Study calls for urgent climate change action to secure global food supply
New Curtin University-led research has found climate change will have a substantial impact on global food production and health if no action is taken by consumers, food industries, government, and international bodies
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) New Curtin University-led research has found climate change will have a substantial impact on global food production and health if no action is taken by consumers, food industries, government, and international bodies.
Published in one of the highest-ranking public health journals, the Annual Review of Public Health, the researchers completed a comprehensive 12-month review of published literature on climate change, healthy diet and actions needed to improve nutrition and health around the world.
Lead researcher John Curtin Distinguished Emeritus Professor Colin Binns, from the Curtin School of Population Health at Curtin University, said climate change has had a detrimental impact on health and food production for the past 50 years and far more needs to be done to overcome its adverse effects.
"The combination of climate change and the quality of nutrition is the major public health challenge of this decade and, indeed, this century. Despite positive advances in world nutrition rates, we are still facing the ongoing threat of climate change to our global food supply, with Sub-Saharan Africa and part of Asia most at risk" Professor Binns said.
"For the time being, it will be possible to produce enough food to maintain adequate intakes, using improved farming practices and technology and more equity in distribution, but we estimate that by 2050 world food production will need to increase by 50 per cent to overcome present shortages and meet the needs of the growing population.
"Our review recommends that by following necessary dietary guidelines and choosing foods that have low environmental impacts, such as fish, whole grain cereals, fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, berries, and olive oil, would improve health, help reduce greenhouse gases and meet the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, which in turn would improve food production levels in the future."
Professor Binns said that while climate change will have a significant effect on food supply, political commitment and substantial investment could go some way to reduce the effects and help provide the foods needed to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals.
"Some changes will need to be made to food production, nutrient content will need monitoring, and more equitable distribution will be required to meet the proposed dietary guidelines. It was also be important to increase breastfeeding rates to improve infant and adult health, while helping to reduce greenhouse gases and benefit the environment," Professor Binns said.
"Ongoing research will be vital to assessing the long-term impacts of climate change on food supply and health in order to adequately prepare for the future."
INFORMATION:
This study was a collaborative effort involving researchers from the Curtin School of Population Health, Murdoch University, University of Exeter, University of Malaya, Oslo Metropolitan University, The University of Tokyo, and Hanoi University of Public Health.
The full paper titled, Climate Change, Food Supply, and Dietary Guidelines, can be found online here.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
A Curtin University study has found the introduced European honeybee could lead to native bee population decline or extinction when colonies compete for the same nectar and pollen sources in urban gardens and areas of bush.
Published in the 'Biological Journal of the Linnean Society', the research found competition between the native bees and the introduced European honeybee could be particularly intense in residential gardens dominated by non-native flowers, and occurred when the bees shared the same flower preferences.
Under these conditions, it would appear that European honeybees, being very abundant, and effective foragers, with the ...
2021-04-08
How can large amounts of data be transferred or processed as quickly as possible? One key to this could be graphene. The ultra-thin material is only one atomic layer thick, and the electrons it contains have very special properties due to quantum effects. It could therefore be very well suited for use in high-performance electronic components. Up to this point, however, there has been a lack of knowledge about how to suitably control certain properties of graphene. A new study by a team of scientists from Bielefeld and Berlin, together with researchers from other research institutes in Germany and Spain, is changing this. The team's findings have been published in the journal Science Advances.
Consisting of carbon atoms, graphene is a material just one atom ...
2021-04-08
As SARS-CoV-2 continues to spread in France, a thorough characterization of hospital care needs and of the trajectories of hospital patients, as well as how they have changed over time, is essential to support planning. This led scientists from the Mathematical Modeling of Infectious Diseases Unit at the Institut Pasteur and the University of Cambridge to develop a probabilistic model that can be used to analyze detailed patient trajectories based on 198,846 hospitalizations in France during the first nine months of the pandemic (from March to No-vember 2020). These findings were published in The Lancet Regional Health Europe on March 20, 2021.
This ...
2021-04-08
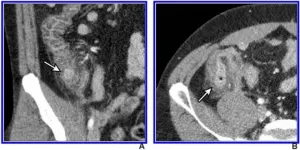
Leesburg, VA, April 8, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), IV contrast-enhanced 2-millisievert CT (2-mSv CT) is comparable to conventional-dose CT (CDCT) for the diagnosis of right colonic diverticulitis.
"By mitigating concern of missed diagnosis of right colonic diverticulitis, our results further support the use of low-dose CT for suspected appendicitis," wrote first author Hae Young Kim from the department of radiology at Korea's Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. "To our knowledge," Kim et al. maintained, "this is the first study to formally measure the diagnostic performance of CT for right colonic diverticulitis."
Kim and colleagues' large pragmatic randomized controlled trial data included 3,074 patients ...
2021-04-08
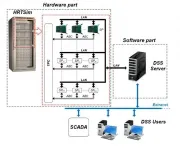
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have created a decision support system (DSS) for dispatching personnel of electric power systems (EPS). The system allows dispatchers to quickly test their actions on the management of the EPS, to control and evaluate their consequences using a digital simulator in a regime faster than real time.
The article devoted to the research work is published in the IEEE Transactions on Power Systems (Q1, IF 6.074) academic journal, one of the most peer-reviewed journals in energy, energy technology, electrical engineering and electronics ...
2021-04-08
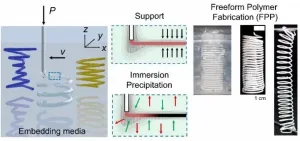
Fabrication of 3D freeform structures of thermoplastics involving overhang (non-anchored) structures is successfully showcased by fused deposition modeling (FDM) and direct ink writing (DIW), yet limited in terms of applicable materials and conditions of printing. 3D printing of freeform structures requires support materials that enable printing of thermoplastics in non-anchored locations.
In order to address the difficulty of freeform fabrication via extrusion-based printing, the use of microparticulate gels as embedding media has been widely explored. Such methods are collectively termed embedded 3D printing (e3DP).
In these demonstrations, ...
2021-04-08
Researchers from the University of Hawai'i (UH) at Mānoa, University of British Columbia (UBC), San Diego State University (SDSU), and elsewhere have created 3D molecular maps of bacteria, viruses, and biochemicals across coral colonies along with their interacting organisms such as algae and other competing corals. This allowed the team to discover specific microbial and viral functions that appear to be key components of the coral microbiome.
The study, published recently in Frontiers of Marine Science, used a novel combination of state-of-the-art molecular methods with cutting-edge 3D imaging techniques to create high-resolution molecular maps on coral reef organisms.
Healthy coral reefs ...
2021-04-08
Forecasts aren't just for the weather. Scientists can use weather radar and related technology to chart the journeys of billions of migratory birds, which can help protect these global travelers from a growing array of threats.
In a new breakthrough on this front, a team led by Colorado State University used millions of observations from 143 weather surveillance radars to evaluate a forecasting system for nocturnal bird migration in the United States.
Using these tools, the team discovered that a mere 10 nights of action are required to reduce risk to 50% of avian migrants passing over a ...
2021-04-08
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 6, 2021--In the vast Colorado River basin, climate change is driving extreme, interconnected events among earth-system elements such as weather and water. These events are becoming both more frequent and more intense and are best studied together, rather than in isolation, according to new research.
"We found that concurrent extreme hydroclimate events, such as high temperatures and unseasonable rain that quickly melt mountain snowpack to cause downstream floods, are projected to increase and intensify within several critical regions of the Colorado ...
2021-04-08
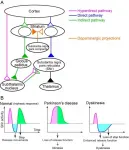
Okazaki, Japan -mm dd, 2021--Many people with Parkinson's disease develop abnormal movements called L-DOPA induced dyskinesia, a major side effect of long-term medication. The mechanism underlying this side effect has been unknown. In this study, researchers have revealed relation between changes of neuronal activities and dyskinesia.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the common age-related neurological disorder affecting 7 - 10 million people worldwide. It is caused by loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain region called the substantia nigra, and induces difficulty in execution of movements (akinesia), muscle stiffness (rigidity), walking difficulty, tremorous hand movements ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study calls for urgent climate change action to secure global food supply
New Curtin University-led research has found climate change will have a substantial impact on global food production and health if no action is taken by consumers, food industries, government, and international bodies