Tattoo made of gold nanoparticles revolutionizes medical diagnostics
Color changes of gold nanoparticles under the skin reveal concentration changes of substances in the body
2021-04-06
(Press-News.org) The idea of implantable sensors that continuously transmit information on vital values and concentrations of substances or drugs in the body has fascinated physicians and scientists for a long time. Such sensors enable the constant monitoring of disease progression and therapeutic success. However, until now implantable sensors have not been suitable to remain in the body permanently but had to be replaced after a few days or weeks. On the one hand, there is the problem of implant rejection because the body recognizes the sensor as a foreign object. On the other hand, the sensor's color which indicates concentration changes has been unstable so far and faded over time. Scientists at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) have developed a novel type of implantable sensor which can be operated in the body for several months. The sensor is based on color-stable gold nanoparticles that are modified with receptors for specific molecules. Embedded into an artificial polymeric tissue, the nanogold is implanted under the skin where it reports changes in drug concentrations by changing its color.
Implant reports information as an "invisible tattoo"
Professor Carsten Soennichsen's research group at JGU has been using gold nanoparticles as sensors to detect tiny amounts of proteins in microscopic flow cells for many years. Gold nanoparticles act as small antennas for light: They strongly absorb and scatter it and, therefore, appear colorful. They react to alterations in their surrounding by changing color. Soennichsen's team has exploited this concept for implanted medical sensing.
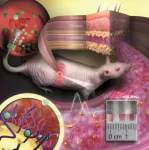
To prevent the tiny particles from swimming away or being degraded by immune cells, they are embedded in a porous hydrogel with a tissue-like consistency. Once implanted under the skin, small blood vessels and cells grow into the pores. The sensor is integrated in the tissue and is not rejected as a foreign body. "Our sensor is like an invisible tattoo, not much bigger than a penny and thinner than one millimeter," said Professor Carsten Soennichsen, head of the Nanobiotechnology Group at JGU. Since the gold nanoparticles are infrared, they are not visible to the eye. However, a special kind of measurement device can detect their color noninvasively through the skin.
In their study published in Nano Letters, the JGU researchers implanted their gold nanoparticle sensors under the skin of hairless rats. Color changes in these sensors were monitored following the administration of various doses of an antibiotic. The drug molecules are transported to the sensor via the bloodstream. By binding to specific receptors on the surface of the gold nanoparticles, they induce color change that is dependent on drug concentration. Thanks to the color-stable gold nanoparticles and the tissue-integrating hydrogel, the sensor was found to remain mechanically and optically stable over several months.
Huge potential of gold nanoparticles as long-lasting implantable medical sensors
"We are used to colored objects bleaching over time. Gold nanoparticles, however, do not bleach but keep their color permanently. As they can be easily coated with various different receptors, they are an ideal platform for implantable sensors," explained Dr. Katharina Kaefer, first author of the study.
The novel concept is generalizable and has the potential to extend the lifetime of implantable sensors. In future, gold nanoparticle-based implantable sensors could be used to observe concentrations of different biomarkers or drugs in the body simultaneously. Such sensors could find application in drug development, medical research, or personalized medicine, such as the management of chronic diseases.
Interdisciplinary team work brought success
Soennichsen had the idea of using gold nanoparticles as implanted sensors already in 2004 when he started his research in biophysical chemistry as a junior professor in Mainz. However, the project was not realized until ten years later in cooperation with Dr. Thies Schroeder and Dr. Katharina Kaefer, both scientists at JGU. Schroeder was experienced in biological research and laboratory animal science and had already completed several years of research work in the USA. Kaefer was looking for an exciting topic for her doctorate and was particularly interested in the complex and interdisciplinary nature of the project. Initial results led to a stipend awarded to Kaefer by the Max Planck Graduate Center (MPGC) as well as financial support from Stiftung Rheinland-Pfalz für Innovation. "Such a project requires many people with different scientific backgrounds. Step by step we were able to convince more and more people of our idea," said Soennichsen happily. Ultimately, it was interdisciplinary teamwork that resulted in the successful development of the first functional implanted sensor with gold nanoparticles.
INFORMATION:
Related links:
https://www.mpgc-mainz.de/ - Max Planck Graduate Center with Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (MPGC)
https://www.uni-mainz.de/presse/aktuell/8359_ENG_HTML.php - press release "Driving chemical reactions with light" (7 May 2019) ;
https://www.uni-mainz.de/presse/16589_ENG_HTML.php - press release "Chemists develop innovative nanosensors for multiple proteins" (31 July 2013) ;
https://www.uni-mainz.de/presse/15119_ENG_HTML.php - press release "Gold nanoantennas detect proteins" (14 March 2012)
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-06
In 2001, the famous herpetologist Joseph B. Slowinski died from snakebite by an immature black-and-white banded krait, while leading an expedition team in northern Myanmar. The very krait that caused his death is now confirmed to belong to the same species identified as a new to science venomous snake, following an examination of samples collected between 2016 and 2019 from Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.
The new krait species, found in Southwestern China and Northern Myanmar, is described by Dr Zening Chen of END ...
2021-04-06
A new study analyzing bean production and food security across 11 countries in sub-Saharan Africa, found COVID-19 pandemic-related restrictions to significantly impact bean production. Border controls and high transport costs have led to drops in production of the key food security crop, threatening to reverse gains made in achieving Sustainable Development Goals 1 and 2, towards no poverty and zero hunger, respectively.
Even before the pandemic, 55% of the world's hungry people and 70% of the world's poorest people lived in Africa, the researchers said. In addition, food systems across Africa were already affected by the adverse impacts of climate change, disease and pests, such as the worst desert locust outbreak in 70 years impacting food security in Kenya, Somalia, ...
2021-04-06
3-D printing has the potential to revolutionize product design and manufacturing in a vast range of fields--from custom components for consumer products, to 3-D printed dental products and bone and medical implants that could save lives. However, the process also creates a large amount of expensive and unsustainable waste and takes a long time, making it difficult for 3-D printing to be implemented on a wide scale.
Each time a 3-D printer produces custom objects, especially unusually-shaped products, it also needs to print supports-printed stands that balance the object as the printer creates layer by layer, ...
2021-04-06
Likely the first extinction event of the 2000s in Europe, the sad history of the Pyrenean Ibex (Capra pyrenaica pyrenaica) is a powerful example of the ever-increasing species loss worldwide due to causes related to human activity. It can, however, give us valuable information on what should be done (or avoided) to halt this extinction vortex.
The distribution of this subspecies of Iberian Ibex was limited to the French and Spanish Pyrenees. Its first mention in an official written document, dating back to 1767, already refers to it as extremely rare. Like many other mountain goats, it was almost hunted to extinction before its killing became prohibited in 1913. Neither the institution ...
2021-04-06
Insomnia is a common problem in patients with schizophrenia, and a new study reinforces a close association between insomnia, more suicidal thoughts and actions and increased problems like anxiety and depression in these patients.
It also provides more evidence that keeping tabs on how patients are sleeping -- and intervening when needed -- is important to their overall care.
"We are now aware that significant insomnia is putting our patients at even higher risk for suicide, so if they are having changes in sleep patterns, if they are having significant insomnia, then we really need to hone in on those questions even more related to suicidal thinking and do what we can to help," says Dr. ...
2021-04-06
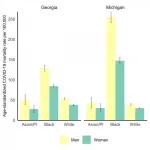
A new paper in the Journal of General Internal Medicine published by the GenderSci Lab at Harvard University shows that Black women are dying at significantly higher rates than white men, and that disparities in mortality rates among women of all races are greater than those between white women and white men.
The study is the first to quantify the inequities in COVID-19 mortality looking at both race and sex group.
"This analysis complicates the simple narrative that men are dying at greater rates of COVID-19 than women," said lead author Tamara Rushovich, Harvard Ph.D. candidate in population health sciences and lab member ...
2021-04-06
The adult human body produces hundreds of billions of blood cells every day. This essential process unavoidably leads to the appearance of mutations in the DNA of the progenitor cells. These are known as somatic mutations because they are acquired, not inherited. While most of these mutations are innocuous, occasionally a mutation gives affected cells a competitive advantage that allows them to expand progressively, generating clonal populations of blood cells. This phenomenon is known as clonal hematopoiesis.
Now, a team of scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) and the Hospital Universitario Virgen de Arrixaca in Murcia has discovered that the presence of these acquired mutations in blood cells increases ...
2021-04-06
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
1. ACP Best Practice Advice: Shorter course of antibiotics may be appropriate for some common infections
HD video soundbites of ACP's president discussing the paper are available to download at http://www.dssimon.com/MM/ACP-antibiotics-paper.
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M20-7355
Free ...
2021-04-06
Researchers at the Human Genome and Stem Cell Research Center (HUG-CELL), hosted by the University of São Paulo's Institute of Biosciences (IB-USP) in Brazil, have developed a technique to reconstruct and produce livers in the laboratory.
The proof-of-concept study was conducted with rat livers. In the next stage of their research, the scientists will adapt the technique for the production of human livers in order in future to increase the supply of these organs for transplantation.
The study was supported by FAPESP and is reported in an article published in Materials Science and Engineering: ...
2021-04-05
PITTSBURGH, April 5, 2021 - "Near-poor" Americans--people just above the federal poverty level but still well below the average U.S. income--who rely on Medicare for health insurance face high medical bills and may forgo essential health care, according to new research led by health policy scientists at the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health. This is due to a coverage "cliff" in Medicaid, which supplements Medicare for people with incomes below poverty but excludes individuals above the federal poverty threshold, including the near-poor.
In a report published today in the April issue of the journal Health Affairs, the authors describe the effects of this cliff and propose solutions to fix it, with the aim of lessening barriers to care among near-poor people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tattoo made of gold nanoparticles revolutionizes medical diagnostics
Color changes of gold nanoparticles under the skin reveal concentration changes of substances in the body