New study examines promising approach to treating attention and working memory difficulties in child
2021-04-08
(Press-News.org) An adaptive cognitive training program could help treat attention and working memory difficulties in children with sickle cell disease (SCD), a new study published in the of Journal of Pediatric Psychology shows.
These neurocognitive difficulties have practical implications for the 100,000 individuals in the U.S. with SCD, as 20-40% of youth with SCD repeat a grade in school and fewer than half of adults with SCD are employed. Interventions to prevent and treat neurocognitive difficulties caused by SCD have the potential to significantly improve academic outcomes, vocational attainment and quality of life.
The study, led by Steven Hardy, Ph.D., director of Psychology and Patient Care Services at the Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders at Children's National Hospital, examined a promising approach using an adaptive cognitive training program (known as Cogmed Working Memory Training) that patients complete at home on an iPad.
Using a randomized controlled trial design, children were asked to complete Cogmed training sessions 3 to 5 times per week for about 30 minutes at a time until they completed 25 sessions. The Cogmed program involves game-like working memory exercises that adapt to the user's performance, gradually becoming more challenging over time as performance improves. The team found that patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) who completed the cognitive training intervention showed significant improvement in visual working memory compared to a waitlist group that used Cogmed after the waiting period. Treatment effects were especially notable for patients who completed a training "dose" of 10 sessions.
"Patients who completed at least 10 cognitive training sessions showed improved visual working memory, verbal short-term memory and math fluency," Dr. Hardy said.
SCD increases risk for neurocognitive difficulties because of cerebrovascular complications (such as overt strokes and silent cerebral infarcts) and underlying disease characteristics (such as chronic anemia). Neurocognitive effects of SCD most commonly involve problems with attention, working memory and other executive functions.
"This study demonstrates that digital working memory training is an effective approach to treating neurocognitive deficits in youth with sickle cell disease," Dr. Hardy added. "We also found that benefits of the training extend to tasks that involve short-term verbal memory and math performance when patients are able to stick with the program and complete at least 10 training sessions. These benefits could have a real impact on daily living, making it easier to remember and follow directions in school and at home, organize tasks or solve math problems that require remembering information for short periods of time."
To date, there have been few efforts to test interventions that address the neurocognitive issues experienced by many individuals with SCD. These findings show that abilities are modifiable and that a non-pharmacological treatment exists.
INFORMATION:
The Comprehensive Sickle Cell Disease Program at Children's National is a leader in pediatric SCD research and clinical innovation. This study was funded by a grant from the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation, which was the only Innovations in Clinical Research Award ever awarded to a psychologist (out of 31 grants totaling over $15 million), since the award established a focus on sickle cell disease in 2009.
Media contact: Ariana Perez | ariana.perez@childrensnational.org
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-04-08
Extremely structured electromagnetic pulse carries not only the ultimate human dream of ultra-fast and ultra-intense energy extraction but also numerous extraordinary fundamental physical effects. As a traditional viewpoint, Electromagnetic pulses are typically treated as space-time (or space-frequency) separable solutions of Maxwell's equations, where spatial and temporal (spectral) dependence can be treated separately. However, recent advances in structured light and topological optics have highlighted the nontrivial wave-matter interactions of pulses with complex space-time separability (STNS), as well as their potential for energy and information transfer.
Recently, a research ...
2021-04-08
Stem cell research has allowed medicine to go places that were once science fiction. Using stem cells, scientists have manufactured heart cells, brain cells and other cell types that they are now transplanting into patients as a form of cell therapy. Eventually, the field anticipates the same will be possible with organs. A new paper written by a group of international researchers led by Tsutomu Sawai, an assistant professor at the Kyoto University Institute for the Advanced Study of Human Biology (ASHBi) and the Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), explains the future ethical implications of this research ...
2021-04-08
Travel and economic slowdowns due to the COVID-19 pandemic combined to put the brakes on shipping, seafloor exploration, and many other human activities in the ocean, creating a unique moment to begin a time-series study of the impacts of sound on marine life.
A community of scientists has identified more than 200 non-military ocean hydrophones worldwide and hopes to make the most of the unprecedented opportunity to pool their recorded data into the 2020 quiet ocean assessment and to help monitor the ocean soundscape long into the future. They aim for a total of 500 hydrophones capturing the signals of whales and other marine life while assessing the racket levels of human activity. ...
2021-04-08
Animals are remarkably diverse in their sleep and activity patterns due to foraging strategies, social behavior and their desire to avoid predators. With more than 3,000 types of cichlids, these freshwater fish may just be one of the most diverse species in the world. Lake Malawi alone, which stretches 350 miles through eastern Africa, is home to more than 500 cichlid species. They evolved from a few species that likely entered the lake about 3 million years ago and now display very different behaviors and inhabit well-defined niches throughout ...
2021-04-08
Scientists are reporting results of the first frontline clinical trial to use targeted therapy to treat high-risk pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma. The study showed that the addition of brentuximab vedotin achieved excellent outcomes, reduced side effects, and allowed for reduced radiation exposures.
The study was the result of work by a multi-site consortium dedicated to pediatric Hodgkin-lymphoma. Collaborating institutions include St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Stanford University School of Medicine, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, Maine Children's Cancer Program and OSF Children's Hospital of Illinois.
A paper detailing the findings was published today in ...
2021-04-08
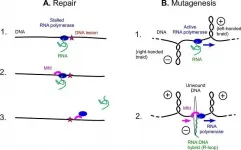
The Mfd protein repairs bacterial DNA, but can also, to scientists' surprise, promote mutation.
Bacterial mutations can lead to antibiotic resistance.
Understanding this second "role" of the Mfd protein opens up opportunities for combating antibiotic resistance, and also the resistance of tumours to anti-cancer drugs and therapies.
Using a specialized protein, all bacteria are capable of rapidly and effectively repairing damage to their DNA from UV. However, this mutation frequency decline (Mfd) protein plays another role and causes mutations. A team involving ...
2021-04-08
In cancer, personalised medicine takes advantage of the unique genetic changes in an individual tumour to find its vulnerabilities and fight it. Many tumours have a higher number of mutations due to a antiviral defence mechanism, the APOBEC system, which can accidentally damage DNA and cause mutations.
Researchers at IRB Barcelona led by Dr. Travis Stracker and Dr. Fran Supek have found the HMCES enzyme to be the Achilles heel of some lung tumours, specifically those with a higher number of mutations caused by the APOBEC system.
"We have discovered that blocking HMCES is very damaging to cells with an activated ...
2021-04-08
Hispanic immigrants of working age -- 20 to 54 years old -- are over 11 times more likely to die of COVID-19 than U.S.-born men and women who are not Hispanic, according to a USC study of California death certificate data from 2020.
The study, published Monday in the END ...
2021-04-08
QUT researchers have used carbon dots, created from human hair waste sourced from a Brisbane barbershop, to create a kind of "armour" to improve the performance of cutting-edge solar technology.
In a study published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A, the researchers led by Professor Hongxia Wang in collaboration with Associate Professor Prashant Sonar of QUT's Centre for Materials Science showed the carbon nanodots could be used to improve the performance of perovskites solar cells.
Perovskites solar cells, a relatively new photovoltaic technology, are seen as the best PV candidate to deliver low-cost, highly efficient solar electricity in coming years. ...
2021-04-08
EUGENE, Ore. -- April 8, 2021 -- Researchers exploring the developing central nervous system of fruit flies have identified nonelectrical cells that transition the brain from highly plastic into a less moldable, mature state.
The cells, known as astrocytes for their star-like shapes, and associated genes eventually could become therapeutic targets, said University of Oregon postdoctoral researcher Sarah Ackerman, who led the research.
"All of the cell types and signaling pathways I looked at are present in humans," Ackerman said. "Two of the genes that I ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New study examines promising approach to treating attention and working memory difficulties in child