How many mothers have lost a child: A global comparison
The first systematic comparison of 170 countries reveals large global inequalities in the number of mothers who have experienced the death of a child
2021-04-06
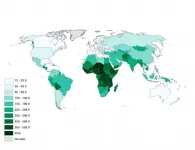
(Press-News.org) The inequality is enormous: Mothers in select African countries are more than 100 times more likely to have had a child die than mothers in high-income countries.
This is what Diego Alburez-Gutierrez (Researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research (MPIDR) in Rostock, Germany), Emily Smith-Greenaway (Researcher at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences in Los Angeles and Guest Researcher at MPIDR), and co-authors found in their recent paper published in BMJ Global Health.
"We offer the first global estimates of the cumulative number of child deaths experienced by mothers between the ages of 20 and 49, in 170 countries," said Smith-Greenaway.
Initially, she and her collaborators did so by drawing from the wealth of publicly available survey data, collected between 2010 and 2018, to calculate the proportion of mothers who have ever lost an offspring in 89 countries.
A new indirect approach to estimate the prevalence of bereaved mothers
"The innovation of our study lies in the fact that we expanded beyond these 89 countries and provided estimates for those lacking recent, nationally representative survey data by leveraging a novel indirect approach that combines formal kinship models and life-table methods," says Alburez-Gutierrez. "That has allowed us to offer a comprehensive look at bereavement worldwide." The estimates generated for these additional 81 countries are interpretable, just as the survey estimates.
International inequalities in mothers' experiences of the death of a child will linger beyond the initial improvement in infant and child mortality conditions, given the varied demographic history of populations. In the seven least affected countries, which includes Japan, Finland, and Spain, fewer than 5 per 1,000 mothers who are between 20 and 44 years old have ever lost an offspring younger than one year old. In Germany, only 6 out of 1,000 mothers have ever lost an infant.
In 34 countries, mostly in Africa, more than 150 per 1,000 mothers have experienced the death of an infant. That means mothers in these countries are more than 30 times as likely to have had a child die than mothers in the seven countries with the lowest numbers. Moreover, in as many as 16 countries--all located in sub-Saharan Africa and the Middle East--more than 200 per 1,000 mothers have lost an infant.
It is concerning that the very parts of the world where the cumulative burden of child death is heaviest for mothers are also the settings where the least is known about the social, economic, relational, and health implications of child death for mothers. "We hope that this work will emphasize that further efforts to lower child deaths will not only improve the quality and length of life for children across the globe, but will also fundamentally improve the lives of parents," said Smith-Greenaway.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
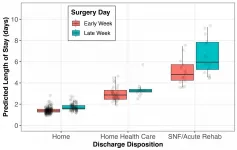
CHARLOTTESVILLE, VA (APRIL 6, 2021). New research by a team from the Cleveland Clinic and the London School of Economics and Political Science (LSE) has determined that surgeries performed late in the workweek, and those culminating in discharge to a specialty care facility, are associated with higher costs and unnecessarily longer stays in the hospital following a common elective spine surgery.
Sebastian Salas-Vega, PhD, and colleagues retrospectively reviewed the data for all adult patients who underwent elective lumbar laminectomy over a nearly three-year period at any Ohio hospital included within ...
2021-04-06
Newer is not always better; a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) led by researchers at the University of Warwick shows that simple fetal heartbeat monitoring is still the best method for determining whether a baby is in distress during delivery and whether cesarean delivery is needed http://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.202538.
Cesarean delivery is the most common surgical procedure worldwide, performed to expedite birth and avoid neonatal complications.
Listening to the fetal heart rate using a stethoscope -- intermittent auscultation -- has been used for years to assess the fetal state and whether the baby is experiencing distress that might require a cesarean delivery. Other monitoring techniques have become ...
2021-04-06
Legalization of recreational cannabis may be associated with an increase in fatal motor vehicle collisions based on data from the United States, and authors discuss the implications for Canada in an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"Analyses of data suggest that legalization of recreational cannabis in United States jurisdictions may be associated with a small but significant increase in fatal motor vehicle collisions and fatalities, which, if extrapolated to the Canadian context, could result in as many as 308 additional driving fatalities annually," says Ms. Sarah Windle, Lady Davis Institute/McGill ...
2021-04-06
Hamilton, ON (April 6, 2021) - If you are one of the millions of people worldwide suffering from allergies, you may take an antihistamine pill to ward off hives, sneezing and watery eyes.
But you may be taking your medications incorrectly, says Derek Chu, a McMaster University allergy expert and clinical scholar.
"People need to rethink what they stock in their home cabinets as allergy medicines, what hospitals keep on formulary, and what policymakers recommend. The message needs to get out. This publication is on time for the spring allergy season and as COVID vaccines roll out, for which rashes are common and antihistamines can be helpful," said Chu.
Co-author Gordon ...
2021-04-06
The idea of implantable sensors that continuously transmit information on vital values and concentrations of substances or drugs in the body has fascinated physicians and scientists for a long time. Such sensors enable the constant monitoring of disease progression and therapeutic success. However, until now implantable sensors have not been suitable to remain in the body permanently but had to be replaced after a few days or weeks. On the one hand, there is the problem of implant rejection because the body recognizes the sensor as a foreign object. On the other hand, the sensor's color which indicates concentration changes has been unstable so far and faded over time. Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have developed a novel type of implantable sensor which can ...
2021-04-06
In 2001, the famous herpetologist Joseph B. Slowinski died from snakebite by an immature black-and-white banded krait, while leading an expedition team in northern Myanmar. The very krait that caused his death is now confirmed to belong to the same species identified as a new to science venomous snake, following an examination of samples collected between 2016 and 2019 from Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.
The new krait species, found in Southwestern China and Northern Myanmar, is described by Dr Zening Chen of END ...
2021-04-06
A new study analyzing bean production and food security across 11 countries in sub-Saharan Africa, found COVID-19 pandemic-related restrictions to significantly impact bean production. Border controls and high transport costs have led to drops in production of the key food security crop, threatening to reverse gains made in achieving Sustainable Development Goals 1 and 2, towards no poverty and zero hunger, respectively.
Even before the pandemic, 55% of the world's hungry people and 70% of the world's poorest people lived in Africa, the researchers said. In addition, food systems across Africa were already affected by the adverse impacts of climate change, disease and pests, such as the worst desert locust outbreak in 70 years impacting food security in Kenya, Somalia, ...
2021-04-06
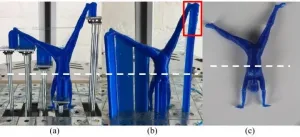
3-D printing has the potential to revolutionize product design and manufacturing in a vast range of fields--from custom components for consumer products, to 3-D printed dental products and bone and medical implants that could save lives. However, the process also creates a large amount of expensive and unsustainable waste and takes a long time, making it difficult for 3-D printing to be implemented on a wide scale.
Each time a 3-D printer produces custom objects, especially unusually-shaped products, it also needs to print supports-printed stands that balance the object as the printer creates layer by layer, ...
2021-04-06
Likely the first extinction event of the 2000s in Europe, the sad history of the Pyrenean Ibex (Capra pyrenaica pyrenaica) is a powerful example of the ever-increasing species loss worldwide due to causes related to human activity. It can, however, give us valuable information on what should be done (or avoided) to halt this extinction vortex.
The distribution of this subspecies of Iberian Ibex was limited to the French and Spanish Pyrenees. Its first mention in an official written document, dating back to 1767, already refers to it as extremely rare. Like many other mountain goats, it was almost hunted to extinction before its killing became prohibited in 1913. Neither the institution ...
2021-04-06
Insomnia is a common problem in patients with schizophrenia, and a new study reinforces a close association between insomnia, more suicidal thoughts and actions and increased problems like anxiety and depression in these patients.
It also provides more evidence that keeping tabs on how patients are sleeping -- and intervening when needed -- is important to their overall care.
"We are now aware that significant insomnia is putting our patients at even higher risk for suicide, so if they are having changes in sleep patterns, if they are having significant insomnia, then we really need to hone in on those questions even more related to suicidal thinking and do what we can to help," says Dr. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How many mothers have lost a child: A global comparison
The first systematic comparison of 170 countries reveals large global inequalities in the number of mothers who have experienced the death of a child