Fireflies have a potential -- protective 'musical armor' against bats
How do fireflies defend themselves against predators?
2021-04-05
(Press-News.org) A new study at Tel Aviv University reveals a possible defense mechanism developed by fireflies for protection against bats that might prey on them. According to the study, fireflies produce strong ultrasonic sounds - soundwaves that the human ear, and more importantly the fireflies themselves, cannot detect. The researchers hypothesize that these sounds are meant for the ears of bats, keeping them away from the poisonous fireflies, and thereby serving as a kind of 'musical armor'. The study was led by Prof. Yossi Yovel, Head of the Sagol School of Neuroscience, and a member of the School of Mechanical Engineering and the School of Zoology at the George S. Wise Faculty of Life Sciences. It was conducted in collaboration with the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST). The paper was published in iScience.
Fireflies are known for their unique glow, used as a mating signal. Since their bodies contain poison, the light flashes probably also serve as an aposematic signal (a warning to potential predators). This signal is also the firefly's weakness, simply because it makes it an easy target for predators. Bats are among the fireflies' most prevalent potential predators, and some bats have poor vision, rendering the flashing signal ineffective. This led the researchers to check whether fireflies had some additional layer of protection against bats.
Prof. Yossi Yovel explains that the idea for this study came up accidentally, during a study that tracked bats' echolocation. "We were wandering around a tropical forest with microphones capable of recording bats' high frequencies, when suddenly, we detected unfamiliar sounds at similar frequencies, coming from fireflies," he recalls. "In-depth research using high-speed video revealed that the fireflies produce the sound by moving their wings, and that the fireflies themselves can't hear this frequency. Consequently we hypothesized that the sound is not intended for any internal communication within the species," adds Ksenia Krivoruchku, the PhD student who led the study.
Following the accidental discovery, the team at Prof. Yovel's laboratory examined three different species of fireflies that are common in Vietnam (Curtos Luciola, Sclerotia) plus one Israeli species (Lampyroidea), and found that they all produce these unique ultrasonic sounds, but cannot hear them.
Can it be concluded that fireflies have developed a special defense mechanism specifically for bats? Prof. Yovel emphasizes that this claim was not proved in the study, but several features do point to this conclusion. First of all, the fact that the fireflies themselves can't hear the sound, while bats can both hear it and use it to find the fireflies - so it's more likely that it serves as a warning signal. Krivoruochku adds that the discovery of ultrasonic sounds in fireflies is in itself an important contribution to the study of predator-prey relations: "The idea of warning signals that the sender itself cannot detect is known from the world of plants but is quite rare among animals. Our discovery of the 'musical battle' between fireflies and bats may pave the way for further research, and possibly the discovery of a new defense mechanism developed by animals against potential predators."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-05
Could the next Hollywood blockbuster be written by a computer? Scientists from the University of Granada (UGR) and the University of Cádiz (UCA) have designed the world's first computer system based on artificial intelligence techniques that can help film scriptwriters create storylines with the best chance of box-office success.
The researchers focused their analysis on the "tropes" of existing films--that is, the commonplace, predictable, and even necessary clichés that repeatedly feature in film plots, based on rhetorical figures. These storytelling devices and conventions enable directors to readily convey scenarios that ...
2021-04-05
A lot of people think regret must be a good thing because it helps you not repeat a mistake, right?
But that turns out not to be the case. Not even when it comes to casual sex, according to new research from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Psychology.
"For the most part, people continue with the same sexual behaviour and the same level of regret," says Professor Leif Edward Ottesen Kennair.
So, we repeat what we thought was a mistake, and we regret it just as much the next time around.
Professor Kennair and colleagues professor Mons Bendixen and postdoctoral ...
2021-04-05
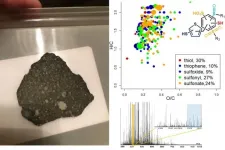
Scientists from Russia and Germany studied the molecular composition of carbonaceous chondrites - the insoluble organic matter of the Murchison and Allende meteorites - in an attempt to identify their origin. Ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry revealed a wide diversity of chemical compositions and unexpected similarities between meteorites from different groups. The research was published in the Scientific Reports.
Carbonaceous chondrites contain nearly the entire spectrum of organic molecules encountered on Earth, including nucleic acids which might have played a pivotal role in the origin of life. Since the majority of modern meteorites are of nearly the same age ...
2021-04-05
WHO Ingrid Katz, MD, MHS, Associate Physician, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; lead author of a new Perspective piece published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
WHAT While the U.S. has begun to vaccinate millions of Americans each day, COVID-19 vaccine supplies around the world remain scarce. Experts estimate that 80 percent of people in low-resource countries will not receive a vaccine in 2021. At the time of the paper's writing, the global vaccination rate was 6.7 million doses per day -- a rate at which it would take 4.6 years to achieve global herd immunity. In a new Perspective piece in the New England Journal of Medicine, Katz and colleagues highlight the need ...
2021-04-05
A recent study of more than 2,000 companies finds that corporations feeling the pinch of financial constraints can benefit significantly from taking a more aggressive stance in their tax planning strategies. One takeaway of the finding is that tax authorities should look closely at the activities of companies facing financial constraints to make sure their tax activities don't become too aggressive.
Financial constraints aren't unusual and occur when a company can't afford to fund a project that would increase its value. Sometimes the constraints are caused by an external event - like a pandemic - that leaves companies with less income than they were anticipating. ...
2021-04-05
Manufacturing - Mighty Mo
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists proved molybdenum titanium carbide, a refractory metal alloy that can withstand extreme temperature environments, can also be crack free and dense when produced with electron beam powder bed fusion. Their finding indicates the material's viability in additive manufacturing.
Molybdenum, or Mo, as well as associated alloys, are difficult to process through traditional manufacturing because of their high melting temperature, reactivity with oxygen and brittleness.
To address these shortcomings, the team formed a Mo metal matrix composite by mixing molybdenum and titanium carbide powders and used an electron beam to melt the ...
2021-04-05
Piping plover breeding groups in the Northern Great Plains are notably connected through movements between habitats and show lower reproductive rates than previously thought, END ...
2021-04-05
A comprehensive assessment of 12 different strategies for reducing beef production emissions worldwide found that industry can reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by as much as 50% in certain regions, with the most potential in the United States and Brazil. The study, " END ...
2021-04-05
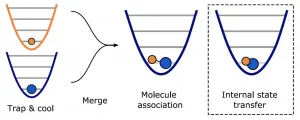
In 2018, Kang-Kuen Ni and her lab earned the cover of Science with an impressive feat: They took two individual atoms, a sodium and a cesium, and forged them into a single dipolar molecule, sodium cesium.
Sodium and cesium normally ignore each other in the wild; but in the Ni lab's carefully calibrated vacuum chamber, she and her team captured each atom using lasers and then forced them to react, a capability that gifted scientists with a new method to study one of the most basic and ubiquitous processes on Earth: the formation of a chemical bond. With Ni's invention, scientists could not only discover more about our chemical underpinnings, they could start creating ...
2021-04-05
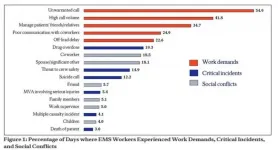
Syracuse, N.Y. - Emergency medical service (EMS) workers face triple the risk for significant mental health problems such as depression and posttraumatic stress disorder compared to the general population, according to a recently published study by researchers from Syracuse University.
The study also showed that daily mental health symptoms for EMS workers can be reduced through recovery activities such as exercising, socializing with other people, and finding meaning in the day's challenges.
The study, " END ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fireflies have a potential -- protective 'musical armor' against bats
How do fireflies defend themselves against predators?