(Press-News.org) Forecasts aren't just for the weather. Scientists can use weather radar and related technology to chart the journeys of billions of migratory birds, which can help protect these global travelers from a growing array of threats.
In a new breakthrough on this front, a team led by Colorado State University used millions of observations from 143 weather surveillance radars to evaluate a forecasting system for nocturnal bird migration in the United States.
Using these tools, the team discovered that a mere 10 nights of action are required to reduce risk to 50% of avian migrants passing over a given area in spring and autumn. Specific actions are as simple as turning off nonessential outdoor lights.
Conservation Biology published the study, " END
Weather radar for ecological forecasting can lessen hazards for migratory birds
2021-04-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
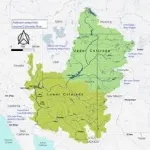
Colorado River basin due for more frequent, intense hydroclimate events
2021-04-08
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., April 6, 2021--In the vast Colorado River basin, climate change is driving extreme, interconnected events among earth-system elements such as weather and water. These events are becoming both more frequent and more intense and are best studied together, rather than in isolation, according to new research.
"We found that concurrent extreme hydroclimate events, such as high temperatures and unseasonable rain that quickly melt mountain snowpack to cause downstream floods, are projected to increase and intensify within several critical regions of the Colorado ...
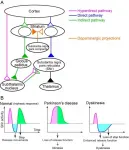
Mechanism of abnormal movements induced by drug treatment of Parkinson's disease
2021-04-08
Okazaki, Japan -mm dd, 2021--Many people with Parkinson's disease develop abnormal movements called L-DOPA induced dyskinesia, a major side effect of long-term medication. The mechanism underlying this side effect has been unknown. In this study, researchers have revealed relation between changes of neuronal activities and dyskinesia.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the common age-related neurological disorder affecting 7 - 10 million people worldwide. It is caused by loss of dopaminergic neurons in the brain region called the substantia nigra, and induces difficulty in execution of movements (akinesia), muscle stiffness (rigidity), walking difficulty, tremorous hand movements ...
How Japanese speakers confuse the pronunciations of /hi/ and /si/
2021-04-08
Details:
According to a linguistic survey report, people often confuse the pronunciation of /hi/ with that of /si/ in the dialect of Tokyo and the Tohoku region of Japan. A team of researchers at Toyohashi University of Technology and the National Institute for Japanese Language and Linguistics (NINJAL) found that the confusion is resulted from the articulation of the tongue varying in the transverse direction while the tongue tip is positioned at the same place of articulation. The study was published online in the Journal of the Acoustical Society of America on April 7, 2021.
In the Japanese language, the consonant /s/ followed by vowel /i/ is distinct ...
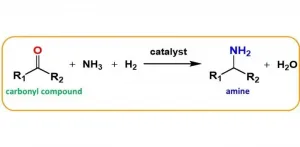
For highly active, sustainable catalysts, just add phosphorus
2021-04-08
Osaka, Japan - Catalysts are crucial to making industrial processes viable. However, many of the non-precious metal catalysts used for synthesis have low activity, are difficult to handle, and/or require harsh reaction conditions. Osaka University researchers have developed a single-crystal cobalt phosphide nanorod catalyst that overcomes several of the limitations of conventional cobalt catalysts. Their findings were published in JACS Au.
Reductive amination is an important chemical reaction that is used to convert carbonyl compounds into amines. It is a key step in the production of many materials such as polymers, dyes, and pharmaceuticals, and is attractive because the reagents are cost effective and widely available, ...
New study examines promising approach to treating attention and working memory difficulties in child
2021-04-08
An adaptive cognitive training program could help treat attention and working memory difficulties in children with sickle cell disease (SCD), a new study published in the of Journal of Pediatric Psychology shows.
These neurocognitive difficulties have practical implications for the 100,000 individuals in the U.S. with SCD, as 20-40% of youth with SCD repeat a grade in school and fewer than half of adults with SCD are employed. Interventions to prevent and treat neurocognitive difficulties caused by SCD have the potential to significantly improve academic outcomes, vocational attainment and quality of life.
The study, led by Steven Hardy, Ph.D., director of Psychology and Patient Care Services at the Center for Cancer and Blood Disorders at Children's ...
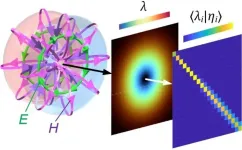
Measuring space-time 'entanglement' of electromagnetic waves
2021-04-08
Extremely structured electromagnetic pulse carries not only the ultimate human dream of ultra-fast and ultra-intense energy extraction but also numerous extraordinary fundamental physical effects. As a traditional viewpoint, Electromagnetic pulses are typically treated as space-time (or space-frequency) separable solutions of Maxwell's equations, where spatial and temporal (spectral) dependence can be treated separately. However, recent advances in structured light and topological optics have highlighted the nontrivial wave-matter interactions of pulses with complex space-time separability (STNS), as well as their potential for energy and information transfer.
Recently, a research ...
Society is not ready to make human brains
2021-04-08
Stem cell research has allowed medicine to go places that were once science fiction. Using stem cells, scientists have manufactured heart cells, brain cells and other cell types that they are now transplanting into patients as a form of cell therapy. Eventually, the field anticipates the same will be possible with organs. A new paper written by a group of international researchers led by Tsutomu Sawai, an assistant professor at the Kyoto University Institute for the Advanced Study of Human Biology (ASHBi) and the Center for iPS Cell Research and Application (CiRA), explains the future ethical implications of this research ...
Year of the quiet ocean: Emerging ocean listening network will study seas uniquely quieted by COVID
2021-04-08
Travel and economic slowdowns due to the COVID-19 pandemic combined to put the brakes on shipping, seafloor exploration, and many other human activities in the ocean, creating a unique moment to begin a time-series study of the impacts of sound on marine life.
A community of scientists has identified more than 200 non-military ocean hydrophones worldwide and hopes to make the most of the unprecedented opportunity to pool their recorded data into the 2020 quiet ocean assessment and to help monitor the ocean soundscape long into the future. They aim for a total of 500 hydrophones capturing the signals of whales and other marine life while assessing the racket levels of human activity. ...
How did 500 species of a fish form in a lake? Dramatically different body clocks
2021-04-08
Animals are remarkably diverse in their sleep and activity patterns due to foraging strategies, social behavior and their desire to avoid predators. With more than 3,000 types of cichlids, these freshwater fish may just be one of the most diverse species in the world. Lake Malawi alone, which stretches 350 miles through eastern Africa, is home to more than 500 cichlid species. They evolved from a few species that likely entered the lake about 3 million years ago and now display very different behaviors and inhabit well-defined niches throughout ...
Excellent outcomes reported for first targeted therapy for pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma
2021-04-08
Scientists are reporting results of the first frontline clinical trial to use targeted therapy to treat high-risk pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma. The study showed that the addition of brentuximab vedotin achieved excellent outcomes, reduced side effects, and allowed for reduced radiation exposures.
The study was the result of work by a multi-site consortium dedicated to pediatric Hodgkin-lymphoma. Collaborating institutions include St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, Stanford University School of Medicine, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, Maine Children's Cancer Program and OSF Children's Hospital of Illinois.
A paper detailing the findings was published today in ...