'Vaccine Nationalism' is a threat to equitable access and herd immunity
2021-04-05
(Press-News.org) WHO Ingrid Katz, MD, MHS, Associate Physician, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; lead author of a new Perspective piece published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
WHAT While the U.S. has begun to vaccinate millions of Americans each day, COVID-19 vaccine supplies around the world remain scarce. Experts estimate that 80 percent of people in low-resource countries will not receive a vaccine in 2021. At the time of the paper's writing, the global vaccination rate was 6.7 million doses per day -- a rate at which it would take 4.6 years to achieve global herd immunity. In a new Perspective piece in the New England Journal of Medicine, Katz and colleagues highlight the need to treat essential medical services as public goods, rather than market commodities. To truly protect U.S. residents and their neighbors, they urge the federal government to reinforce global vaccine distribution efforts.
"The early competitive procurement of vaccines by the United States and purchases by other high-resource countries have fed a widespread assumption that each country will be solely responsible for its own population," the authors write. "Such vaccine nationalism perpetuates the long history of powerful countries securing vaccines and therapeutics at the expense of less-wealthy countries; it is short-sighted, ineffective, and deadly."
Through the COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access (COVAX) program, the U.S. and the G7 nations have committed to vaccinating at least 20 percent of the populations of participating low- and middle-income countries by the end of 2021. But this falls far below the broader goal of achieving herd immunity by vaccinating at least 70 to 85 percent of the population and substantially increases the likelihood that new viral variants will emerge.
Drawing upon lessons learned from the HIV pandemic, when most low-resource countries could not access lifesaving therapies, the authors argue that the government should invest in what some experts are calling the President's Emergency Plan for Vaccine Access and Relief (PEPVAR), a spin-off of the 2003 President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR). This latter plan was founded to deliver antiretroviral therapies globally, and a program like PEPVAR could draw upon pre-existing strategies to scale up the delivery of vaccines beyond COVAX's commitments. Like the plan for AIDS relief, it could leverage partnerships with governmental and multilateral organizations to improve vaccine access. Equally important is ensuring vaccine supply, and the authors posit that the World Trade Organization may be justified in temporarily waiving pharmaceutical patent protections to substantially reduce the costs of manufacturing vaccines.
"The United States has an unusual and urgent opportunity to ensure that COVID-19 vaccines are available to all," the authors write. "By investing in multilateral partnerships with a sense of shared commitment and employing a global allocation strategy that increases supply and manufacturing, we can meet the urgent challenge of COVID-19, while creating sustainable infrastructures and health systems for the future."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-05
A recent study of more than 2,000 companies finds that corporations feeling the pinch of financial constraints can benefit significantly from taking a more aggressive stance in their tax planning strategies. One takeaway of the finding is that tax authorities should look closely at the activities of companies facing financial constraints to make sure their tax activities don't become too aggressive.
Financial constraints aren't unusual and occur when a company can't afford to fund a project that would increase its value. Sometimes the constraints are caused by an external event - like a pandemic - that leaves companies with less income than they were anticipating. ...
2021-04-05
Manufacturing - Mighty Mo
Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists proved molybdenum titanium carbide, a refractory metal alloy that can withstand extreme temperature environments, can also be crack free and dense when produced with electron beam powder bed fusion. Their finding indicates the material's viability in additive manufacturing.
Molybdenum, or Mo, as well as associated alloys, are difficult to process through traditional manufacturing because of their high melting temperature, reactivity with oxygen and brittleness.
To address these shortcomings, the team formed a Mo metal matrix composite by mixing molybdenum and titanium carbide powders and used an electron beam to melt the ...
2021-04-05
Piping plover breeding groups in the Northern Great Plains are notably connected through movements between habitats and show lower reproductive rates than previously thought, END ...
2021-04-05
A comprehensive assessment of 12 different strategies for reducing beef production emissions worldwide found that industry can reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by as much as 50% in certain regions, with the most potential in the United States and Brazil. The study, " END ...
2021-04-05
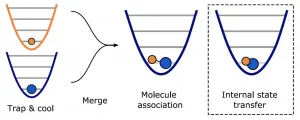
In 2018, Kang-Kuen Ni and her lab earned the cover of Science with an impressive feat: They took two individual atoms, a sodium and a cesium, and forged them into a single dipolar molecule, sodium cesium.
Sodium and cesium normally ignore each other in the wild; but in the Ni lab's carefully calibrated vacuum chamber, she and her team captured each atom using lasers and then forced them to react, a capability that gifted scientists with a new method to study one of the most basic and ubiquitous processes on Earth: the formation of a chemical bond. With Ni's invention, scientists could not only discover more about our chemical underpinnings, they could start creating ...
2021-04-05
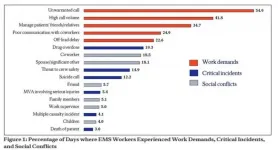
Syracuse, N.Y. - Emergency medical service (EMS) workers face triple the risk for significant mental health problems such as depression and posttraumatic stress disorder compared to the general population, according to a recently published study by researchers from Syracuse University.
The study also showed that daily mental health symptoms for EMS workers can be reduced through recovery activities such as exercising, socializing with other people, and finding meaning in the day's challenges.
The study, " END ...
2021-04-05
Patients with a high number of genes most associated with pathways that lead to cell death in lung cancer are at increased risk of dying early from their disease, researchers report.
Also seemingly paradoxically, patients with high expression of this "21-gene cell death signature" the researchers have identified, have indicators that their immune system is attacking the cancer, like higher levels of cytotoxic T cells, which typically kill cancer.
But they also have high levels of molecules that can suppress those T cells, helping transform them into dysfunctional, "exhausted" T cells, they report in the journal Cancers.
This novel genomic signature can be used both to better predict how a patient with ...
2021-04-05
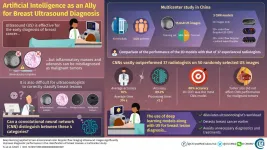
In 2020, the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization stated that breast cancer accounts for most cancer morbidities and mortalities in women worldwide. This alarming statistic not only necessitates newer methods for the early diagnosis of breast cancer, but also brings to light the importance of risk prediction of the occurrence and development of this disease. Ultrasound is an effective and noninvasive diagnostic procedure that truly saves lives; however, it is sometimes difficult for ultrasonologists to distinguish between malignant tumors and other ...
2021-04-05
X-Ray Experiments, Machine Learning Could Trim Years Off Battery R&D
By Glenn Roberts Jr.
An X-ray instrument at Berkeley Lab contributed to a battery study that used an innovative approach to machine learning to speed up the learning curve about a process that shortens the life of fast-charging lithium batteries.
Researchers used Berkeley Lab's Advanced Light Source, a synchrotron that produces light ranging from the infrared to X-rays for dozens of simultaneous experiments, to perform a chemical imaging technique known as scanning transmission ...
2021-04-05
Parkinson's disease (PD) is well known as a debilitating disease that gradually worsens over time. Although the disease's progression has been largely tied to the loss of motor functions, non-motor symptoms, including the loss of cognitive abilities, often emerge early in the disease.
Much less understood is the role that specific neural circuits play in these distinct motor and non-motor functions.
A new study led by neurobiologists at the University of California San Diego and their colleagues found that specific, identifiable neural pathways are charged with particular functions during stages of the disease. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Vaccine Nationalism' is a threat to equitable access and herd immunity