Evolution of outcomes for patients hospitalized during the COVID pandemic
Evolution of outcomes for patients hospitalized during the first nine months of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in France: a retrospective analysis of national sur-veillance data
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) As SARS-CoV-2 continues to spread in France, a thorough characterization of hospital care needs and of the trajectories of hospital patients, as well as how they have changed over time, is essential to support planning. This led scientists from the Mathematical Modeling of Infectious Diseases Unit at the Institut Pasteur and the University of Cambridge to develop a probabilistic model that can be used to analyze detailed patient trajectories based on 198,846 hospitalizations in France during the first nine months of the pandemic (from March to No-vember 2020). These findings were published in The Lancet Regional Health Europe on March 20, 2021.
This model takes into account variations in the age and sex of the patients over time, and explores changes in probabilities of ICU admission, death and hospital discharge, as well as variations in the length of hospital stays.
The scientists observed major changes in the age and sex of the patients hospitalized during the study period. In particular, the proportion of hospitalized patients aged over 80 varied be-tween 27% and 48% during the epidemic and was lower during the two waves. The proportion of women among the hospitalized patients varied between 45% and 53% during the epidemic.
The scientists also demonstrated that the outcome of hospitalized patients varied substantial-ly during the pandemic. For example, the probability of hospitalized patients being admitted to an ICU fell from 25.4% (24.4%-26.4%) to 12.6% (11.6%-13.6%) during the first four months (from March to June) in parallel with the decrease in case numbers, before rising to 19.3% (18.9%-19.7%) during the second wave. The probability of death followed a similar path, fall-ing from 24.9% (24%-25.9%) to 10% (8.7%-11.3%) after the first wave before increasing again to 18.6% (18.1%-19%) during the second wave. These trends were similar for both men and women.
"These major variations in the probabilities of ICU admission and death need to be taken into account when planning hospital care needs", explains Simon Cauchemez, Head of the Math-ematical Modeling of Infectious Diseases Unit at the Institut Pasteur and last author of the study.
"The reasons for these large-scale changes in patient mortality since the start of the pandem-ic remain unclear but are likely to represent a combination of changes in healthcare seeking behaviour by patients, changing strains on healthcare centres, as well as improvements in treatments as physicians have learnt more about the disease", concludes Noémie Lefrancq, a PhD student in the Department of Genetics at the University of Cambridge and first author of the study.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
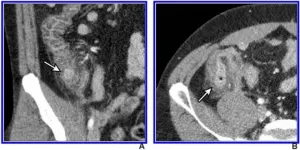
Leesburg, VA, April 8, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), IV contrast-enhanced 2-millisievert CT (2-mSv CT) is comparable to conventional-dose CT (CDCT) for the diagnosis of right colonic diverticulitis.
"By mitigating concern of missed diagnosis of right colonic diverticulitis, our results further support the use of low-dose CT for suspected appendicitis," wrote first author Hae Young Kim from the department of radiology at Korea's Seoul National University Bundang Hospital. "To our knowledge," Kim et al. maintained, "this is the first study to formally measure the diagnostic performance of CT for right colonic diverticulitis."
Kim and colleagues' large pragmatic randomized controlled trial data included 3,074 patients ...
2021-04-08
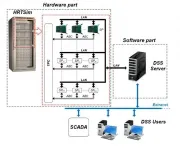
Scientists of Tomsk Polytechnic University have created a decision support system (DSS) for dispatching personnel of electric power systems (EPS). The system allows dispatchers to quickly test their actions on the management of the EPS, to control and evaluate their consequences using a digital simulator in a regime faster than real time.
The article devoted to the research work is published in the IEEE Transactions on Power Systems (Q1, IF 6.074) academic journal, one of the most peer-reviewed journals in energy, energy technology, electrical engineering and electronics ...
2021-04-08
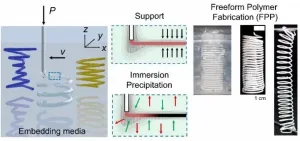
Fabrication of 3D freeform structures of thermoplastics involving overhang (non-anchored) structures is successfully showcased by fused deposition modeling (FDM) and direct ink writing (DIW), yet limited in terms of applicable materials and conditions of printing. 3D printing of freeform structures requires support materials that enable printing of thermoplastics in non-anchored locations.
In order to address the difficulty of freeform fabrication via extrusion-based printing, the use of microparticulate gels as embedding media has been widely explored. Such methods are collectively termed embedded 3D printing (e3DP).
In these demonstrations, ...
2021-04-08
Researchers from the University of Hawai'i (UH) at Mānoa, University of British Columbia (UBC), San Diego State University (SDSU), and elsewhere have created 3D molecular maps of bacteria, viruses, and biochemicals across coral colonies along with their interacting organisms such as algae and other competing corals. This allowed the team to discover specific microbial and viral functions that appear to be key components of the coral microbiome.
The study, published recently in Frontiers of Marine Science, used a novel combination of state-of-the-art molecular methods with cutting-edge 3D imaging techniques to create high-resolution molecular maps on coral reef organisms.
Healthy coral reefs ...
2021-04-08
Forecasts aren't just for the weather. Scientists can use weather radar and related technology to chart the journeys of billions of migratory birds, which can help protect these global travelers from a growing array of threats.
In a new breakthrough on this front, a team led by Colorado State University used millions of observations from 143 weather surveillance radars to evaluate a forecasting system for nocturnal bird migration in the United States.
Using these tools, the team discovered that a mere 10 nights of action are required to reduce risk to 50% of avian migrants passing over a ...
2021-04-08
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 6, 2021--In the vast Colorado River basin, climate change is driving extreme, interconnected events among earth-system elements such as weather and water. These events are becoming both more frequent and more intense and are best studied together, rather than in isolation, according to new research.
"We found that concurrent extreme hydroclimate events, such as high temperatures and unseasonable rain that quickly melt mountain snowpack to cause downstream floods, are projected to increase and intensify within several critical regions of the Colorado ...
2021-04-08
Okazaki, Japan -mm dd, 2021--Many people with Parkinson's disease develop abnormal movements called L-DOPA induced dyskinesia, a major side effect of long-term medication. The mechanism underlying this side effect has been unknown. In this study, researchers have revealed relation between changes of neuronal activities and dyskinesia.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the common age-related neurological disorder affecting 7 - 10 million people worldwide. It is caused by loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain region called the substantia nigra, and induces difficulty in execution of movements (akinesia), muscle stiffness (rigidity), walking difficulty, tremorous hand movements ...
2021-04-08
Details:
According to a linguistic survey report, people often confuse the pronunciation of /hi/ with that of /si/ in the dialect of Tokyo and the Tohoku region of Japan. A team of researchers at Toyohashi University of Technology and the National Institute for Japanese Language and Linguistics (NINJAL) found that the confusion is resulted from the articulation of the tongue varying in the transverse direction while the tongue tip is positioned at the same place of articulation. The study was published online in the Journal of the Acoustical Society of America on April 7, 2021.
In the Japanese language, the consonant /s/ followed by vowel /i/ is distinct ...
2021-04-08
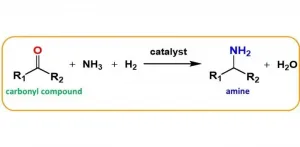
Osaka, Japan - Catalysts are crucial to making industrial processes viable. However, many of the non-precious metal catalysts used for synthesis have low activity, are difficult to handle, and/or require harsh reaction conditions. Osaka University researchers have developed a single-crystal cobalt phosphide nanorod catalyst that overcomes several of the limitations of conventional cobalt catalysts. Their findings were published in JACS Au.
Reductive amination is an important chemical reaction that is used to convert carbonyl compounds into amines. It is a key step in the production of many materials such as polymers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals, and is attractive because the reagents are cost effective and widely available, ...
2021-04-08
An adaptive cognitive training program could help treat attention and working memory difficulties in children with sickle cell disease (SCD), a new study published in the of Journal of Pediatric Psychology shows.
These neurocognitive difficulties have practical implications for the 100,000 individuals in the U.S. with SCD, as 20-40% of youth with SCD repeat a grade in school and fewer than half of adults with SCD are employed. Interventions to prevent and treat neurocognitive difficulties caused by SCD have the potential to significantly improve academic outcomes, vocational attainment and quality of life.
The study, led by Steven Hardy, Ph.D., director of Psychology and Patient Care Services at the Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders at Children's ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Evolution of outcomes for patients hospitalized during the COVID pandemic
Evolution of outcomes for patients hospitalized during the first nine months of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in France: a retrospective analysis of national sur-veillance data