(Press-News.org) For many parents, the COVID-19 pandemic has made life's everyday juggling act--managing work, school, extracurricular, and household responsibilities--much, much harder. And according to a new study led by Penn sociologists, those extra burdens have fallen disproportionately on mothers.
The research, shared in the April issue of the journal Gender and Society, investigated how shifts in work and school that arose due to the pandemic triggered changes in the division of labor in families. Using data on two-parent households from a nationwide survey conducted in April 2020, the researchers found that gender disparities in unpaid labor were most apparent when a mother was the only parent working from home, or when neither parent was able to work remotely.
"It turns out that when the mother is working remotely and her partner isn't, she ends up taking on a ton more responsibilities," says Jerry Jacobs, a sociology professor in Penn's School of Arts & Sciences and one of the paper's authors. "When a father is working remotely and his partner isn't, somehow he doesn't take on as much extra work. This seems to be a deeply gendered issue."
As the pandemic has worn on, the toll on women has been hard to ignore. Each month, hundreds of thousands of women lost their jobs or dropped out of the workforce to meet new demands at home.
Yet remote work also seemed to open the possibility of greater equity between the genders in domestic responsibility, as two parents would be at home and accessible.
To tease out the effects of a shift to remote work on domestic labor during the pandemic, Jacobs, Penn doctoral student Allison Dunatchik, and colleagues turned to data from a New York Times survey, conducted by marketing research firm Morning Consult. Of 2,200 respondents, 478 were partnered parents, and 151 were single parents.
While the gender of each survey respondent's partner was unknown, the gender of the respondents themselves played a key role in how the pandemic affected their domestic responsibilities, which, with children largely at home, increased across the board.
Families where both partners worked remotely had the most egalitarian split of household and parenting duties, the researchers found. Both mothers and fathers reported similar increases in housework and childcare responsibilities, as well as in the pressure they felt about managing their children's schooling. Yet even this best-case-scenario was imbued with gender disparity, as pre-pandemic disparities endured. Mothers working remotely whose partners were also were more than twice as likely as fathers to report being the partner primarily responsible for housework and child care.
When only one parent worked remotely and the other worked out of the home, the gender disparity in domestic labor was far more evident. Mothers who worked from home essentially absorbed the extra labor, while fathers who worked remotely reported less uptake of the extra housework and child care than either mothers working from home alone or fathers who worked at home along with their partner.
"The disparity, how this affected remote dads versus remote moms, was just so stark," says Jacobs. "Even for a hard-boiled, data-driven sociologist like me, I was surprised."
"I had a similar reaction," Dunatchik says. "It's interesting when you compare the fathers working remotely alone to the fathers whose partners are also working from home. There's something interesting about the partner dynamics, it seems, that makes fathers more likely to pitch in in the presence of a partner."
When neither partner was able to work remotely, again mothers bore the brunt of the extra labor. In these couples, mothers were twice as likely as fathers to report increases in time spent on household labor and were seven times as likely to say they were the person responsible for the majority of children's home learning.
While the survey data had only 151 responses from single parents, most of which were women, the researchers found that, perhaps unsurprisingly, single mothers were spending more time on domestic labor, though they were less likely to have increased their time spent on housework during the pandemic than partnered mothers. "They were also less likely to report feeling significant pressure about their children's home learning compared to partnered mothers," says Dunatchik.
The survey was conducted about one month into the pandemic, so the researchers can only speculate about the lingering impact on gendered division of labor. Yet the researchers' findings provide a window into the pressures that may have driven some women's voluntary exit from the labor market. As more children return to in-person school, "some of that pressure will be reduced," Jacobs says. The longer-term impacts on women's seniority and loss of wages, however, could be significant and enduring, he says even if they do eventually return to full-time work.
One silver lining of the pandemic's "natural experiment" on remote work, the researchers say, may be increased work flexibility. With more opportunities for all parents to work from home, there may be more opportunities to move toward a more egalitarian division of responsibilities. "That's something that scholars have been pushing for a long time," Jacobs says.
INFORMATION:
Allison Dunatchik is a doctoral student in the Department of Sociology in the University of Pennsylvania School of Arts & Sciences.
Jerry Jacobs is a professor of sociology in the University of Pennsylvania School of Arts & Sciences.
In addition to Dunatchik and Jacobs, coauthors of the study were Kathleen Gerson of New York University and Jennifer Glass and Haley Strizel of the University of Texas at Austin.
The research was supported in part by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (Grant CHD042849).
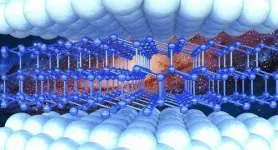
Scientists from the Skoltech Center for Energy Science and Technology (CEST) have developed a method for modeling the behavior of 2D materials under pressure. The research will help create pressure sensors based on silicene or other 2D materials. The paper was published in the ACS Nano journal.
Silicene, which is regarded as the silicon analog of graphene, is a two-dimensional allotrope of silicon. In its normal state, bulk silicon is a semiconductor with a diamond crystal type structure. As it thins down to one or several layers, its properties change dramatically. However, it has not yet been possible to study the change in the electronic properties of 2D materials at high pressure.
Scientists from Russia, Italy, the United ...
In a longitudinal study published earlier this month in the Journal of the American Dental Association, researchers analyzed untreated decay in a cohort of nearly 7,000 children enrolled in the ForsythKids preventive dentistry program. Over the course of six years, the percentage of children with untreated cavities in the program decreased from 39 to 19 percent, suggesting that school-based prevention programs are effective in combating childhood dental disease.
Tooth decay is the most common chronic early childhood disease in the United States. More than half of children aged 6-8 years old have had a cavity, and kids from low-income families ...
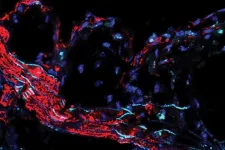
High cholesterol is the most commonly understood cause of atherosclerosis, a hardening of the arteries that raises the risk of heart attack and stroke. But now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a gene that likely plays a causal role in coronary artery disease independent of cholesterol levels. The gene also likely has roles in related cardiovascular diseases, including high blood pressure and diabetes.
The study appears March 24 in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Studying mice and genetic data from people, the researchers found ...
LA JOLLA--(March 31, 2021) Clinicians using a new viral screening test can not only diagnose COVID-19 in a matter of minutes with a portable, pocket-sized machine, but can also simultaneously test for other viruses--like influenza--that might be mistaken for the coronavirus. At the same time, they can sequence the virus, providing valuable information on the spread of COVID-19 mutations and variants. The new test, dubbed NIRVANA, was described online today by a multi-institution team of scientists in the journal Med.
"This is a virus detection and surveillance method that doesn't require an expensive infrastructure like other approaches," says Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte, co-corresponding author and a professor in Salk's Gene Expression ...
AURORA, Colo. (March 31, 2021) - A new study published in Frontiers in Psychiatry finds that patients with Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) as well as other psychiatric comorbidities, such as autism spectrum or tic disorders, may respond well to Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS).
DBS is a minimally invasive neurosurgical procedure that uses coordinates to target certain areas of the brain, implanting electrodes that can help regulate abnormal brain activity. DBS procedures are rare for OCD in the United States; only a couple hundred patients have received this treatment for OCD management since its FDA approval ...
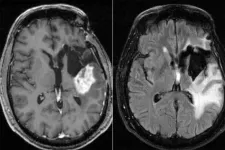
An aggressive type of brain cancer, glioblastoma has no cure. Patients survive an average of 15 months after diagnosis, with fewer than 10% of patients surviving longer than five years. While researchers are investigating potential new therapies via ongoing clinical trials, a new study from Washington University in St. Louis suggests that a minor adjustment to the current standard treatment -- giving chemotherapy in the morning rather than the evening -- could add a few months to patients' survival.
The study appears online in the journal Neuro-Oncology Advances.
Average overall survival ...
AURORA, Colo. (March 30, 2021 - Researchers at the University of Colorado College of Nursing have found that nearly one-quarter of graduate nursing students have reported elevated levels of stress, anxiety and depression, compounded in the past year by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Study findings, published recently in END ...
A new invention that uses sunlight to drive water purification could help solve the problem of providing clean water off the grid.
The device resembles a large sponge that soaks up water but leaves contaminants - like lead, oil and pathogens - behind. To collect the purified water from the sponge, one simply places it in sunlight. The researchers described the device in a paper published this week in the journal Advanced Materials.
The inspiration for the device came from the pufferfish, a species that takes in water to swell its body when threatened, and then releases water when danger passes, said the device's co-inventor END ...
When it comes to powering mobile robots, batteries present a problematic paradox: the more energy they contain, the more they weigh, and thus the more energy the robot needs to move. Energy harvesters, like solar panels, might work for some applications, but they don't deliver power quickly or consistently enough for sustained travel.
James Pikul, assistant professor in Penn Engineering's Department of Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, is developing robot-powering technology that has the best of both worlds. His environmentally controlled voltage source, or ECVS, works like a battery, in that the energy is produced by repeatedly breaking ...
In looking at the broader impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on health and wellbeing, public health experts are examining screening rates for cancer. A new study looking at U.S. mammography screening rates during the first five months of the pandemic found both a strong rebound in breast cancer screening rates and a concerning cumulative deficit in mammograms due to missed appointments, as well as uncovering disparities when looking at screening according to race.
The study was released this week in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Conducted by investigators from the Breast Cancer Surveillance Coalition (BCSC), a federally-funded, national network of breast imaging registries, the study sought to quantify the impact of the COVID-19 ...