(Press-News.org) In the 1960s, a national focus on hunger was essential to address major problems of undernutrition after World War II. In the 1990s, the nation shifted away from hunger toward "food insecurity" to better capture and address the challenges of food access and affordability.
Now, a END
Time to shift from 'food security' to 'nutrition security' to increase health and well-being
Tufts and Georgetown scientists, and humanitarian José Andrés, call for a new approach to address food and nutrition inequities
2021-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Distant, spiralling stars give clues to the forces that bind sub-atomic particles
2021-04-01
Space scientists at the University of Bath in the UK have found a new way to probe the internal structure of neutron stars, giving nuclear physicists a novel tool for studying the structures that make up matter at an atomic level.
Neutron stars are dead stars that have been compressed by gravity to the size of small cities. They contain the most extreme matter in the universe, meaning they are the densest objects in existence (for comparison, if Earth were compressed to the density of a neutron star, it would measure just a few hundred meters in diameter, and all humans would fit in a teaspoon). This makes neutron stars unique natural laboratories ...
Finnish study detects lottery-like behavior in cryptocurrency market
2021-04-01
Recent research from the University of Vaasa and the University of Jyväskyla shows that speculation and lottery-like behavior is a fundamental factor for the pricing of cryptocurrencies. Speculation could explain the enormous increase in the market capitalizations of cryptocurrencies.
Nowadays more than 8000 cryptocurrencies have been launched. Unlike traditional assets like stocks, research has shown that investments in cryptocurrencies are associated with a considerably higher level of uncertainty. The price of Bitcoin, which is the first traded cryptocurrency, increased by from $7,200.17 to $29,374.15 in January 1, 2020 ...
U of A team identifies protein that blocks body's ability to clear bad cholesterol
2021-04-01
A team of researchers at the University of Alberta has uncovered a long-sought link in the battle to control cholesterol and heart disease.
The protein that interferes with low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors that clear "bad" cholesterol from the blood was identified in END ...
Disrupted biochemical pathway in the brain linked to bipolar disorder
2021-04-01
MADISON - Bipolar disorder affects millions of Americans, causing dramatic swings in mood and, in some people, additional effects such as memory problems.
While bipolar disorder is linked to many genes, each one making small contributions to the disease, scientists don't know just how those genes ultimately give rise to the disorder's effects.
However, in new research, scientists at the University of Wisconsin-Madison have found for the first time that disruptions to a particular protein called Akt can lead to the brain changes characteristic of bipolar disorder. The results offer a foundation for research into treating the often-overlooked cognitive impairments of bipolar disorder, ...
NASA OSIRIS-REx's final asteroid observation run
2021-04-01
NASA's OSIRIS-REx mission is on the brink of discovering the extent of the mess it made on asteroid Bennu's surface during last fall's sample collection event. On Apr. 7, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft will get one last close encounter with Bennu as it performs a final flyover to capture images of the asteroid's surface. While performing the flyover, the spacecraft will observe Bennu from a distance of about 2.3 miles (3.7 km) - the closest it's been since the Touch-and-Go Sample Collection event on Oct. 20, 2020.
The OSIRIS-REx team decided to add this last flyover after Bennu's surface was significantly disturbed by the sample collection event. During touchdown, the spacecraft's ...
BrainGate: First human use of high-bandwidth wireless brain-computer interface
2021-04-01
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University and Providence Veterans Affairs Medical Center] -- Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are an emerging assistive technology, enabling people with paralysis to type on computer screens or manipulate robotic prostheses just by thinking about moving their own bodies. For years, investigational BCIs used in clinical trials have required cables to connect the sensing array in the brain to computers that decode the signals and use them to drive external devices.
Now, for the first time, BrainGate clinical trial participants with tetraplegia have demonstrated use of an intracortical wireless BCI with an external wireless transmitter. The system is capable of transmitting brain signals at single-neuron resolution and ...
Titanium dioxide stars in the first IFJ PAN research at the Cracow synchrotron
2021-04-01
Few compounds are as important to industry and medicine today as titanium dioxide. Despite the variety and popularity of its applications, many issues related to the surface structure of materials made of this compound and the processes taking place therein remain unclear. Some of these secrets have just been revealed to scientists from the Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Polish Academy of Sciences. It was the first time they had used the SOLARIS synchrotron in their research.
It is found in many chemical reactions as a catalyst, as a pigment in plastics, paints or cosmetics and in medical implants it ...
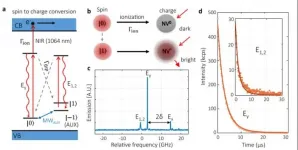
Spin-to-charge conversion achieves 95% overall qubit readout fidelity
2021-04-01
The team led by Professor DU Jiangfeng and Professor WANG Ya from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Key Laboratory of Microscale Magnetic Resonance of the University of Science and Technology of China put forward an innovative spin-to-charge conversion method to achieve high-fidelity readout of qubits, stepping closer towards fault-tolerant quantum computing.
Quantum supremacy over classical computers has been fully exhibited in some specific problems, yet the next milestone, fault-tolerant quantum computing, still requires the accumulated logic gate error and the spin readout fidelity to exceed the fault-tolerant threshold. DU's team has resolved the first requirement in the nitrogen-vacancy (NV) center system ...
Pollen season in Switzerland earlier and more intense due to climate change
2021-04-01
Pollen from trees, grasses and weeds are causing seasonal allergies for approximately one fifth of the Swiss population every year. A study now found that due to climate change, the pollen season has shifted substantially over the past 30 years in onset, duration and intensity. "For at least four allergenic species, the tree pollen season now starts earlier than 30 years ago - sometimes even before January," said Marloes Eeftens, Principal Investigator and Group Leader at Swiss TPH. "The duration and intensity of the pollen season have also increased for several species, meaning that allergic people not only suffer for a longer period of time but also react stronger to these higher concentrations."
The researchers analysed pollen data from 1990 ...
Low risk of researchers passing coronavirus to North American bats
2021-04-01
The risk is low that scientists could pass coronavirus to North American bats during winter research, according to a new study led by the U.S. Geological Survey. Scientists find the overall risk to be 1 in 1,000 if no protective measures are taken, and the risk falls lower, to 1 in 3,333 or less, with proper use of personal protective equipment or if scientists test negative for COVID-19 before beginning research.
The research specifically looked at the potential transmission of SARS-CoV-2, which is the type of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, from people to bats. Scientists did not examine potential ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Time to shift from 'food security' to 'nutrition security' to increase health and well-beingTufts and Georgetown scientists, and humanitarian José Andrés, call for a new approach to address food and nutrition inequities