example. In contrast to carbon, which is stable in both 3D and 2D states, silicene is metastable and easy to interact with the environment.
"Silicon is a semiconductor in its bulk state and a metal in the 2D state. The properties of monolayer and multilayered silicene are extensively studied theoretically. Silicene is corrugated rather than flat due to the interactions between the neighboring silicon atoms. An increase in pressure should flatten silicene and change its properties, but this effect cannot yet been investigated experimentally," explains Skoltech research scientist Christian Tantardini.
In most cases, experimental tools used to apply pressure to the material along the axis normal to its plane simultaneously produce compression in the in-plane directions of 2D material. Thus, the resulting measurements would hardly be accurate, so right now modeling appears to be the only plausible approach.
"In our case, a new theoretical approach was the only solution. As pressure is applied only along one direction, we simulate the compression of our material and try to figure out what is the reason for the changes in the electronic structure, arrangement of silicon atoms and their hybridization under different pressures, and why the layers flatten," Skoltech Senior Research Scientist Alexander Kvashnin comments.
Accurate prediction of the behavior of silicene or other 2D materials under pressure would make silicene a promising candidate for pressure sensors. When placed inside the sensor, silicene could help determine pressure based on the material's response to compression. This kind of sensor could be used, for instance, in drilling rigs with a high requirement for pressure control to increase the drilling force without damaging the equipment.
"We used silicene in our modeling study to test the method which could also work for other 2D materials, including more stable ones that are already manufactured and used extensively, at zero pressure," says Xavier Gonze, a visiting professor at Skoltech and a professor at the Université Catholique de Louvain (UCLouvain) in Belgium.
INFORMATION:
Skoltech is a private international university located in Russia. Established in 2011 in collaboration with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Skoltech is cultivating a new generation of leaders in the fields of science, technology and business, is conducting research in breakthrough fields, and is promoting technological innovation with the goal of solving critical problems that face Russia and the world. Skoltech is focusing on six priority areas: data science and artificial intelligence, life sciences, advanced materials and modern design methods, energy efficiency, photonics and quantum technologies, and advanced research. Web: https://www.skoltech.ru/.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
In a longitudinal study published earlier this month in the Journal of the American Dental Association, researchers analyzed untreated decay in a cohort of nearly 7,000 children enrolled in the ForsythKids preventive dentistry program. Over the course of six years, the percentage of children with untreated cavities in the program decreased from 39 to 19 percent, suggesting that school-based prevention programs are effective in combating childhood dental disease.
Tooth decay is the most common chronic early childhood disease in the United States. More than half of children aged 6-8 years old have had a cavity, and kids from low-income families ...
2021-03-31
High cholesterol is the most commonly understood cause of atherosclerosis, a hardening of the arteries that raises the risk of heart attack and stroke. But now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a gene that likely plays a causal role in coronary artery disease independent of cholesterol levels. The gene also likely has roles in related cardiovascular diseases, including high blood pressure and diabetes.
The study appears March 24 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Studying mice and genetic data from people, the researchers found ...
2021-03-31
LA JOLLA--(March 31, 2021) Clinicians using a new viral screening test can not only diagnose COVID-19 in a matter of minutes with a portable, pocket-sized machine, but can also simultaneously test for other viruses--like influenza--that might be mistaken for the coronavirus. At the same time, they can sequence the virus, providing valuable information on the spread of COVID-19 mutations and variants. The new test, dubbed NIRVANA, was described online today by a multi-institution team of scientists in the journal Med.
"This is a virus detection and surveillance method that doesn't require an expensive infrastructure like other approaches," says Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, co-corresponding author and a professor in Salk's Gene Expression ...
2021-03-31
AURORA, Colo. (March 31, 2021) - A new study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry finds that patients with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) as well as other psychiatric comorbidities, such as autism spectrum or tic disorders, may respond well to Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS).
DBS is a minimally invasive neurosurgical procedure that uses coordinates to target certain areas of the brain, implanting electrodes that can help regulate abnormal brain activity. DBS procedures are rare for OCD in the United States; only a couple hundred patients have received this treatment for OCD management since its FDA approval ...
2021-03-31
An aggressive type of brain cancer, glioblastoma has no cure. Patients survive an average of 15 months after diagnosis, with fewer than 10% of patients surviving longer than five years. While researchers are investigating potential new therapies via ongoing clinical trials, a new study from Washington University in St. Louis suggests that a minor adjustment to the current standard treatment -- giving chemotherapy in the morning rather than the evening -- could add a few months to patients' survival.
The study appears online in the journal Neuro-Oncology Advances.
Average overall survival ...
2021-03-31
AURORA, Colo. (March 30, 2021 - Researchers at the University of Colorado College of Nursing have found that nearly one-quarter of graduate nursing students have reported elevated levels of stress, anxiety and depression, compounded in the past year by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Study findings, published recently in END ...
2021-03-31
A new invention that uses sunlight to drive water purification could help solve the problem of providing clean water off the grid.
The device resembles a large sponge that soaks up water but leaves contaminants - like lead, oil and pathogens - behind. To collect the purified water from the sponge, one simply places it in sunlight. The researchers described the device in a paper published this week in the journal Advanced Materials.
The inspiration for the device came from the pufferfish, a species that takes in water to swell its body when threatened, and then releases water when danger passes, said the device's co-inventor END ...
2021-03-31
When it comes to powering mobile robots, batteries present a problematic paradox: the more energy they contain, the more they weigh, and thus the more energy the robot needs to move. Energy harvesters, like solar panels, might work for some applications, but they don't deliver power quickly or consistently enough for sustained travel.
James Pikul, assistant professor in Penn Engineering's Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, is developing robot-powering technology that has the best of both worlds. His environmentally controlled voltage source, or ECVS, works like a battery, in that the energy is produced by repeatedly breaking ...
2021-03-31
In looking at the broader impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health and wellbeing, public health experts are examining screening rates for cancer. A new study looking at U.S. mammography screening rates during the first five months of the pandemic found both a strong rebound in breast cancer screening rates and a concerning cumulative deficit in mammograms due to missed appointments, as well as uncovering disparities when looking at screening according to race.
The study was released this week in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Conducted by investigators from the Breast Cancer Surveillance Coalition (BCSC), a federally-funded, national network of breast imaging registries, the study sought to quantify the impact of the COVID-19 ...
2021-03-31
Denver, CO, March 31, 2020 - Children with Down syndrome are 20-times more likely to develop acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and 150-times more likely to develop acute myeloid leukemia (AML) compared to their typical peers. According to a new study by researchers at the Linda Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome, the reason could be that children with Down syndrome are more likely to present with clonal hematopoiesis (CH), a process in which a blood stem cell acquires a genetic mutation that promotes replication.
The findings, published online by Blood Advances, add to a growing body of evidence, much of which has been established ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A Skoltech method helps model the behavior of 2D materials under pressure