Researchers extend the life of a dipolar molecule
Static, long-lasting molecules are key to molecule-based quantum simulation and information processing
2021-04-05
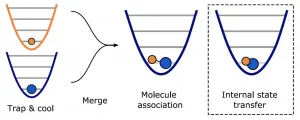
(Press-News.org) In 2018, Kang-Kuen Ni and her lab earned the cover of Science with an impressive feat: They took two individual atoms, a sodium and a cesium, and forged them into a single dipolar molecule, sodium cesium.
Sodium and cesium normally ignore each other in the wild; but in the Ni lab's carefully calibrated vacuum chamber, she and her team captured each atom using lasers and then forced them to react, a capability that gifted scientists with a new method to study one of the most basic and ubiquitous processes on Earth: the formation of a chemical bond. With Ni's invention, scientists could not only discover more about our chemical underpinnings, they could start creating bespoke molecules for novel uses like qubits for quantum computers.
But there was one flaw in their original sodium cesium molecule: "That molecule was lost soon after it's made," said Ni, the Morris Kahn associate professor of chemistry and chemical biology and of physics. Now, in a new study published in Physics Review Letters, Ni and her team report a new feat: They granted their molecule an extended lifetime of up to almost three and a half seconds--a luxury of time in the quantum realm--by controlling all the degrees of freedom (including its motion) of an individual dipolar molecule for the first time. During those precious seconds, the researchers can maintain the full quantum control necessary for stable qubits, the building blocks for a wide variety of exciting quantum applications.
According to the paper, "These long-lived, fully quantum state-controlled individual dipolar molecules provide a key resource for molecule-based quantum simulation and information processing." For example, such molecules could accelerate progress toward quantum simulation of new phases of matter (faster than any known computer), high-fidelity quantum information processing, precision measurements, and basic research in the field of cold chemistry (one of Ni's specialties).
And, by forming obedient molecules in their quantum ground states (basically, their simplest, most pliant form), the researchers created more reliable qubits with electric handles, which, like the magnetic handles of a magnet, allow researchers to interact with them in new ways (for example, with microwaves and electric fields).
Next, the team is working on scaling their process: They plan to assemble not just one molecule from two atoms but force larger collections of atoms to interact and form molecules in parallel. In so doing, they can also start to perform long-range entanglement interactions between molecules, the basis for information transfer in quantum computing.
"With the addition of microwave and electric field control," said Ni, "molecular qubits for quantum computing applications and simulations that further our understanding of quantum phases of matter are within experimental reach."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-05
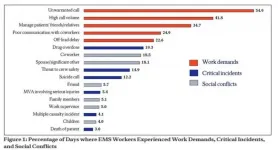
Syracuse, N.Y. - Emergency medical service (EMS) workers face triple the risk for significant mental health problems such as depression and posttraumatic stress disorder compared to the general population, according to a recently published study by researchers from Syracuse University.
The study also showed that daily mental health symptoms for EMS workers can be reduced through recovery activities such as exercising, socializing with other people, and finding meaning in the day's challenges.
The study, " END ...
2021-04-05
Patients with a high number of genes most associated with pathways that lead to cell death in lung cancer are at increased risk of dying early from their disease, researchers report.
Also seemingly paradoxically, patients with high expression of this "21-gene cell death signature" the researchers have identified, have indicators that their immune system is attacking the cancer, like higher levels of cytotoxic T cells, which typically kill cancer.
But they also have high levels of molecules that can suppress those T cells, helping transform them into dysfunctional, "exhausted" T cells, they report in the journal Cancers.
This novel genomic signature can be used both to better predict how a patient with ...
2021-04-05
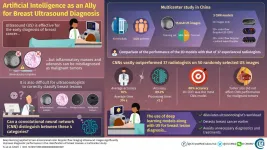
In 2020, the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization stated that breast cancer accounts for most cancer morbidities and mortalities in women worldwide. This alarming statistic not only necessitates newer methods for the early diagnosis of breast cancer, but also brings to light the importance of risk prediction of the occurrence and development of this disease. Ultrasound is an effective and noninvasive diagnostic procedure that truly saves lives; however, it is sometimes difficult for ultrasonologists to distinguish between malignant tumors and other ...
2021-04-05
X-Ray Experiments, Machine Learning Could Trim Years Off Battery R&D
By Glenn Roberts Jr.
An X-ray instrument at Berkeley Lab contributed to a battery study that used an innovative approach to machine learning to speed up the learning curve about a process that shortens the life of fast-charging lithium batteries.
Researchers used Berkeley Lab's Advanced Light Source, a synchrotron that produces light ranging from the infrared to X-rays for dozens of simultaneous experiments, to perform a chemical imaging technique known as scanning transmission ...
2021-04-05
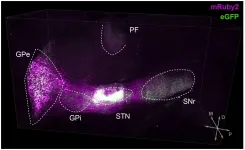
Parkinson's disease (PD) is well known as a debilitating disease that gradually worsens over time. Although the disease's progression has been largely tied to the loss of motor functions, non-motor symptoms, including the loss of cognitive abilities, often emerge early in the disease.
Much less understood is the role that specific neural circuits play in these distinct motor and non-motor functions.
A new study led by neurobiologists at the University of California San Diego and their colleagues found that specific, identifiable neural pathways are charged with particular functions during stages of the disease. ...
2021-04-05
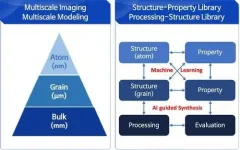
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global ...
2021-04-05
Researchers at the Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center have developed DeepTCR, a software package that employs deep-learning algorithms to analyze T-cell receptor (TCR) sequencing data. T-cell receptors are found on the surface of immune T cells. These receptors bind to certain antigens, or proteins, found on abnormal cells, such as cancer cells and cells infected with a virus or bacteria, to guide the T cells to attack and destroy the affected cells.
"DeepTCR is an open-source software that ...
2021-04-05
A research team led by Professor PAN Jianwei and Professor XU Feihu from University of Science and Technology of China achieved single-photon 3D imaging over 200 km using high-efficiency optical devices and a new noise-suppression technique, which is commented by the reviewer as an almost "heroic" attempt at single photon lidar imaging at very long distances.
Lidar imaging technology has enabled high precision 3D imaging of target scene in recent year. Single photon imaging lidar is an ideal technology for remote optical imaging with single-photon level sensitivity and picosecond resolution, yet its imaging range is strictly limited by the quadratically decreasing count of photons that echo back.
Researchers first optimized transceiver optics. The lidar system setup adopted ...
2021-04-05
A new automated process prints a peptide-based hydrogel scaffold containing uniformly distributed cells. The scaffolds hold their shapes well and successfully facilitate cell growth that lasts for weeks.
"Bioprinting" -- 3D printing that incorporates living cells -- has the potential to revolutionize tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Scientists have experimented with natural and synthetic "bioinks" to print out scaffolds that hold cells in place as they grow and form a tissue with a specific shape. But there are challenges with cell survival. Natural bioinks, such as gelatin and collagen, need to be treated with chemicals or ultraviolet light to hold their shape, which affects ...
2021-04-05
A new analysis of the entire genetic makeup of more than 53,000 people offers a bonanza of valuable insights into heart, lung, blood and sleep disorders, paving the way for new and better ways to treat and prevent some of the most common causes of disability and death.
The analysis from the Trans-Omics for Precision Medicine (TOPMed) program examines the complete genomes of 53,831 people of diverse backgrounds on different continents. Most are from minority groups, which have been historically underrepresented in genetic studies. The increased representation should translate into better understanding of how heart, lung, blood and sleep disorders affect minorities and should help reduce longstanding health disparities.
"The Human Genome Project has generated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers extend the life of a dipolar molecule
Static, long-lasting molecules are key to molecule-based quantum simulation and information processing