National study examines US mammography screening rates during COVID-19 pandemic
Despite a strong rebound in mammography volume, missed mammograms remain an issue
2021-03-31
(Press-News.org) In looking at the broader impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health and wellbeing, public health experts are examining screening rates for cancer. A new study looking at U.S. mammography screening rates during the first five months of the pandemic found both a strong rebound in breast cancer screening rates and a concerning cumulative deficit in mammograms due to missed appointments, as well as uncovering disparities when looking at screening according to race.
The study was released this week in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Conducted by investigators from the Breast Cancer Surveillance Coalition (BCSC), a federally-funded, national network of breast imaging registries, the study sought to quantify the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on both breast cancer screening and diagnostic mammography services in the U.S. Results suggest that, despite huge declines in the early months of the pandemic, mammography volumes rebounded strongly in summer 2020, as healthcare facilities adapted new protocols to ensure staff and patient safety.
In April 2020, screening mammography utilization was only 1% of expected volume based on comparative historical data. However, by July 2020, rates had rebounded to approximately 90% of pre-pandemic volume. Similar results were observed for diagnostic breast imaging, as opposed to screening imaging, with volumes rebounding to 100% by July 2020. However, researchers note that a substantial cumulative deficit in mammography screening remains, due to missed exam appointments from March through May 2020, and in an effort to reduce that deficit, screening rates will need to be above pre-pandemic levels.
The researchers found that trends in mammography screening were similar by age and risk factors, but identified disparities by race, with the rebound in mammography volume being lower among Hispanic and Asian women.
Reductions in screening and diagnostic imaging rates could lead to delays in diagnosis that cause increased morbidity and mortality due to breast cancer. The BCSC emphasizes that increased attention is needed to better understand specific barriers to healthcare utilization during the pandemic and to develop interventions to overcome these barriers.
Lead author and UVM Cancer Center researcher Brian Sprague, PhD, associate professor of surgery at the University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, notes that further BCSC research is ongoing to understand the impact of reduced mammography utilization during the pandemic on breast cancer detection and outcomes. "This national snapshot is important to help us focus research, outreach and intervention to close gaps that were perhaps created or made worse by the pandemic," said Sprague.
INFORMATION:
The BCSC research team included researchers from: University of Vermont Cancer Center and University of Vermont Larner College of Medicine, Burlington, VT; University of Washington and Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Seattle, WA; University of California Davis, Davis, CA; Advocate Caldwell Breast Center, Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, IL; Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, Seattle, WA; Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice and Norris Cotton Cancer Center, Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Lebanon, NH; University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL; Carbone Cancer Center, School of Medicine and Public Health, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI; Harvard Medical School and Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, MA; University of California, San Francisco, CA; Department of Veterans Affairs, University of California, San Francisco, CA
More about the BCSC: https://www.bcsc-research.org/
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-31
Denver, CO, March 31, 2020 - Children with Down syndrome are 20-times more likely to develop acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and 150-times more likely to develop acute myeloid leukemia (AML) compared to their typical peers. According to a new study by researchers at the Linda Crnic Institute for Down Syndrome, the reason could be that children with Down syndrome are more likely to present with clonal hematopoiesis (CH), a process in which a blood stem cell acquires a genetic mutation that promotes replication.
The findings, published online by Blood Advances, add to a growing body of evidence, much of which has been established ...
2021-03-31
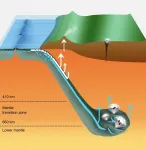
Washington, DC-- Diamonds that formed deep in the Earth's mantle contain evidence of chemical reactions that occurred on the seafloor. Probing these gems can help geoscientists understand how material is exchanged between the planet's surface and its depths.
New work published in Science Advances confirms that serpentinite--a rock that forms from peridotite, the main rock type in Earth's mantle, when water penetrates cracks in the ocean floor--can carry surface water as far as 700 kilometers deep by plate tectonic processes.
"Nearly all tectonic plates that make up the seafloor eventually bend and slide down into ...
2021-03-31
PITTSBURGH --31 March 2021 - A detailed examination of more than 10,000 medical records at maternity clinics and hospitals in urban Malawi, South Africa, Uganda and Zimbabwe has yielded important insight about pregnancy and neonatal outcomes in these communities as well as the frequency with which different complications occur. The findings, which were published in PLOS ONE, include data not often available or reported in much of eastern and southern Africa.
The medical chart review was undertaken by researchers from the National Institutes of Health-funded Microbicide Trials Network ...
2021-03-31
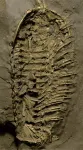
A new study has found the first evidence of sophisticated breathing organs in 450-million-year-old sea creatures. Contrary to previous thought, trilobites were leg breathers, with structures resembling gills hanging off their thighs.
Trilobites were a group of marine animals with half-moon-like heads that resembled horseshoe crabs, and they were wildly successful in terms of evolution. Though they are now extinct, they survived for more than 250 million years -- longer than the dinosaurs.
Thanks to new technologies and an extremely rare set of fossils, scientists from UC Riverside can now show that trilobites breathed oxygen and explain how ...
2021-03-31
March 31, 2021 - The United States is facing a persistent and worsening shortage of physicians specializing in preventive medicine, reports a study in the Journal of Public Health Management and Practice. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"The number of preventive medicine physicians is not likely to match population needs in the United States in the near term and beyond," according to the new research by Thomas Ricketts, Ph.D., MPH, and colleagues of University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. The study appears ...
2021-03-31
DETROIT (March 31, 2021) - In a study that looked at racial differences in outcomes of COVID-19 patients admitted to the intensive care unit, researchers at Henry Ford Hospital in Detroit found that patients of color had a lower 28-day mortality than white patients.
Race, however, was not a factor in overall hospital mortality, length of stay in the ICU or in the rate of patients placed on mechanical ventilation, researchers said.
The findings, published in Critical Care Medicine, are believed to be one of the first in the United States to study racial differences and outcomes specific to patients hospitalized ...
2021-03-31
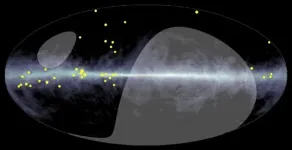
An enormous telescope complex in Tibet has captured the first evidence of ultrahigh-energy gamma rays spread across the Milky Way. The findings offer proof that undetected starry accelerators churn out cosmic rays, which have floated around our galaxy for millions of years. The research is to be published in the journal Physical Review Letters on Monday, April 5.
"We found 23 ultrahigh-energy cosmic gamma rays along the Milky Way," said Kazumasa Kawata, a coauthor from the University of Tokyo. "The highest energy among them amounts to a world record: nearly one petaelectron volt."
That's three ...
2021-03-31
DURHAM, N.H.-- As the Biden administration announces a plan to expand the development of offshore wind energy development (OWD) along the East Coast, research from the University of New Hampshire shows significant support from an unlikely group, coastal recreation visitors. From boat enthusiasts to anglers, researchers found surprisingly widespread support with close to 77% of coastal recreation visitors supporting potential OWD along the N.H. Seacoast.
"This study takes a closer look at the lingering assumption that offshore wind in the United States might hurt coastal recreation ...
2021-03-31
The first imaging of substantial freshwater plumes west of Hawai'i Island may help water planners to optimize sustainable yields and aquifer storage calculations. University of Hawai'i at Mānoa researchers demonstrated a new method to detect freshwater plumes between the seafloor and ocean surface in a study recently published in Geophysical Research Letters.
The research, supported by the Hawai'i EPSCoR 'Ike Wai project, is the first to demonstrate that surface-towed marine controlled-source electromagnetic (CSEM) imaging can be used to map oceanic freshwater plumes in high-resolution. It is an extension of the groundbreaking discovery of freshwater beneath the seafloor in 2020. Both are important findings in a world facing climate change, where ...
2021-03-31
LOWELL, Mass. - Researchers studying mercury gas in the atmosphere with the aim of reducing the pollutant worldwide have determined a vast amount of the toxic element is absorbed by plants, leading it to deposit into soils.
Hundreds of tons of mercury each year are emitted into the atmosphere as a gas by burning coal, mining and other industrial and natural processes. These emissions are absorbed by plants in a process similar to how they take up carbon dioxide. When the plants shed leaves or die, the mercury is transferred to soils where large amounts also make their way into watersheds, threatening wildlife and people who eat contaminated fish.
Exposure to high levels of mercury over long ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] National study examines US mammography screening rates during COVID-19 pandemic
Despite a strong rebound in mammography volume, missed mammograms remain an issue