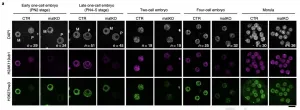
New Lyme disease test distinguishes between early and late-stage disease
New test targets genetic sequences in Lyme-causing bacteria and is highly sensitive, detecting just one bacterial cell in a blood sample
2021-04-07
(Press-News.org) For those who live in an area blighted by ticks, the threat of Lyme disease can cast a shadow over the joy of spring and summer. These blood-sucking arachnids can transmit bacteria into the bloodstream of their unsuspecting host, causing the disease. Early treatment is essential, but current tests are not usually sensitive enough to detect the disease in early-stage patients. A recent study in open-access journal END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists discover two new species of ancient, burrowing mammal ancestors
2021-04-07
A joint research team led by Dr. MAO Fangyuan and Dr. ZHANG Chi from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Prof. MENG Jin from the American Museum of Natural History have discovered two new species of mammal-like, burrowing animals that lived about 120 million years ago in what is now northeastern China.
The new species, described in Nature on April 7, are distantly related. However, they independently evolved traits to support their digging lifestyle. They represent the first "scratch diggers" discovered in this ecosystem.
"There are many hypotheses about why animals dig into the soil and live underground," said Prof. MENG, lead author of the study. "For protection against predators, ...
Study finds late night snacks may hurt your workplace performance
2021-04-07
A recent study finds that unhealthy eating behaviors at night can make people less helpful and more withdrawn the next day at work.
"For the first time, we have shown that healthy eating immediately affects our workplace behaviors and performance," says Seonghee "Sophia" Cho, corresponding author of the study and an assistant professor of psychology at North Carolina State University. "It is relatively well established that other health-related behaviors, such as sleep and exercise, affect our work. But nobody had looked at the short-term effects of unhealthy eating."
Fundamentally, the researchers had two questions: Does unhealthy eating behavior affect you at work the next day? And, if so, why?
For the study, ...
Inheriting acquired traits requires trailblazer modifications to unfertilized eggs
2021-04-07
An epigenetic study at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences shows that in mouse egg cells, modifications to histone H2A at lysine 119 lay the groundwork for inherited DNA functional modifications from the mother.
In books and the movies, a group of people on a special mission always sends out a scout to do reconnaissance before they proceed. Sometimes, the scouts leave signs or markers that allow the group to know where there should go. Researchers led by Azusa Inoue at the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences in Japan have discovered a mark left behind in unfertilized egg cells that determine which DNA modifications ...
A new mouse model gave surprising findings about Folling Disease
2021-04-07
In Norway, all newborn children are tested for 25 rare genetic diseases through the Newborn Screening program, and the most common of these is phenylketonuria (abbreviated to PKU), known as Folling Disease.
Every year, between 3-7 children are born in Norway with PKU, and this diagnosis has a great impact on the rest of their lives. People with PKU must follow a very strict diet all their lives, where they must avoid almost all foods that contain proteins.
"Failure to implement the diet from birth may result in irreversible physical problems and brain damage, and optimal brain function requires life-long adherence", explains Professor ...
UMD tracks the adoption of green infrastructure, from water conservation to policy
2021-04-07
In a new paper published in the Journal of Environmental Policy & Planning, the University of Maryland teamed up with local researchers to examine green infrastructure adoption and leadership in Tucson, Arizona, an interesting case study where grassroots efforts have helped to drive policy change in a growing urban area surrounded by water-constrained desert. Green infrastructure (any installation that manages water or environmental factors, such as rain gardens, stormwater basins, or urban tree cover) is slowly transitioning from a fringe activity to an important part of the way governments and municipalities are dealing with water and the local effects of a changing climate. By examining ...
Study revises understanding of cancer metabolism
2021-04-07
Tumors consume glucose at high rates, but a team of Vanderbilt researchers has discovered that cancer cells themselves are not the culprit, upending models of cancer metabolism that have been developed and refined over the last 100 years.
Instead, non-cancer cells in a tumor -- primarily immune cells called macrophages -- have the highest glucose uptake, the group reported April 7 in the journal Nature. The findings that different cells in the tumor microenvironment use distinct nutrients according to their own metabolic programs could be exploited to develop new therapies and imaging strategies, ...
Early indicators of magma viscosity could help forecast a volcano's eruption style
2021-04-07
Washington, DC-- The 2018 eruption of Kīlauea Volcano in Hawai'i provided scientists with an unprecedented opportunity to identify new factors that could help forecast the hazard potential of future eruptions.
The properties of the magma inside a volcano affect how an eruption will play out. In particular, the viscosity of this molten rock is a major factor in influencing how hazardous an eruption could be for nearby communities.
Very viscous magmas are linked with more powerful explosions because they can block gas from escaping through vents, allowing pressure ...
Childhood cognitive problems could lead to mental health issues in later life
2021-04-07
Children experiencing cognitive problems such as low attention, poor memory or lack of inhibition may later suffer mental health issues as teenagers and young adults, a new study reveals.
Targeting specific markers in childhood for early treatment may help to minimise the risk of children developing certain psychopathological problems in adolescence and adult life, such as borderline personality disorder, depression and psychosis.
Cognitive deficits are core features of mental disorders and important in predicting long-term prognosis - the researchers' work indicates that individual patterns of such deficits predate ...
Ocular assessments of newborns gestationally exposed to maternal COVID-19 infection
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: This case series examines whether maternal SARS-CoV-2 is associated with outcomes in the eyes of their newborns.
Authors: Olívia Pereira Kiappe, M.D., M.Sc., of Universidade Federal de São Paulo in Brazil, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2021.1088)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
Association of race/ethnicity, sex, income with well-being during COVID-19
2021-04-07
What The Study Did: This observational study identifies and quantifies the association of race/ethnicity, sex and income, as well as state-specific lockdown measures, with six well-being dimensions in the United States.
Authors: Leigh C. Hamlet, B.S., of the University of Washington in Seattle, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.7373)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
[Press-News.org] New Lyme disease test distinguishes between early and late-stage diseaseNew test targets genetic sequences in Lyme-causing bacteria and is highly sensitive, detecting just one bacterial cell in a blood sample